
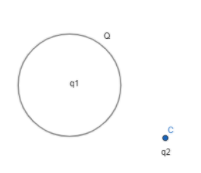
A thin metallic spherical shell contains a charge Q on its surface. A point charge q1 is placed at the centre of the shell and another charge q2 is placed outside the shell. All three charges are positive. Then, the force on the charge q1 is,
(A). Towards left
(B). Towards right
(C). Upward
(D). Zero

Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: Electric field inside a metallic sphere is always zero. We can use gauss’s law to prove this. Find the force on the charge q1 due to the charge q2 which is placed outside the metallic shell. Use the concept of electrostatic shielding to solve this question.
Complete step by step answer:
We have a metallic spherical shell with positive charge Q on its surface. Inside the sphere there is a point charge q1 and outside the sphere we have another point charge q2.
Electric field inside the gaussian surface is zero. We can find out this by using the gauss’s law. If we imagine a gaussian surface inside a metallic spherical shell with charge on its surface, charge enclosed by the gaussian surface will be zero.
So, the force on the charge due to the shell will be zero since the electric field inside the shell is zero.
Again, if we consider the outer electron q2 it also doesn’t have any effect on the charge q1 inside the metallic spherical shell. This is due to the process called electrostatic shielding.
Electrostatic shielding the process of shielding the inside of a conductor from any influence of the outside charges or outside electric field. The electric field inside the cavity will be always zero.
So, the force on the charge inside the metallic spherical charge will be zero.
The correct option is (A)
Note: The concept of electrostatic shielding is used to protect electric appliances from the external field. Faraday cage applies the concept of electrostatic shielding Faraday cage is used to block any external influences to the internal components.
Complete step by step answer:
We have a metallic spherical shell with positive charge Q on its surface. Inside the sphere there is a point charge q1 and outside the sphere we have another point charge q2.
Electric field inside the gaussian surface is zero. We can find out this by using the gauss’s law. If we imagine a gaussian surface inside a metallic spherical shell with charge on its surface, charge enclosed by the gaussian surface will be zero.
So, the force on the charge due to the shell will be zero since the electric field inside the shell is zero.
Again, if we consider the outer electron q2 it also doesn’t have any effect on the charge q1 inside the metallic spherical shell. This is due to the process called electrostatic shielding.
Electrostatic shielding the process of shielding the inside of a conductor from any influence of the outside charges or outside electric field. The electric field inside the cavity will be always zero.
So, the force on the charge inside the metallic spherical charge will be zero.
The correct option is (A)
Note: The concept of electrostatic shielding is used to protect electric appliances from the external field. Faraday cage applies the concept of electrostatic shielding Faraday cage is used to block any external influences to the internal components.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




