
A thin uniform circular ring is rolling down an inclined plane of inclination $30^\circ $ without slipping. Its linear acceleration along the inclined plane will be
A. $\dfrac{g}{2}$
B. $\dfrac{g}{3}$
C. $\dfrac{g}{4}$
D. $\dfrac{{2g}}{3}$
Answer
476.4k+ views
Hint:First, the diagram has to be drawn as per the given problems. The moment of inertia for a ring is needed here. Also, the formula of the acceleration has to be applied maintaining the condition for the object rolling on a plane. The inclination is given and this is to be used in the formula of acceleration. The acceleration will be in terms of the gravitational acceleration.
Complete step by step answer:
There may be a kind of acceleration to check translational and rotational. An example for this is the stimpmeter in golf. It has a constant translational acceleration and increasing translational velocity here, it has a constant rotational angular acceleration so the angular velocity gets increased.
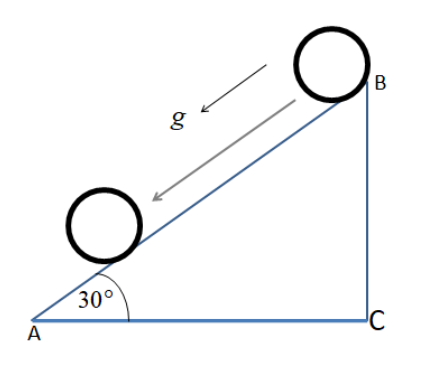
For ring,
\[I = M{R^2}\]
When the object rolling on a plane then the acceleration will be as follows,
$a = \dfrac{{g\sin \theta }}{{1 + \dfrac{I}{{M{R^2}}}}}$
The given plane inclination is $30^\circ $.Now substitute this value in the above equation we get,
$a = \dfrac{{g\sin 30^\circ }}{{1 + \dfrac{{M{R^2}}}{{M{R^2}}}}}$
For further simplification, the acceleration will be,
$a = \dfrac{{g\sin 30^\circ }}{{2}}$
On putting $\sin 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{2}$, we get
$\therefore a = \dfrac{g}{4}$
Hence, the correct answer is an option C.
Note:If the velocity is increased constantly concerning the time then the acceleration will be constant the rate of displacement gets increased. The angular acceleration and rolling velocity are directly proportional to each other. If the air resistance is zero then the acceleration will be constant. And hence the velocity will be increased. If the air resistance is present the examples are, inflated beach balls, the net force drops with increasing speed. if the acceleration is reduced then the velocity increases more slowly.
Complete step by step answer:
There may be a kind of acceleration to check translational and rotational. An example for this is the stimpmeter in golf. It has a constant translational acceleration and increasing translational velocity here, it has a constant rotational angular acceleration so the angular velocity gets increased.

For ring,
\[I = M{R^2}\]
When the object rolling on a plane then the acceleration will be as follows,
$a = \dfrac{{g\sin \theta }}{{1 + \dfrac{I}{{M{R^2}}}}}$
The given plane inclination is $30^\circ $.Now substitute this value in the above equation we get,
$a = \dfrac{{g\sin 30^\circ }}{{1 + \dfrac{{M{R^2}}}{{M{R^2}}}}}$
For further simplification, the acceleration will be,
$a = \dfrac{{g\sin 30^\circ }}{{2}}$
On putting $\sin 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{2}$, we get
$\therefore a = \dfrac{g}{4}$
Hence, the correct answer is an option C.
Note:If the velocity is increased constantly concerning the time then the acceleration will be constant the rate of displacement gets increased. The angular acceleration and rolling velocity are directly proportional to each other. If the air resistance is zero then the acceleration will be constant. And hence the velocity will be increased. If the air resistance is present the examples are, inflated beach balls, the net force drops with increasing speed. if the acceleration is reduced then the velocity increases more slowly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




