
A student obtains a blurred image of an object on a screen by using a concave mirror. In order to obtain a sharp image on the screen, he will have to shift the mirror:
A. towards the screen
B. away from the screen.
C. either towards or away from the screen depending upon the position of the screen.
D. to a position very far away from the screen.
Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: Recollect the properties of real and virtual images as well as the image formation in a concave mirror. Draw the image formation of a concave mirror by placing the object at different positions.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Mirrors have a specific property of which we are very familiar with. They can reflect the clear image of the object which is placed in front of it. Concave mirror comes under the category of curved mirror. Since the light rays converge at a point in the principal axis after the reflection, it’s also known as converging mirror. Focus is the point where all the light rays coincide after reflection.
Concave mirror can form both real and virtual images depending on the distance between the mirror and the object.
How can we identify whether the image is real or virtual?
Real image: The image formed when rays of light meet at a point after reflection/refraction is called real image. It will be inverted, sharp and its height will be always equal or less than the size of the object. It is formed on the same side of the object.
Virtual image: The image formed when rays of light appear to meet (when diverging rays are extended) at a point. Its height will be always greater than the height of the object and appear to be formed on the other side of the object. And it is always erect and blurred.
Case 1. If the object is placed in front of the mirror.
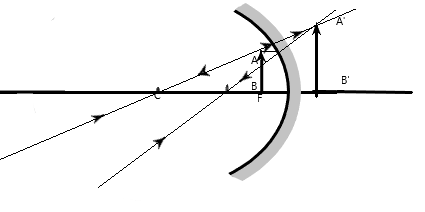
Here the image is formed at the back side of the mirror. It is erect and magnified. So, it is a virtual image.
Case2: If the object is placed at the F.
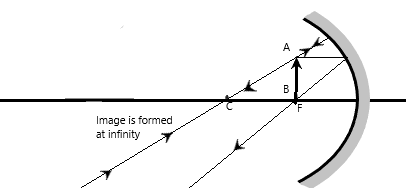
Here the image formed in front of the mirror. The image is formed at infinity. It is inverted and the height of the image is the same as that of the object. Hence, it’s a real image. Then we will get a sharp image.
Case 3: If the object is placed beyond C.
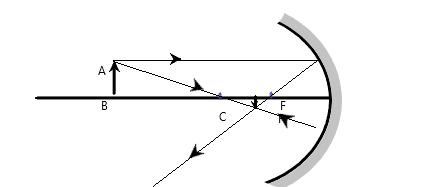
Here also the image is formed on the same side of the mirror. It is inverted and smaller than the object. So, by looking into the properties we can conclude, it is a real image.
In conclusion, we can say that it depends on the position of the object whether we need to move the screen away or close to the mirror. Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Don’t get confused with the images formed by a convex mirror. Even though a concave mirror is converging in nature, the concave lens is actually diverging in nature. Similarly, a convex mirror is diverging but the convex lens is converging in nature.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Mirrors have a specific property of which we are very familiar with. They can reflect the clear image of the object which is placed in front of it. Concave mirror comes under the category of curved mirror. Since the light rays converge at a point in the principal axis after the reflection, it’s also known as converging mirror. Focus is the point where all the light rays coincide after reflection.
Concave mirror can form both real and virtual images depending on the distance between the mirror and the object.
How can we identify whether the image is real or virtual?
Real image: The image formed when rays of light meet at a point after reflection/refraction is called real image. It will be inverted, sharp and its height will be always equal or less than the size of the object. It is formed on the same side of the object.
Virtual image: The image formed when rays of light appear to meet (when diverging rays are extended) at a point. Its height will be always greater than the height of the object and appear to be formed on the other side of the object. And it is always erect and blurred.
Case 1. If the object is placed in front of the mirror.

Here the image is formed at the back side of the mirror. It is erect and magnified. So, it is a virtual image.
Case2: If the object is placed at the F.

Here the image formed in front of the mirror. The image is formed at infinity. It is inverted and the height of the image is the same as that of the object. Hence, it’s a real image. Then we will get a sharp image.
Case 3: If the object is placed beyond C.

Here also the image is formed on the same side of the mirror. It is inverted and smaller than the object. So, by looking into the properties we can conclude, it is a real image.
In conclusion, we can say that it depends on the position of the object whether we need to move the screen away or close to the mirror. Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Don’t get confused with the images formed by a convex mirror. Even though a concave mirror is converging in nature, the concave lens is actually diverging in nature. Similarly, a convex mirror is diverging but the convex lens is converging in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




