
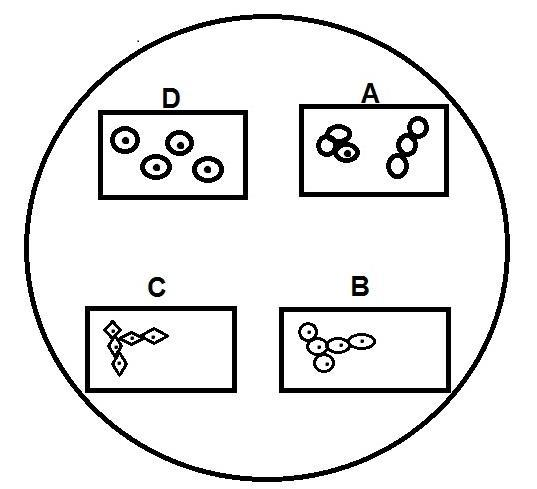
A student observed a slide of yeast under a microscope and saw a collection of cells in different parts of the slides marked A, B, C and D as shown below. Which one of the following parts of slide shows budding in yeast?

Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: Budding is a type of asexual reproduction. Some organisms like hydra and yeast reproduce in this manner. Here, small buds are produced from the parent cell, get separated and mature into a new organism.
Complete answer:
We all know that asexual reproduction is the method by which organisms reproduce in an asexual manner involving only a single parent. Note that it differs from sexual reproduction as the latter involves both parents. Keep in mind that all the off springs produced by asexual reproduction are not only identical to the parent, but also to one another. It is sexual reproduction that brings in variation to the offsprings.
We must know about the examples of asexual reproduction. They are binary fission, budding, zoospore formation, conidia formation and via gemmules.
Budding is the method in which several buds are formed on the parent cell or body. Note that this division is unequal. The bud which gets initially attached to the parent body eventually falls off and matures into a new organism. Budding is seen in yeast (Saccharomyces) and hydra.
In the given figure, B shows budding in yeast. We can see that lateral buds are produced from the parent similar to the budding process. Yeast cells are oval in shape.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B)
Note: Option C shows a phenomenon similar to budding but it cannot be the answer because cells are not oval or spherical in shape as in yeast cells. Keep in mind that budding is an example for both asexual and asymmetric division.
Complete answer:
We all know that asexual reproduction is the method by which organisms reproduce in an asexual manner involving only a single parent. Note that it differs from sexual reproduction as the latter involves both parents. Keep in mind that all the off springs produced by asexual reproduction are not only identical to the parent, but also to one another. It is sexual reproduction that brings in variation to the offsprings.
We must know about the examples of asexual reproduction. They are binary fission, budding, zoospore formation, conidia formation and via gemmules.
Budding is the method in which several buds are formed on the parent cell or body. Note that this division is unequal. The bud which gets initially attached to the parent body eventually falls off and matures into a new organism. Budding is seen in yeast (Saccharomyces) and hydra.
In the given figure, B shows budding in yeast. We can see that lateral buds are produced from the parent similar to the budding process. Yeast cells are oval in shape.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B)
Note: Option C shows a phenomenon similar to budding but it cannot be the answer because cells are not oval or spherical in shape as in yeast cells. Keep in mind that budding is an example for both asexual and asymmetric division.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




