
A string of length l tied to the top of a pole, carries a ball at its other end as shown. On giving the ball, a single hand blow perpendicular to the string, it acquires an initial velocity in the horizontal plane and moves in a spiral of decreasing radius by curling itself around the pole. Therefore:
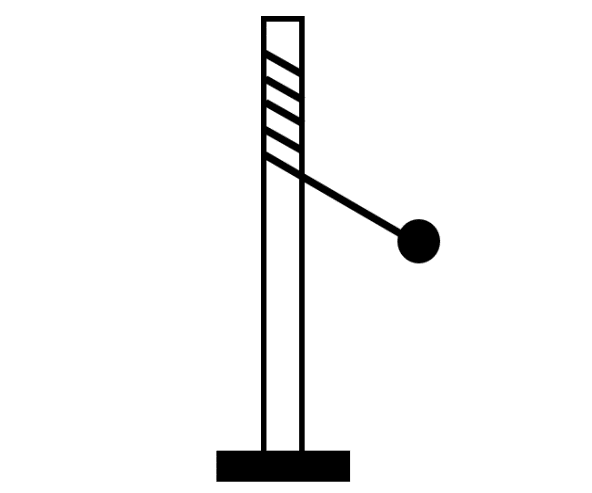
(A) the instantaneous center of revolution of the ball is the point of contact of the string with the pole at that instant.
(B) the instantaneous center of revolution of the ball will be fixed at the point where the string was initially fixed.
(C) the angular momentum of the system will not be conserved
(D) the angular momentum of the system will be conserved

Answer
535.8k+ views
Hint: The instantaneous center of revolution of an object is the point about which an object is performing pure rotation, that is, rotation without slipping. Also, the angular momentum of the ball will be conserved or not will depend on the fact that is there any torque acting on the ball that can bring about a change in its angular velocity.
Complete step-by-step answer:
After the ball has been pushed by a blow perpendicular to the string, the ball starts curling. The phenomenon of curling states that the point of contact of the end string on the pole is continuously changing. Since, the ball is revolving about this point of contact, therefore it is the instantaneous center of revolution. This also implies that the instantaneous point of revolution of the ball is continuously changing.
This statement implies option (A) is correct and option (B) is incorrect.
Now, we have to discuss the conservation of angular momentum. Angular momentum of the ball will be conserved only if the net torque on the ball is zero.
The initial angular velocity of the ball is in counter clockwise direction. And, there are two forces acting on the ball, namely Tension and Force of gravity.
Since the length of wire is slanted, the torque due to tension will be a non-zero quantity and in clockwise direction. Also, the torque due to gravity will be in a counter clockwise direction. These torques do not balance each other. And hence, a net torque about the point of contact acts on the ball.
Hence, the angular momentum of the ball is not conserved.
This implies, option (C) is correct and option (D) is incorrect.
Hence, option (A) and (C) are the correct options.
So, the correct answers are “Option A and C”.
Note: If the same experiment would have been carried out on a smooth table with the length of string purely horizontal. Then, the net torque on the ball would be zero. And hence, the angular momentum of the system would be conserved. We need to differentiate between these almost identical cases carefully.
Complete step-by-step answer:
After the ball has been pushed by a blow perpendicular to the string, the ball starts curling. The phenomenon of curling states that the point of contact of the end string on the pole is continuously changing. Since, the ball is revolving about this point of contact, therefore it is the instantaneous center of revolution. This also implies that the instantaneous point of revolution of the ball is continuously changing.
This statement implies option (A) is correct and option (B) is incorrect.
Now, we have to discuss the conservation of angular momentum. Angular momentum of the ball will be conserved only if the net torque on the ball is zero.
The initial angular velocity of the ball is in counter clockwise direction. And, there are two forces acting on the ball, namely Tension and Force of gravity.
Since the length of wire is slanted, the torque due to tension will be a non-zero quantity and in clockwise direction. Also, the torque due to gravity will be in a counter clockwise direction. These torques do not balance each other. And hence, a net torque about the point of contact acts on the ball.
Hence, the angular momentum of the ball is not conserved.
This implies, option (C) is correct and option (D) is incorrect.
Hence, option (A) and (C) are the correct options.
So, the correct answers are “Option A and C”.
Note: If the same experiment would have been carried out on a smooth table with the length of string purely horizontal. Then, the net torque on the ball would be zero. And hence, the angular momentum of the system would be conserved. We need to differentiate between these almost identical cases carefully.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




