
A straight line through a fixed point (2, 3) intersects the coordinate axes at distinct points P and Q. If O is the origin and the rectangle OPRQ is completed, then the locus of R is:
(a)$3x+2y=xy$
(b)$3x+2y=6xy$
(c)$3x+2y=6$
(d)$2x+3y=xy$
Answer
534.9k+ views
Hint: First of all draw a line which is passing through (2, 3). Now, mark the points where this straight line is cutting x and y axes which are P and Q then mark a point R and name the coordinates as (h, k). And join the points P and Q to R in such a way so that it will form a rectangle. Now, we can write the equation of a straight line passing through the point (2, 3) as $\dfrac{x}{h}+\dfrac{y}{k}=1$. And then satisfy the point (2, 3) to it and will get the relation in h and k. Then we are going to replace h by x and k by y to get the locus of the point R.
Complete step by step solution:
In the above problem, it is given that a straight line is passing through a point (2, 3) so in the below, we are going to draw a straight line which is passing through a point (2, 3).
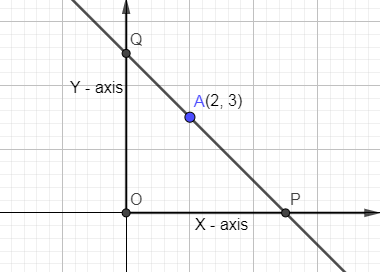
Now, it is given that a rectangle OPRQ has been formed so drawing perpendiculars from P and Q and the intersection of these perpendiculars is point R.

We know that from the straight line chapter, we can write the equation of a straight line passing through point (2, 3) and having x intercept as h and y intercept as k as follows:
$\dfrac{x}{h}+\dfrac{y}{k}=1$
Now, satisfying the point (2, 3) in the above equation because the point (2, 3) is passing through this straight line and we get,
$\dfrac{2}{h}+\dfrac{3}{k}=1$
Solving the above equation by taking h and k as L.C.M and we get,
$\dfrac{2k+3h}{hk}=1$
On cross multiplying the above equation we get,
$2k+3h=hk$
Now, substituting h as x and k as y in the above equation and we get,
$2y+3x=xy$
Rearranging the above equation we get,
$3x+2y=xy$
So, the correct answer is “Option a”.
Note: The above problem has been solved easily because we know that if we have x and y intercept then how can we write the equation of a straight line. If you do not use this intercept form of a straight line then it will be very difficult for you to solve this problem.
Complete step by step solution:
In the above problem, it is given that a straight line is passing through a point (2, 3) so in the below, we are going to draw a straight line which is passing through a point (2, 3).

Now, it is given that a rectangle OPRQ has been formed so drawing perpendiculars from P and Q and the intersection of these perpendiculars is point R.

We know that from the straight line chapter, we can write the equation of a straight line passing through point (2, 3) and having x intercept as h and y intercept as k as follows:
$\dfrac{x}{h}+\dfrac{y}{k}=1$
Now, satisfying the point (2, 3) in the above equation because the point (2, 3) is passing through this straight line and we get,
$\dfrac{2}{h}+\dfrac{3}{k}=1$
Solving the above equation by taking h and k as L.C.M and we get,
$\dfrac{2k+3h}{hk}=1$
On cross multiplying the above equation we get,
$2k+3h=hk$
Now, substituting h as x and k as y in the above equation and we get,
$2y+3x=xy$
Rearranging the above equation we get,
$3x+2y=xy$
So, the correct answer is “Option a”.
Note: The above problem has been solved easily because we know that if we have x and y intercept then how can we write the equation of a straight line. If you do not use this intercept form of a straight line then it will be very difficult for you to solve this problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




