
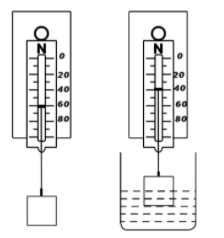
A student notes down the observations in the two spring balances and the measuring cylinder as shown in the diagram. How much is the volume of the solid? Mass of solid is 60 g. What will be the density of the material of the solid?

Answer
572.4k+ views
Hint: In this question we are asked to calculate the density of the material of the solid. We know that density is given by mass over volume. We have been given the value if mass is 60 g. Also, we have been given the readings of weight on spring balance in air and in water. We know that, reductio in weight of solid will be due to buoyant force. Therefore, using this we will calculate the volume and thus, our final answer.
Complete answer:
We have been given readings of a spring balance for a solid in air \[{{W}_{1}}=60\] and \[{{W}_{2}}=40\] as well as water. We know that the reduction in weight of solid in water is due to the buoyant force. Buoyant force will act in opposition of gravity and reduce the readings on spring balance.
Therefore, we can say that,
\[{{W}_{1}}-{{W}_{2}}={{\rho }_{w}}Vg\]
Where, \[{{\rho }_{w}}\]is density of water, V is the volume of the liquid displaced due to mass
Therefore, on substituting values
We get,
\[(60-40)g=1\times Vg\]
Therefore,
\[V=20c{{m}^{3}}\]
Now, we know that the density of a material is given by its mass over volume. Therefore,
\[\rho =\dfrac{m}{V}\]
On substituting values
We get,
\[\rho =\dfrac{60}{20}\]
Therefore,
\[\rho =3g/c{{m}^{3}}\]
Therefore, the density of the material of the solid is 3 g/cc.
Note: - Buoyancy, also called as upward thrust, is an upward force exerted by the fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or completely submerged solid. Buoyant force is the force based on Archimedes Principle. If the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the object the object will float. As pressure in liquid increases towards the depth of the liquid, the force on the lower part of the object submerged in liquid is always greater than the force on the upper part. Hence, the net force acts upwards.
Complete answer:
We have been given readings of a spring balance for a solid in air \[{{W}_{1}}=60\] and \[{{W}_{2}}=40\] as well as water. We know that the reduction in weight of solid in water is due to the buoyant force. Buoyant force will act in opposition of gravity and reduce the readings on spring balance.
Therefore, we can say that,
\[{{W}_{1}}-{{W}_{2}}={{\rho }_{w}}Vg\]
Where, \[{{\rho }_{w}}\]is density of water, V is the volume of the liquid displaced due to mass
Therefore, on substituting values
We get,
\[(60-40)g=1\times Vg\]
Therefore,
\[V=20c{{m}^{3}}\]
Now, we know that the density of a material is given by its mass over volume. Therefore,
\[\rho =\dfrac{m}{V}\]
On substituting values
We get,
\[\rho =\dfrac{60}{20}\]
Therefore,
\[\rho =3g/c{{m}^{3}}\]
Therefore, the density of the material of the solid is 3 g/cc.
Note: - Buoyancy, also called as upward thrust, is an upward force exerted by the fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or completely submerged solid. Buoyant force is the force based on Archimedes Principle. If the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the object the object will float. As pressure in liquid increases towards the depth of the liquid, the force on the lower part of the object submerged in liquid is always greater than the force on the upper part. Hence, the net force acts upwards.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




