
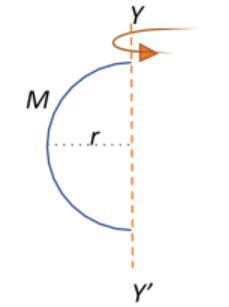
A thin wire of length l and mass M is bent in the form of a semicircle. What is its moment of inertia about an axis passing through the ends of the wire?

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: Begin by taking an elementary mass over the circumference of the semi-circle spanning an elementary angle of $\theta$. Then, obtain an expression for the elementary moment of inertia MI and integrate this over the entire angular span (0 to $\pi$) of the semi-circle. Remember to consider the linear distance between the axis of rotation and the elementary mass while taking the distance of the elementary mass. This will be an angular component of the radius of the semi-circle. Once you have obtained the expression for MI, substitute r in terms of l given that the length of the wire forms the circumference, and to this end, arrive at the appropriate result.
Formula used: Moment of inertia for a half-ring: $I = \dfrac{Mr^2}{2} $
Complete step by step answer:
Since the thin wire is bent into a semi-circle, the length of the wire becomes the circumference of the semi-circle, i.e.,
$l = \pi r \Rightarrow r = \dfrac{l}{\pi}$
The moment of inertia of the semicircle about the axis YY’ can be derived by first taking an elementary mass dm over the circumference of the semi-circle, and integrating the elementary moment of inertia over the entire circumference to obtain the total inertia.
$I = \int dI = \int dm\;r^{\prime^2}$, where $r^{\prime} = r cos\theta$ is the linear distance to the circumference from the axis of rotation YY’.
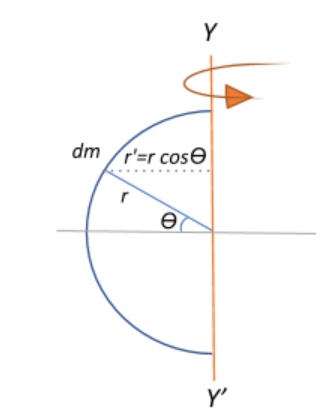
We know that the elementary mass is an angular unit of the entire mass of the semi-circle ${dm} = \dfrac{M}{\pi}d\theta$, where $\pi$ is the angular span of the semi-circle.
$\Rightarrow I = \int \dfrac{M}{\pi}d\theta. r^2cos^2\theta = \dfrac{Mr^2}{\pi} {}\int_0^{\pi}cos^2\theta d\theta$
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{Mr^2}{\pi}\left|\dfrac{1}{2}\theta + \dfrac{sin2\theta}{4} \right|_{0}^{\pi}$
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{Mr^2}{\pi}\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2} + 0\right)$
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{Mr^2}{2} $
Now, given that $r = \dfrac{l}{\pi}$
$I = \dfrac{1}{2}M\left(\dfrac{l}{\pi}\right)^2 = \dfrac{Ml^2}{2\pi^2}$
Note: To explain the integral of $cos^2\theta\;d\theta$:
$\int cos^2\theta\;d\theta = \int \dfrac{1+cos2\theta}{2}d\theta = \int \dfrac{1}{2}d\theta + \dfrac{1}{2}\int cos2\theta\;d\theta$
$\Rightarrow \int cos^2\theta\;d\theta = \dfrac{1}{2}\theta + \dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{sin2\theta}{2} = \dfrac{\theta}{2}+\dfrac{sin2\theta}{4}$
Also, remember that the moment of inertia is dependent on the distribution of mass of the system about the axis of rotation, the position and orientation of the axis of rotation and the shape of the body constituting the system.
Formula used: Moment of inertia for a half-ring: $I = \dfrac{Mr^2}{2} $
Complete step by step answer:
Since the thin wire is bent into a semi-circle, the length of the wire becomes the circumference of the semi-circle, i.e.,
$l = \pi r \Rightarrow r = \dfrac{l}{\pi}$
The moment of inertia of the semicircle about the axis YY’ can be derived by first taking an elementary mass dm over the circumference of the semi-circle, and integrating the elementary moment of inertia over the entire circumference to obtain the total inertia.
$I = \int dI = \int dm\;r^{\prime^2}$, where $r^{\prime} = r cos\theta$ is the linear distance to the circumference from the axis of rotation YY’.

We know that the elementary mass is an angular unit of the entire mass of the semi-circle ${dm} = \dfrac{M}{\pi}d\theta$, where $\pi$ is the angular span of the semi-circle.
$\Rightarrow I = \int \dfrac{M}{\pi}d\theta. r^2cos^2\theta = \dfrac{Mr^2}{\pi} {}\int_0^{\pi}cos^2\theta d\theta$
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{Mr^2}{\pi}\left|\dfrac{1}{2}\theta + \dfrac{sin2\theta}{4} \right|_{0}^{\pi}$
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{Mr^2}{\pi}\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2} + 0\right)$
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{Mr^2}{2} $
Now, given that $r = \dfrac{l}{\pi}$
$I = \dfrac{1}{2}M\left(\dfrac{l}{\pi}\right)^2 = \dfrac{Ml^2}{2\pi^2}$
Note: To explain the integral of $cos^2\theta\;d\theta$:
$\int cos^2\theta\;d\theta = \int \dfrac{1+cos2\theta}{2}d\theta = \int \dfrac{1}{2}d\theta + \dfrac{1}{2}\int cos2\theta\;d\theta$
$\Rightarrow \int cos^2\theta\;d\theta = \dfrac{1}{2}\theta + \dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{sin2\theta}{2} = \dfrac{\theta}{2}+\dfrac{sin2\theta}{4}$
Also, remember that the moment of inertia is dependent on the distribution of mass of the system about the axis of rotation, the position and orientation of the axis of rotation and the shape of the body constituting the system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




