
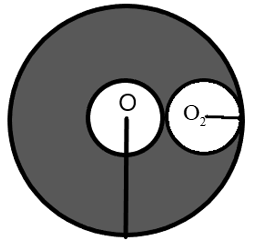
A thick shell with inner radius R and outer radius 3R has uniform charge density $\rho$ \[C{{m}^{-3}}\]. It has a spherical cavity of radius R as shown in the figure. What is the electric field at the centre \[{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] of the cavity?

Answer
588k+ views
Hint: We have to consider the given spherical shell to find the electric field at the given point. We can find the electric field at the center of the cavity using the relation between the electric field and the point under consideration logically keeping the potential conditions in mind.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that a thick shell of outer radius 3R and inner radius R consists of a uniform electric field density. The uniform charge density is spread across the volume of the thick shell. We need to analyse this situation and find the electric field at the point \[{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]which is the centre of a cavity of the than the cavity if the shell.
When we closely look at the shell, we know that the cavity regions are within the shell that encloses the uniform charge density, but the cavity doesn’t hold an electric field when inside a conducting sphere.
According to the Gauss’ law of electrostatics, the region bounded by a conductor is devoid of any electric field. It is because the surface of the region will be in an equipotential state. i.e.,
\[\oint{E.dA}=\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\]
Where, q is the charge enclosed by the area under consideration. We understand from the figure of the shell that there exists no electric charge in the cavity, therefore, the electric field enclosed by the area will be zero.
The electric field at the centre \[{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] is zero.
Note: The Gauss law of electricity is the closed integral over the area enclosed by the surface in which an electric charge is supposed to be present. A cavity inside a conductor acts as a Faraday’s cage, which doesn’t allow an electric field to pass through.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that a thick shell of outer radius 3R and inner radius R consists of a uniform electric field density. The uniform charge density is spread across the volume of the thick shell. We need to analyse this situation and find the electric field at the point \[{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]which is the centre of a cavity of the than the cavity if the shell.

When we closely look at the shell, we know that the cavity regions are within the shell that encloses the uniform charge density, but the cavity doesn’t hold an electric field when inside a conducting sphere.
According to the Gauss’ law of electrostatics, the region bounded by a conductor is devoid of any electric field. It is because the surface of the region will be in an equipotential state. i.e.,
\[\oint{E.dA}=\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\]
Where, q is the charge enclosed by the area under consideration. We understand from the figure of the shell that there exists no electric charge in the cavity, therefore, the electric field enclosed by the area will be zero.
The electric field at the centre \[{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] is zero.
Note: The Gauss law of electricity is the closed integral over the area enclosed by the surface in which an electric charge is supposed to be present. A cavity inside a conductor acts as a Faraday’s cage, which doesn’t allow an electric field to pass through.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




