
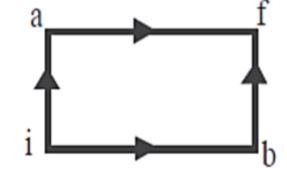
When a system is taken from state \[{\text{i}}\] to state \[{\text{f}}\] along the path \[iaf\], it is found that \[Q = 50{\text{ cal}}\] and \[W = 20{\text{ }}cal{\text{ }}\]. Along the path \[ibf\], \[Q = 36{\text{ cal}}\], \[W\] along the path \[ibf\] is:
A. \[{\text{6 cal}}\]
B. \[{\text{16 cal}}\]
C. \[{\text{66 cal}}\]
D. \[{\text{14 cal}}\]

Answer
480.6k+ views
Hint: In order to answer this question, we need to understand the first law of thermodynamics. First law of thermodynamics states that we know that both the total work done W and the total heat transfer \[Q\] to or from the system depend on the thermodynamics path. However, the difference \[Q - W\] is small for all paths between the given initial and final equilibrium states, and it is equal to the change in internal energy \[\Delta U\] of the system. Using this law and making some modification to the law we can get the answer.
Formula Used:
\[\Delta U = Q - W\]
Where, $\Delta U$ is the change in the internal energy of the system, $W$ is the work done by the system on the surrounding, $Q$is the heat supplied to the system on the surrounding.
Complete step by step answer:
First law states that whenever heat is being added in a system from the external source. Some of the energy stays with the system, and the rest of it gets consumed from work. The energy left in the system increases the internal energy. Internal energy is the total of your kinetic energy and potential energy. According to the first law of thermodynamics for the path \[iaf,\]
\[{Q_{iaf}} = \Delta {U_{iaf}} + {W_{iaf}}\]
Rearranging the terms,
\[\Delta {U_{iaf}} = {Q_{iaf}} - {W_{iaf}}\]
Here we know that,
\[{Q_{iaf}} = 50\]
\[{W_{iaf}} = 20\]
Substituting the values we get,
\[\Delta {U_{iaf}} = {Q_{iaf}} - {W_{iaf}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta {U_{iaf}} = 50 - 30\]
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta {U_{iaf}} = 30\]
For the path ibf,
\[{Q_{ibf}} = \Delta {U_{ibf}} + {W_{ibf}}\]
Since, \[\Delta {U_{ibf}} = \Delta {U_{iaf}}\] changes in internal energy are path independent.We know,
\[{W_{ibf}} = {Q_{ibf}} - \Delta {U_{ibf}}\]
Substituting the values we get,
\[{Q_{ibf}} = 36{\text{ cal}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \Delta {U_{ibf}} = 30{\text{ cal}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {W_{ibf}} = 36 - 30\]
\[ \therefore {W_{ibf}} = 6{\text{ cal}}{\text{.}}\]
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: It should be remembered that there are four main laws of thermodynamics, but in most cases, we only need the first three. In addition to this, the potential of molecular networks and every other minute detail of its design can be studied using thermodynamics. When heat is supplied to the system, then \[\Delta Q\] is positive and when heat is withdrawn from the system, \[\Delta Q\] is negative.
Formula Used:
\[\Delta U = Q - W\]
Where, $\Delta U$ is the change in the internal energy of the system, $W$ is the work done by the system on the surrounding, $Q$is the heat supplied to the system on the surrounding.
Complete step by step answer:
First law states that whenever heat is being added in a system from the external source. Some of the energy stays with the system, and the rest of it gets consumed from work. The energy left in the system increases the internal energy. Internal energy is the total of your kinetic energy and potential energy. According to the first law of thermodynamics for the path \[iaf,\]
\[{Q_{iaf}} = \Delta {U_{iaf}} + {W_{iaf}}\]
Rearranging the terms,
\[\Delta {U_{iaf}} = {Q_{iaf}} - {W_{iaf}}\]
Here we know that,
\[{Q_{iaf}} = 50\]
\[{W_{iaf}} = 20\]
Substituting the values we get,
\[\Delta {U_{iaf}} = {Q_{iaf}} - {W_{iaf}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta {U_{iaf}} = 50 - 30\]
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta {U_{iaf}} = 30\]
For the path ibf,
\[{Q_{ibf}} = \Delta {U_{ibf}} + {W_{ibf}}\]
Since, \[\Delta {U_{ibf}} = \Delta {U_{iaf}}\] changes in internal energy are path independent.We know,
\[{W_{ibf}} = {Q_{ibf}} - \Delta {U_{ibf}}\]
Substituting the values we get,
\[{Q_{ibf}} = 36{\text{ cal}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \Delta {U_{ibf}} = 30{\text{ cal}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {W_{ibf}} = 36 - 30\]
\[ \therefore {W_{ibf}} = 6{\text{ cal}}{\text{.}}\]
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: It should be remembered that there are four main laws of thermodynamics, but in most cases, we only need the first three. In addition to this, the potential of molecular networks and every other minute detail of its design can be studied using thermodynamics. When heat is supplied to the system, then \[\Delta Q\] is positive and when heat is withdrawn from the system, \[\Delta Q\] is negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




