
A thin diamagnetic rod is placed vertically between the poles of an electromagnet When the current in the electromagnet is switched on, then the diamagnetic rod is pushed up, out of the horizontal magnetic field. Hence the rod gains gravitational potential energy. The work required to do this comes from.
A. The lattice structure of the material of the rod
B. The current source
C. The induced electric field due to the changing magnetic field
D. The magnetic field
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: The only force acting on the vertical rod in the magnetic field is by the electrical field generated by the current flowing in it. The rest all are either not the reason or do not act in the direction of horizontal potential energy.
Complete step by step answer:
The rod is placed vertically in between the two poles of a magnet. It can be picturised as below:
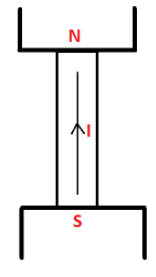
When current is made to flow in it, an electromagnetic field is induced. This force acts perpendicularly on the rod, that is, it pushes the rod horizontally out of the bounds of the magnetic poles.
This is the direction of the gravitational potential energy. Therefore it is safe to say that the work done by the horizontal gravitational force on the rod is contributed by the electrical current flowing in it.
The lattice structure of the rod has nothing to do with the induction of a horizontal gravitational potential energy on it. This is so because gravity works on the mass as a whole. Option A is not the answer to our question.
The magnetic field acts in between the poles normally, that I, parallel to the rod. Therefore, it does not contribute to the work. Option D is rendered invalid.
And finally, the magnetic flux in contact with the rod does not change. Therefore, option C is invalid as well.
In conclusion, the correct option is A.
Note:Magnetic field, magnetic flux should not be confused. One is a force field and the other is the number of force lines in that force field. In this case, neither contribute to the work done by the gravitational potential energy.
Complete step by step answer:
The rod is placed vertically in between the two poles of a magnet. It can be picturised as below:

When current is made to flow in it, an electromagnetic field is induced. This force acts perpendicularly on the rod, that is, it pushes the rod horizontally out of the bounds of the magnetic poles.
This is the direction of the gravitational potential energy. Therefore it is safe to say that the work done by the horizontal gravitational force on the rod is contributed by the electrical current flowing in it.
The lattice structure of the rod has nothing to do with the induction of a horizontal gravitational potential energy on it. This is so because gravity works on the mass as a whole. Option A is not the answer to our question.
The magnetic field acts in between the poles normally, that I, parallel to the rod. Therefore, it does not contribute to the work. Option D is rendered invalid.
And finally, the magnetic flux in contact with the rod does not change. Therefore, option C is invalid as well.
In conclusion, the correct option is A.
Note:Magnetic field, magnetic flux should not be confused. One is a force field and the other is the number of force lines in that force field. In this case, neither contribute to the work done by the gravitational potential energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




