
A student plotted a graph from his readings on the determination of Young’s modulus of a metal wire but forgotten to label. The quantities on x and y can not represent
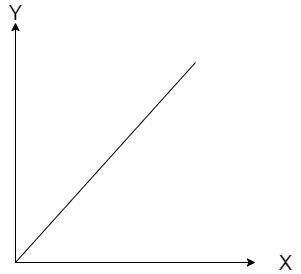
A.Weight hung and extension
B.Stress applied and extension
C.Stress applied and strain produced
D.Stress applied and energy stored

Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint: Young’s modulus is also called the modulus of elasticity. Young’s modulus is used to describe the relation between stress and strain. It is a measure of the properties of the solids like rods, wires etc. It is denoted as E or Y. If Young’s modulus of a body is known, then the rigidity of the material can be determined.
Complete answer:
Step I:
The formula for Young’s modulus is
$Y = \dfrac{{Stress}}{{Strain}}$
$Stress = Y \times Strain$---(i)
Step II:
Stress is defined as force applied per unit area. It’s formula is
$\sigma = \dfrac{F}{A}$
Where F is the force applied
A is the area
$\sigma $is the stress applied
Strain is the ratio of the amount of deformation experienced by the body in the direction of force applied and the initial dimensions of the body.
$e = \dfrac{{\delta l}}{L}$
Where e is the strain
$\delta l$is the change in length
$L$is the original length
Step III:
Substitute the values in equation (i),
$\dfrac{F}{A} = Y.\dfrac{{\delta l}}{L}$
$F = (A.\dfrac{{\delta l}}{L}).Y$
It is clear that
$F \propto l$
Step IV:
If weight is loaded to the string, then its length will increase. Also when weight is loaded, stress is produced in the string. Also when stress is applied, then strain is produced. Since both the X and Y axes values are not known, hence any of the axes can increase the length of the string.
Step V:
$ \Rightarrow $The quantities on x and y can not represent the weight hung, stress applied, energy stored, strain produced and extension.
Therefore all the options given are true.
Note:
As already told, the Young’s modulus determines the hardness or rigidity. If the value of Young’s modulus is high, the value of stress applied will also be high and the body will be hard. But in case of a soft material the value of Young’s modulus is zero.
Complete answer:
Step I:
The formula for Young’s modulus is
$Y = \dfrac{{Stress}}{{Strain}}$
$Stress = Y \times Strain$---(i)
Step II:
Stress is defined as force applied per unit area. It’s formula is
$\sigma = \dfrac{F}{A}$
Where F is the force applied
A is the area
$\sigma $is the stress applied
Strain is the ratio of the amount of deformation experienced by the body in the direction of force applied and the initial dimensions of the body.
$e = \dfrac{{\delta l}}{L}$
Where e is the strain
$\delta l$is the change in length
$L$is the original length
Step III:
Substitute the values in equation (i),
$\dfrac{F}{A} = Y.\dfrac{{\delta l}}{L}$
$F = (A.\dfrac{{\delta l}}{L}).Y$
It is clear that
$F \propto l$
Step IV:
If weight is loaded to the string, then its length will increase. Also when weight is loaded, stress is produced in the string. Also when stress is applied, then strain is produced. Since both the X and Y axes values are not known, hence any of the axes can increase the length of the string.
Step V:
$ \Rightarrow $The quantities on x and y can not represent the weight hung, stress applied, energy stored, strain produced and extension.
Therefore all the options given are true.
Note:
As already told, the Young’s modulus determines the hardness or rigidity. If the value of Young’s modulus is high, the value of stress applied will also be high and the body will be hard. But in case of a soft material the value of Young’s modulus is zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




