
A tangent to the parabola ${{x}^{2}}+4ay=0$ cuts the parabola ${{x}^{2}}=4by$ at two points A, B. Find the locus of the midpoint of AB.
[a] $\left( a+2b \right){{x}^{2}}=4{{b}^{2}}y$
[b] $\left( b+2a \right){{x}^{2}}=4{{b}^{2}}y$
[c] $\left( a+2b \right){{y}^{2}}=4{{b}^{2}}x$
[d] $\left( b+2x \right){{x}^{2}}=4{{a}^{2}}y$
Answer
608.1k+ views
- Hint: Use the property that the tangent of the slope of m to the parabola ${{x}^{2}}=-4ay$ is given by $y=mx+a{{m}^{2}}$. Hence find the coordinates of the point of intersection of this line with the parabola and hence find the locus of midpoint of AB.
Complete step-by-step solution -
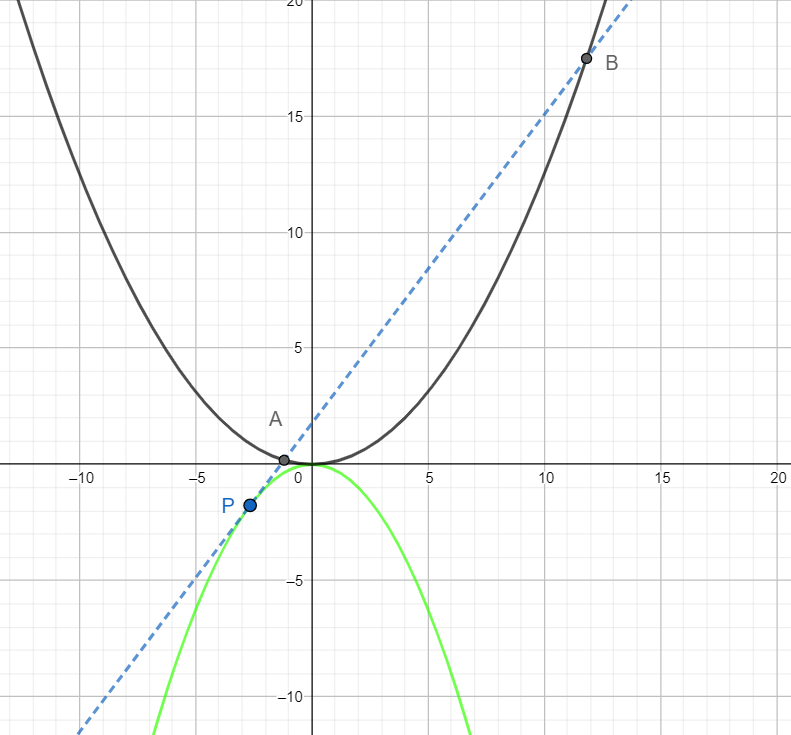
Let the slope of the tangent at P be m.
We know that the tangent of the slope of m to the parabola ${{x}^{2}}=-4ay$ is given by $y=mx+a{{m}^{2}}$.
Hence the equation of PB is $y=mx+a{{m}^{2}}$
Finding the points of intersection of P with the parabola ${{x}^{2}}=4by$:
Substituting the value of y from the equation of PB in the equation of the parabola ${{x}^{2}}=4by$, we get
${{x}^{2}}=4b\left( mx+a{{m}^{2}} \right)$
Hence we have ${{x}^{2}}-4bmx-4ab{{m}^{2}}=0\text{ (i)}$
Let $A\equiv \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and $B\equiv \left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$, we have ${{x}_{1}},{{x}_{2}}$ are the roots of equation (i)
Hence we have ${{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}=4bm$
Also $x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}={{\left( {{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}-2{{x}_{1}}{{x}_{2}}=16{{b}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+8ab{{m}^{2}}$
Let $D\equiv \left( h,k \right)$ be the midpoint of AB.
Hence we have $h=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2}=\dfrac{4bm}{2}=2bm$ and $k=\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2}$
Since $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right),\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ lie on ${{x}^{2}}=4by$, we have
$\begin{align}
& x_{1}^{2}=4b{{y}_{1}},x_{2}^{2}=4b{{y}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{x_{1}^{2}}{4b},{{y}_{2}}=\dfrac{x_{2}^{2}}{4b} \\
\end{align}$
Hence we have $k=\dfrac{x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}}{8b}=\dfrac{16{{b}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+8ab{{m}^{2}}}{8b}=2b{{m}^{2}}+a{{m}^{2}}$
Since $h=2bm$, we have $m=\dfrac{h}{2b}$
Hence we have
$\begin{align}
& k=2b{{\left( \dfrac{h}{2b} \right)}^{2}}+a{{\left( \dfrac{h}{2b} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \left( a+2b \right){{h}^{2}}=4{{b}^{2}}k \\
\end{align}$
Replacing h by x and k by y, we get locus of the midpoint of AB is
$\left( a+2b \right){{x}^{2}}=4{{b}^{2}}y$
Hence option [a] is correct.
Note: Alternatively, you can use the parametric form of the parabola to find A, B.
Let $P\equiv \left( 2at,-a{{t}^{2}} \right)$
We know that the equation of the tangent at $P\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ to the parabola ${{x}^{2}}=-4ay$ is given by $x{{x}_{1}}=-2a\left( y+{{y}_{1}} \right)$
Hence we have the equation of the tangent at P is
$\begin{align}
& x\left( 2at \right)=-2a\left( y-a{{t}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=a{{t}^{2}}-tx \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the value of y in ${{x}^{2}}=4by$, we get
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}=4b\left( a{{t}^{2}}-xt \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+4bxt-4ab{{t}^{2}}=0 \\
\end{align}$
Hence we have ${{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}=-4bt$ and $x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}=16{{b}^{2}}{{t}^{2}}+8ab{{t}^{2}}$
Hence, we have $h=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2}=-2bt$ and $k=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}+{{x}_{2}}^{2}}{8b}=2b{{t}^{2}}+a{{t}^{2}}$
Hence we have
$\begin{align}
& k=2b{{\left( \dfrac{-h}{2b} \right)}^{2}}+a{{\left( \dfrac{-h}{2b} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \left( a+2b \right){{h}^{2}}=4{{b}^{2}}k \\
\end{align}$
Replacing h by x and k by y, we get
$\left( a+2b \right){{x}^{2}}=4{{b}^{2}}y$, which is the same equation as obtained above.
Hence option [a] is correct.
Complete step-by-step solution -

Let the slope of the tangent at P be m.
We know that the tangent of the slope of m to the parabola ${{x}^{2}}=-4ay$ is given by $y=mx+a{{m}^{2}}$.
Hence the equation of PB is $y=mx+a{{m}^{2}}$
Finding the points of intersection of P with the parabola ${{x}^{2}}=4by$:
Substituting the value of y from the equation of PB in the equation of the parabola ${{x}^{2}}=4by$, we get
${{x}^{2}}=4b\left( mx+a{{m}^{2}} \right)$
Hence we have ${{x}^{2}}-4bmx-4ab{{m}^{2}}=0\text{ (i)}$
Let $A\equiv \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and $B\equiv \left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$, we have ${{x}_{1}},{{x}_{2}}$ are the roots of equation (i)
Hence we have ${{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}=4bm$
Also $x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}={{\left( {{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}-2{{x}_{1}}{{x}_{2}}=16{{b}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+8ab{{m}^{2}}$
Let $D\equiv \left( h,k \right)$ be the midpoint of AB.
Hence we have $h=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2}=\dfrac{4bm}{2}=2bm$ and $k=\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2}$
Since $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right),\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ lie on ${{x}^{2}}=4by$, we have
$\begin{align}
& x_{1}^{2}=4b{{y}_{1}},x_{2}^{2}=4b{{y}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{x_{1}^{2}}{4b},{{y}_{2}}=\dfrac{x_{2}^{2}}{4b} \\
\end{align}$
Hence we have $k=\dfrac{x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}}{8b}=\dfrac{16{{b}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+8ab{{m}^{2}}}{8b}=2b{{m}^{2}}+a{{m}^{2}}$
Since $h=2bm$, we have $m=\dfrac{h}{2b}$
Hence we have
$\begin{align}
& k=2b{{\left( \dfrac{h}{2b} \right)}^{2}}+a{{\left( \dfrac{h}{2b} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \left( a+2b \right){{h}^{2}}=4{{b}^{2}}k \\
\end{align}$
Replacing h by x and k by y, we get locus of the midpoint of AB is
$\left( a+2b \right){{x}^{2}}=4{{b}^{2}}y$
Hence option [a] is correct.
Note: Alternatively, you can use the parametric form of the parabola to find A, B.
Let $P\equiv \left( 2at,-a{{t}^{2}} \right)$
We know that the equation of the tangent at $P\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ to the parabola ${{x}^{2}}=-4ay$ is given by $x{{x}_{1}}=-2a\left( y+{{y}_{1}} \right)$
Hence we have the equation of the tangent at P is
$\begin{align}
& x\left( 2at \right)=-2a\left( y-a{{t}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=a{{t}^{2}}-tx \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the value of y in ${{x}^{2}}=4by$, we get
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}=4b\left( a{{t}^{2}}-xt \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+4bxt-4ab{{t}^{2}}=0 \\
\end{align}$
Hence we have ${{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}=-4bt$ and $x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}=16{{b}^{2}}{{t}^{2}}+8ab{{t}^{2}}$
Hence, we have $h=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2}=-2bt$ and $k=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}+{{x}_{2}}^{2}}{8b}=2b{{t}^{2}}+a{{t}^{2}}$
Hence we have
$\begin{align}
& k=2b{{\left( \dfrac{-h}{2b} \right)}^{2}}+a{{\left( \dfrac{-h}{2b} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \left( a+2b \right){{h}^{2}}=4{{b}^{2}}k \\
\end{align}$
Replacing h by x and k by y, we get
$\left( a+2b \right){{x}^{2}}=4{{b}^{2}}y$, which is the same equation as obtained above.
Hence option [a] is correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




