
A student added a few pieces of aluminium metal to two test tubes A and B containing aqueous solutions of iron sulphate and copper sulphate. In the second part of her experiment, she added iron metal to another test tube C and D containing aqueous solutions of aluminium sulphate and copper sulphate. In which test tube or test tubes will she observe the colour change? Based on this experiment, state which one is the most reactive metal and why?
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: The reactivity of metal towards the other metal is determined on the basis of the electrochemical series. The metal which is at the higher end of the reactivity series displaces the lower reactivity metal. The reaction is also known as the single displacements reaction. The general depiction is as shown below:
$\text{ }{{\text{M}}_{\text{1}}}^{\text{n+}}\text{ + }{{\text{M}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }\to \text{ }{{\text{M}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ + }{{\text{M}}_{\text{2}}}^{\text{m+}}\text{ }$
Where, $\text{ }{{\text{M}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ }$ has lower activity and $\text{ }{{\text{M}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }$ has the high activity.
Complete Solution :
- The metal which is in the elemental state when placed in the solution of the metal salt of the metal than the more energetic ‘elemental metal ‘exists as an ion and the ‘ionic metal’ exist as an element .in other words, the elements present in the zero oxidation state oxides and the ion in the solution reduces to the zero oxidation state.
- The reaction of the replacement of one of the metal by the other metal in the solution is called the single displacement reaction.
- According to the reactivity series, the metal which has the highest position in the activity series will displace the other metal.
Let's have a look at the experiment.
Part A) the aluminium has a higher position in the reactivity series in comparison with iron and copper. The reaction of the single displacement between the aluminium with iron and copper is as depicted below,
$\begin{align}
& \text{ CuS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ + Al }\to \text{ A}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{(S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}})}_{3}}\text{ + Cu } \\
& \text{ FeS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ + Al }\to \text{ A}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{(S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}})}_{3}}\text{ + Fe } \\
\end{align}$
The aluminium sulphate is colourless, thus the colour of the is due to the free State metal in the solution.
Thus, both the A and B test tube exhibits the colours.
Part B) in this part of the experiment, the student added the pure iron metal to the aqueous solution of aluminium sulphate and copper sulphate .the iron has a higher reactivity as compared to the copper sulphate and less reactivity compare to the aluminium sulphate. Thus, iron can only displace the iron from the iron sulphate. The reactions are as follows,
$\begin{align}
& \text{ CuS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ + Fe }\to \text{ Fe(S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{{)}_{3}}\text{ + Cu } \\
& \text{ A}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{(S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}})}_{3}}\text{ + Fe }\to \text{ No reaction } \\
\end{align}$
Thus, only the D test tube exhibits the colour change.
Hence, A, B, and D test tubes show the colour change in the solution.
Note: the electrochemical series is given as the follows:
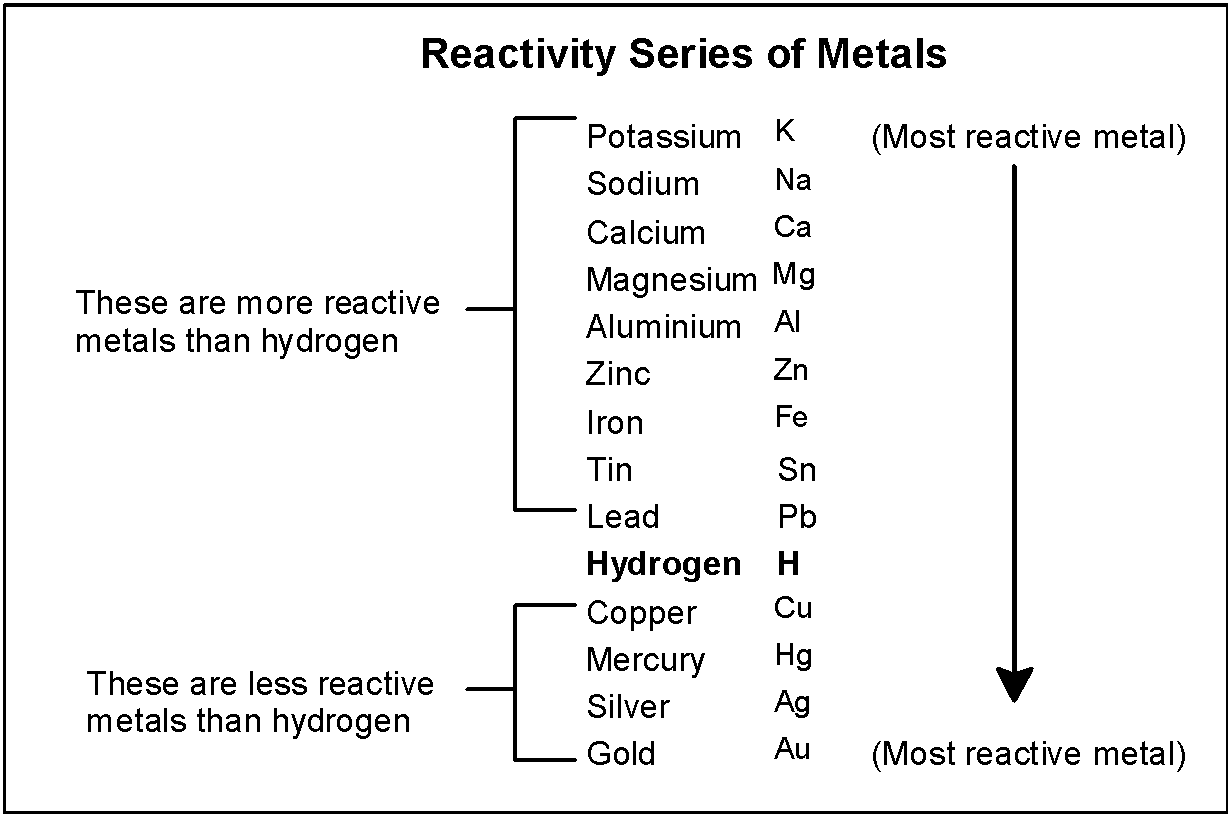
$\text{ }{{\text{M}}_{\text{1}}}^{\text{n+}}\text{ + }{{\text{M}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }\to \text{ }{{\text{M}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ + }{{\text{M}}_{\text{2}}}^{\text{m+}}\text{ }$
Where, $\text{ }{{\text{M}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ }$ has lower activity and $\text{ }{{\text{M}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }$ has the high activity.
Complete Solution :
- The metal which is in the elemental state when placed in the solution of the metal salt of the metal than the more energetic ‘elemental metal ‘exists as an ion and the ‘ionic metal’ exist as an element .in other words, the elements present in the zero oxidation state oxides and the ion in the solution reduces to the zero oxidation state.
- The reaction of the replacement of one of the metal by the other metal in the solution is called the single displacement reaction.
- According to the reactivity series, the metal which has the highest position in the activity series will displace the other metal.
Let's have a look at the experiment.
Part A) the aluminium has a higher position in the reactivity series in comparison with iron and copper. The reaction of the single displacement between the aluminium with iron and copper is as depicted below,
$\begin{align}
& \text{ CuS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ + Al }\to \text{ A}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{(S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}})}_{3}}\text{ + Cu } \\
& \text{ FeS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ + Al }\to \text{ A}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{(S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}})}_{3}}\text{ + Fe } \\
\end{align}$
The aluminium sulphate is colourless, thus the colour of the is due to the free State metal in the solution.
Thus, both the A and B test tube exhibits the colours.
Part B) in this part of the experiment, the student added the pure iron metal to the aqueous solution of aluminium sulphate and copper sulphate .the iron has a higher reactivity as compared to the copper sulphate and less reactivity compare to the aluminium sulphate. Thus, iron can only displace the iron from the iron sulphate. The reactions are as follows,
$\begin{align}
& \text{ CuS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ + Fe }\to \text{ Fe(S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{{)}_{3}}\text{ + Cu } \\
& \text{ A}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{(S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}})}_{3}}\text{ + Fe }\to \text{ No reaction } \\
\end{align}$
Thus, only the D test tube exhibits the colour change.
Hence, A, B, and D test tubes show the colour change in the solution.
Note: the electrochemical series is given as the follows:

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




