
A test cross is carried out to
A. Predict whether two traits are linked
B. Assess the number of alleles of a gene
C. Determine whether two species or varieties will breed successfully
D. Determine the genotype of a plant at \[{{F}_{2}}\]
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: A test cross happens in between a double recessive parent and \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation. Moreover, it tells that if an organism is showing the dominant trait is homozygous or heterozygous.
Complete step by step answer: Gregor Mendel introduced the idea of a test cross. He introduced this technique to know that if an organism is exhibiting a dominant trait is homozygous or heterozygous.
-The physical characters or phenotype of an organism are characterized by its genetic constitution. This genetic framework of an individual is called its genotype. Thus, a test cross is simply a test to determine the genotype of an organism.
-Let us understand the test cross with the help of an example and determine what character can be identified from a test cross.
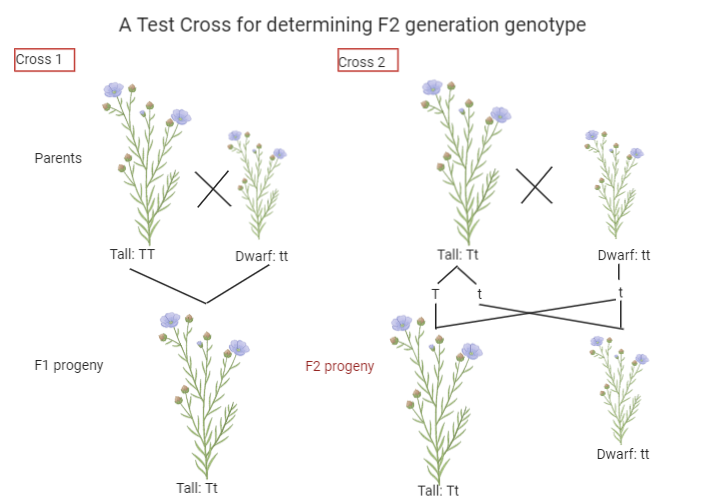
-Consider a cross between a tall and dwarf plant with genotypes homozygous tall TT and homozygous dwarf tt. Where T represents a tall trait and t represents a dwarf trait. When they will be crossed their progeny comes out to be all tall plants as the T is a dominant trait and expresses itself whenever it will pair with t. so, this will be the \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation.
-The test cross will be done to know that the \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation obtained has a homozygous tall combination or a heterozygous tall combination. The homozygous will be TT and the heterozygous will be Tt. So, a test cross will be done between the dwarf parent plant with genotype tt and \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation plants.
-After the cross is done we will obtain the progeny that will be \[{{F}_{2}}\] progeny. Here it will be noticed that half of the progeny is tall with genotype Tt and half is dwarf with genotype tt. This means that the \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation is having a heterozygous tall genotype that is Tt.
-Therefore, after a test cross, we came to know about the type of genotype of \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation. Also, we can determine what is the genotype of \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation.
Hence, the right answer is option D. A test cross is carried out to determine the genotype of the plant at \[{{F}_{2}}\].
Note: In \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation, if all the progeny are recessive then the unknown dominant genotype will always be heterozygous. Heterozygous means a genotype having a combination of two different alleles for a single trait like Tt. In the case of all dominant phenotypes \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation, the unknown dominant will be homozygous. This means a genotype that will have double the same allele for a single trait like TT.
Complete step by step answer: Gregor Mendel introduced the idea of a test cross. He introduced this technique to know that if an organism is exhibiting a dominant trait is homozygous or heterozygous.
-The physical characters or phenotype of an organism are characterized by its genetic constitution. This genetic framework of an individual is called its genotype. Thus, a test cross is simply a test to determine the genotype of an organism.
-Let us understand the test cross with the help of an example and determine what character can be identified from a test cross.

-Consider a cross between a tall and dwarf plant with genotypes homozygous tall TT and homozygous dwarf tt. Where T represents a tall trait and t represents a dwarf trait. When they will be crossed their progeny comes out to be all tall plants as the T is a dominant trait and expresses itself whenever it will pair with t. so, this will be the \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation.
-The test cross will be done to know that the \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation obtained has a homozygous tall combination or a heterozygous tall combination. The homozygous will be TT and the heterozygous will be Tt. So, a test cross will be done between the dwarf parent plant with genotype tt and \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation plants.
-After the cross is done we will obtain the progeny that will be \[{{F}_{2}}\] progeny. Here it will be noticed that half of the progeny is tall with genotype Tt and half is dwarf with genotype tt. This means that the \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation is having a heterozygous tall genotype that is Tt.
-Therefore, after a test cross, we came to know about the type of genotype of \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation. Also, we can determine what is the genotype of \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation.
Hence, the right answer is option D. A test cross is carried out to determine the genotype of the plant at \[{{F}_{2}}\].
Note: In \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation, if all the progeny are recessive then the unknown dominant genotype will always be heterozygous. Heterozygous means a genotype having a combination of two different alleles for a single trait like Tt. In the case of all dominant phenotypes \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation, the unknown dominant will be homozygous. This means a genotype that will have double the same allele for a single trait like TT.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

a What type of deviation is shown by a mixture of ethanol class 12 chemistry CBSE

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE




