
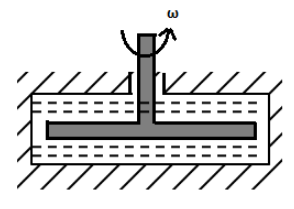
A thin horizontal disc of radius $R = 10\;cm$ is located within a cylindrical cavity filled with oil whose viscosity $\eta = 0.08\;P$(figure shown above). The clearance between the disc and the horizontal planes of the cavity is equal to$h = 1.0\;mm$. Find the power developed by the viscous forces acting on the disc when it rotates with the angular velocity $\omega = 60\;rad/s$. The end effects are to be neglected. Round off to the closest integer.

Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint:As the disc is rotating, four of viscosity arises due to velocity gradient. A torque is developed on the both upper and the lower clearance ends and thus power is developed. The power is the product of torque and angular velocity.
Formula used:
1. Four of viscosity, $F = \eta A\dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}}$
2. Torque, $\tau = rF$
3. Power, $P = \tau \times \omega $
Where $\eta $ is the coefficient of velocity, $A$ is the area of surfaces in contact, $\dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}}$ is the velocity gradient, $r$ is the radius and $\omega$ is the angular velocity.
Complete step by step answer:
When the disc rotates the fluid in contact also rotates in the same manner as the disc. However, the fluid with the walls of the cavity does not rotate. So, there is a difference in velocity with distance. This leads to a set up of velocity gradient due to viscous forces. Now, the linear velocity at distance r from axis, $v = r\omega $. As it varies with h, so, velocity gradient,
$\dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{\omega r}}{h}$ …. (1)
Where, $\omega $ denotes the angular velocity.
So, the viscosity force by Newton’s law is given by
$F = \eta A\dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}}$
Now, area, $A = 2\pi rdr$
So, from equation (1), we can write, $df = \eta 2\pi rdr \times \dfrac{{\omega r}}{h}$
$df = n\,2\pi \,{r^2}dr \times \dfrac{\omega }{h}$
So, the torque due to this force is
$d\tau = rdF\;\;\; \\
\Rightarrow \;\;\;d\tau = r \times \eta 2\pi {r^2}dr\dfrac{\omega }{h}$
$\Rightarrow d\tau = \eta 2\pi {r^3}dr\dfrac{\omega }{h}$
Net torque due to upper and lower clearance is,
\[
\tau = \int\limits_{ - R}^R {d\tau = \int\limits_{ - R}^R {\eta \;2\pi {r^3}dr\dfrac{\omega }{h}} } \\
\Rightarrow\tau = 2\int\limits_o^R \eta \;2\pi \;{r^3}dr\dfrac{\omega }{h} \\
\Rightarrow\tau = \eta \;4\pi \dfrac{{{r^4}}}{4} \times \dfrac{\omega }{h}\int\limits_o^R {} \\
\Rightarrow\tau = \eta \dfrac{{4\pi \;{R^4}\;\omega }}{{4\,h}} \\
\Rightarrow\tau = \eta \dfrac{{\pi \;{R^4}\;\omega }}{{4\,h}} \\
\]
Now, power developed, $P = \tau \,\omega $
$P = \eta \dfrac{{\pi {R^4}{\omega ^2}}}{h}$
As R $ = $ radius of disc $ = $$10\;cm = 0.1\;m$
$
\eta = 0.08\;p \\
\Rightarrow h = 1.0\;mm = 1 \times {10^{ - 3}}m \\
\Rightarrow\omega = 60\;rad/\sec $
So, $P = \dfrac{{0.08 \times 3.14 \times {{(0.1)}^4} \times {{(60)}^2}}}{{{{10}^{ - 3}}}}$
$\therefore P = 9.05\;watt$
Hence, the power developed by viscous force is $9.05\;watt$.
Note:As the disc has Radius R. So, considering the centre of disc as origin, the value of ends is from –R to R, So, dr varies from –R to R. In linear motion, the power is the product of the force and velocity but in the rotational motion, the force is replaced by the torque and the velocity is replaced by the angular velocity. Note that the units of all the quantities must be in the S.I units.
Formula used:
1. Four of viscosity, $F = \eta A\dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}}$
2. Torque, $\tau = rF$
3. Power, $P = \tau \times \omega $
Where $\eta $ is the coefficient of velocity, $A$ is the area of surfaces in contact, $\dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}}$ is the velocity gradient, $r$ is the radius and $\omega$ is the angular velocity.
Complete step by step answer:
When the disc rotates the fluid in contact also rotates in the same manner as the disc. However, the fluid with the walls of the cavity does not rotate. So, there is a difference in velocity with distance. This leads to a set up of velocity gradient due to viscous forces. Now, the linear velocity at distance r from axis, $v = r\omega $. As it varies with h, so, velocity gradient,
$\dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{\omega r}}{h}$ …. (1)
Where, $\omega $ denotes the angular velocity.
So, the viscosity force by Newton’s law is given by
$F = \eta A\dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}}$
Now, area, $A = 2\pi rdr$
So, from equation (1), we can write, $df = \eta 2\pi rdr \times \dfrac{{\omega r}}{h}$
$df = n\,2\pi \,{r^2}dr \times \dfrac{\omega }{h}$
So, the torque due to this force is
$d\tau = rdF\;\;\; \\
\Rightarrow \;\;\;d\tau = r \times \eta 2\pi {r^2}dr\dfrac{\omega }{h}$
$\Rightarrow d\tau = \eta 2\pi {r^3}dr\dfrac{\omega }{h}$
Net torque due to upper and lower clearance is,
\[
\tau = \int\limits_{ - R}^R {d\tau = \int\limits_{ - R}^R {\eta \;2\pi {r^3}dr\dfrac{\omega }{h}} } \\
\Rightarrow\tau = 2\int\limits_o^R \eta \;2\pi \;{r^3}dr\dfrac{\omega }{h} \\
\Rightarrow\tau = \eta \;4\pi \dfrac{{{r^4}}}{4} \times \dfrac{\omega }{h}\int\limits_o^R {} \\
\Rightarrow\tau = \eta \dfrac{{4\pi \;{R^4}\;\omega }}{{4\,h}} \\
\Rightarrow\tau = \eta \dfrac{{\pi \;{R^4}\;\omega }}{{4\,h}} \\
\]
Now, power developed, $P = \tau \,\omega $
$P = \eta \dfrac{{\pi {R^4}{\omega ^2}}}{h}$
As R $ = $ radius of disc $ = $$10\;cm = 0.1\;m$
$
\eta = 0.08\;p \\
\Rightarrow h = 1.0\;mm = 1 \times {10^{ - 3}}m \\
\Rightarrow\omega = 60\;rad/\sec $
So, $P = \dfrac{{0.08 \times 3.14 \times {{(0.1)}^4} \times {{(60)}^2}}}{{{{10}^{ - 3}}}}$
$\therefore P = 9.05\;watt$
Hence, the power developed by viscous force is $9.05\;watt$.
Note:As the disc has Radius R. So, considering the centre of disc as origin, the value of ends is from –R to R, So, dr varies from –R to R. In linear motion, the power is the product of the force and velocity but in the rotational motion, the force is replaced by the torque and the velocity is replaced by the angular velocity. Note that the units of all the quantities must be in the S.I units.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




