
A taxi charge \[{\text{Rs}}.20\] for the first \[km\]& @ \[{\text{Rs}}{\text{.1}}2\] per \[km\] for subsequent distance covered. Taking the distance as \[x{\text{ }}km\] and a total fare \[{\text{Rs}}{\text{. }}y\], write a linear equation depicting the relation in \[x{\text{ and }}y\]. From your graph find the taxi charges for covering \[{\text{16 }}km\].
Answer
525.1k+ views
Hint: In this question, the linear equation is formed by equating the taxi charges and the distance covered multiplied with their respective charges. Then plot the graph for the obtained linear equation in two variables and then find the point at which the distance covered is \[{\text{16 }}km\] to find the required taxi charges.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given taxi charges for the first \[km\] = \[{\text{Rs}}.20\]
Taxi charges for next subsequent distance in \[km\] = \[{\text{Rs}}{\text{.1}}2\]
The total distance covered = \[x{\text{ }}km\]
The total fare = \[{\text{Rs}}{\text{. }}y\]
So, the total fare is given by
\[ \Rightarrow y = 20\left( {{\text{for first }}km} \right) + 12\left[ {\left( {{\text{total distance}} - 1} \right){\text{ in }}km} \right]\]
By using the above data, we have
\[
\Rightarrow y = 20 + 12\left( {x - 1} \right) \\
\Rightarrow y = 20 + 12x - 12 \\
\therefore y = 12x + 8 \\
\]
Thus, the linear equation depicting the relation in \[x{\text{ and }}y\] is \[y = 12x + 8\].
Drawing graph to the linear equation, by using the given below table, we have
So, the graph is shown below:
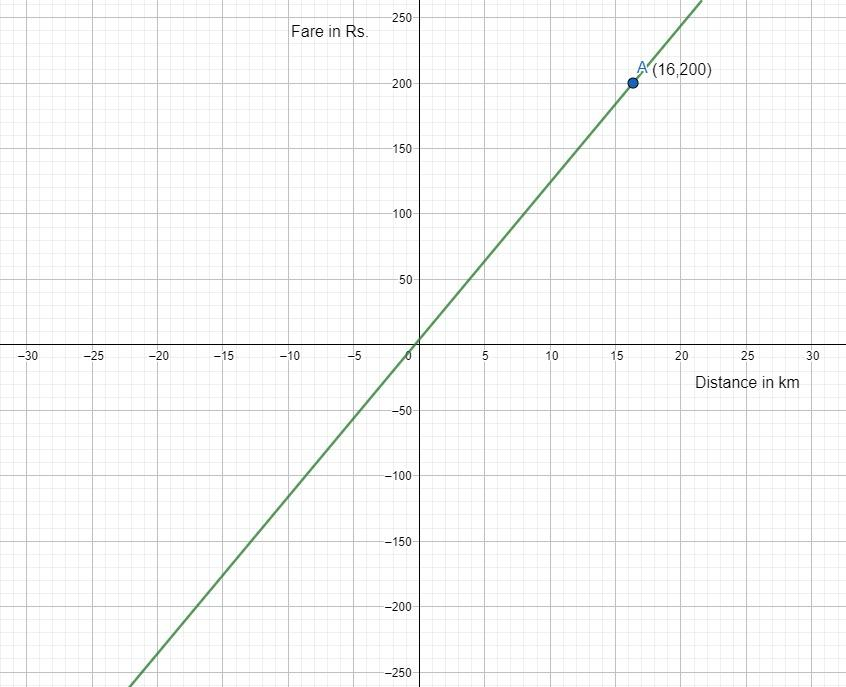
Now we have to plot the point at which the distance covered is \[16{\text{ }}km\]i.e., \[x = 16\]
So, clearly from the graph \[y = 200\] when \[x = 16\].
Therefore, the taxi charges are Rs. 200.
Note: The graph is taken on the bases of the scale 1 unit = \[5{\text{ }}km\]on x-axis at which distance is covered and 1 unit = \[{\text{Rs}}.50\] on y-axis at which taxi charges are mentioned. The taxi charges cannot be negative as the distance covered is positive.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given taxi charges for the first \[km\] = \[{\text{Rs}}.20\]
Taxi charges for next subsequent distance in \[km\] = \[{\text{Rs}}{\text{.1}}2\]
The total distance covered = \[x{\text{ }}km\]
The total fare = \[{\text{Rs}}{\text{. }}y\]
So, the total fare is given by
\[ \Rightarrow y = 20\left( {{\text{for first }}km} \right) + 12\left[ {\left( {{\text{total distance}} - 1} \right){\text{ in }}km} \right]\]
By using the above data, we have
\[
\Rightarrow y = 20 + 12\left( {x - 1} \right) \\
\Rightarrow y = 20 + 12x - 12 \\
\therefore y = 12x + 8 \\
\]
Thus, the linear equation depicting the relation in \[x{\text{ and }}y\] is \[y = 12x + 8\].
Drawing graph to the linear equation, by using the given below table, we have
| For equation \[y = 12x + 8\] | |||||
| \[x\] | - 2 | - 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| \[y\] | - 16 | - 4 | 8 | 20 | 32 |
So, the graph is shown below:

Now we have to plot the point at which the distance covered is \[16{\text{ }}km\]i.e., \[x = 16\]
So, clearly from the graph \[y = 200\] when \[x = 16\].
Therefore, the taxi charges are Rs. 200.
Note: The graph is taken on the bases of the scale 1 unit = \[5{\text{ }}km\]on x-axis at which distance is covered and 1 unit = \[{\text{Rs}}.50\] on y-axis at which taxi charges are mentioned. The taxi charges cannot be negative as the distance covered is positive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




