
When a thin metal wire is stretched, it becomes longer and thinner. This causes a change in the resistance of the wire. The volume of the wire remains constant. Which graph could represent the variation with extension $x$ of the resistance R of the wire?
A.
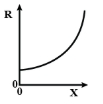
B.
C.
D.




Answer
567.9k+ views
Hint: First establish a proportionality relation between length and area of cross-section. Now describe the proportionality relation between resistance, length and area of cross-section. Now use both these relations to figure out the graph.
Complete answer:
Let the length of the wire before and after stretching be ${L_1}$ and ${L_2}$ respectively. Also let the area of cross-section of the wire before and after stretching be ${A_1}$ and ${A_2}$ respectively.
Now, we know that the volume of the wire remains constant on stretching, so
${L_1}{A_1} = {L_2}{A_2} = $Volume of the wire
$ \Rightarrow {A_2} = \dfrac{{{L_1}{A_1}}}{{{L_2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {A_2}\propto \dfrac{1}{{{L_2}}}$
So, area of cross-section decreases as the length increases
Now, we know that
$R\propto L$,
$R\propto \dfrac{1}{A}$,
And $R\propto \dfrac{L}{A}$
$ \Rightarrow R = \rho \dfrac{{{L_2}{L_2}}}{{{L_1}{A_1}}}$
$ \Rightarrow R = \rho \dfrac{{{{({L_2})}^2}}}{{{L_1}{A_1}}}$
$ \Rightarrow R\propto {({L_2})^2}$
So, there is an exponential increase in resistance with increase in length.
The graph of exponential growth look like this
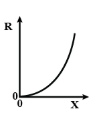
But we know even before stretching the wire, it has some initial resistance, so the graph becomes like this
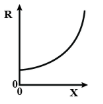
So, the option A is the correct choice.
Note:
The resistance of the wire changes on increase in the length, because increase in length of the wire means that there will be more collisions between the electrons as it passes through the wire. Another reason is that with increase in length there is a decrease $A$ in area of cross-section, which leaves a narrower path for electrons to move in, hence increasing collisions and resistance.
Complete answer:
Let the length of the wire before and after stretching be ${L_1}$ and ${L_2}$ respectively. Also let the area of cross-section of the wire before and after stretching be ${A_1}$ and ${A_2}$ respectively.
Now, we know that the volume of the wire remains constant on stretching, so
${L_1}{A_1} = {L_2}{A_2} = $Volume of the wire
$ \Rightarrow {A_2} = \dfrac{{{L_1}{A_1}}}{{{L_2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {A_2}\propto \dfrac{1}{{{L_2}}}$
So, area of cross-section decreases as the length increases
Now, we know that
$R\propto L$,
$R\propto \dfrac{1}{A}$,
And $R\propto \dfrac{L}{A}$
$ \Rightarrow R = \rho \dfrac{{{L_2}{L_2}}}{{{L_1}{A_1}}}$
$ \Rightarrow R = \rho \dfrac{{{{({L_2})}^2}}}{{{L_1}{A_1}}}$
$ \Rightarrow R\propto {({L_2})^2}$
So, there is an exponential increase in resistance with increase in length.
The graph of exponential growth look like this

But we know even before stretching the wire, it has some initial resistance, so the graph becomes like this

So, the option A is the correct choice.
Note:
The resistance of the wire changes on increase in the length, because increase in length of the wire means that there will be more collisions between the electrons as it passes through the wire. Another reason is that with increase in length there is a decrease $A$ in area of cross-section, which leaves a narrower path for electrons to move in, hence increasing collisions and resistance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




