
A student is viewing under a microscope a permanent slide showing various stages of asexual reproduction by budding in yeast. Draw diagrams of what he observes (in proper sequence).
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint:The method of budding may be a sort of asexual reproduction where a new living being is made from an outgrowth or bud developing on parent organism due to cell division happening at one particular area. A small bulb-like outgrowth anticipating from the parent yeast cell is called a bud.
Complete answer:
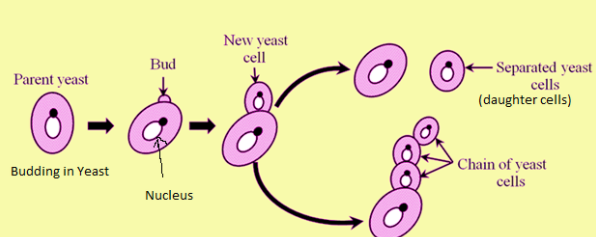
The first common mode of vegetative improvement in yeast is the abiogenetic generation by budding, where a small bud (besides known as a bleb or girl cell) is formed on the parent cell. The centre of the parent cell parts into a young lady centre and moves into the young lady cell. Yeast budding is an imperative preparation to get its cell polarization and symmetry breaking. Studies utilizing both test and illustrating approaches have been broadly conducted on yeast budding. In the midst of budding, a modern girl cell creates from a mother cell through polarized cell improvement. Yeast is single-celled infectious life forms that are Eukaryotes. The most commonly copy asexually by mitosis, but the strategy is to some degree unmistakable from other shapes of Mitosis, in that it incorporates budding.
Additional information:
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. The species has been instrumental in winemaking, heating, and brewing since old times. It is accepted to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes.
Note:Yeast could be a unicellular life form whereas Hydra may be a multicellular life form within the yeast, the bud begins from a little bulge on the parent body, whereas in Hydra the bud emerges due to the rehashed mitotic division.
Complete answer:
The first common mode of vegetative improvement in yeast is the abiogenetic generation by budding, where a small bud (besides known as a bleb or girl cell) is formed on the parent cell. The centre of the parent cell parts into a young lady centre and moves into the young lady cell. Yeast budding is an imperative preparation to get its cell polarization and symmetry breaking. Studies utilizing both test and illustrating approaches have been broadly conducted on yeast budding. In the midst of budding, a modern girl cell creates from a mother cell through polarized cell improvement. Yeast is single-celled infectious life forms that are Eukaryotes. The most commonly copy asexually by mitosis, but the strategy is to some degree unmistakable from other shapes of Mitosis, in that it incorporates budding.

Additional information:
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. The species has been instrumental in winemaking, heating, and brewing since old times. It is accepted to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes.
Note:Yeast could be a unicellular life form whereas Hydra may be a multicellular life form within the yeast, the bud begins from a little bulge on the parent body, whereas in Hydra the bud emerges due to the rehashed mitotic division.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




