
A stone is dropped from the top of the building and at the same time a $2nd$ stone is thrown vertically upward from the bottom of the building with the speed of $20{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{s}$. They pass each other $3{\text{ }}s$ later. What is the height of the building?
Answer
490.2k+ views
Hint: For the given question we have to find the distance traversed by the stones for two separate cases. The first one for the stone dropped from the top of the building and the other for the stone thrown from the bottom of the building. Then the summation of them will give the height of the building.
Complete step by step answer:
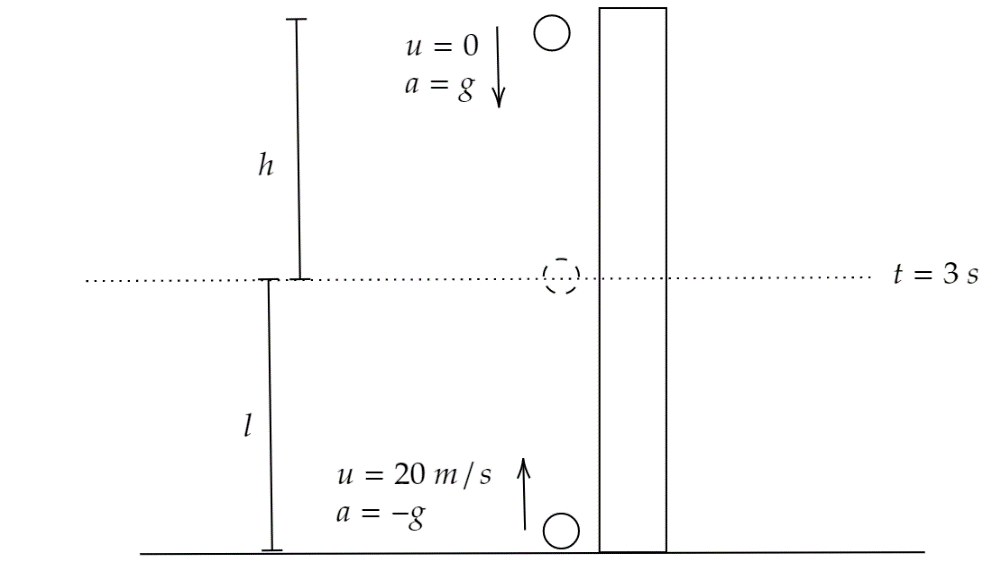
Let us consider that the distance covered by the stone which is dropped from the top of the building be $h$.
According to the given question, the stone which is dropped from the top meets the stone which is thrown upward after $3{\text{ }}s$.
Let us use the motion’s equation,
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} - - - - \left( 1 \right)$
The variables are defined as,
$s = $ distance traversed by the body
$u = $ initial velocity
$a = $ acceleration of the body
$t = $ time
Case-1: The stone which is dropped from the top of the building
$s = h$
$u = 0$ [As the stone is dropped from rest]
$a = g = $ acceleration due to gravity$ = 9.8{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$
$t = 3{\text{ }}s$
Substituting all the values in equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get,
$h = 0 \times 3 + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 9.8 \times {3^2} = 44.1$
The distance covered by the stone dropped from the top of the building in $3{\text{ }}s$ is $44.1{\text{ }}m$.
Case-2: The stone thrown upward from the bottom of the building
Let the distance covered be $l$ in $3{\text{ }}s$.
Hence, $s = l$
$u = 20{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{s}$
$a = g = - 9.8\,{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$
$t = 3{\text{ }}s$
Substituting all the values in equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get,
$l = 20 \times 3 - \dfrac{1}{2} \times 9.8 \times {3^2} = 15.9$
The distance covered by the stone thrown upward from the bottom of the building is $15.9{\text{ }}m$.
Hence, the total height of the building$ = (44.1 + 15.9)m = 60{\text{ }}m$.
Note:It must be noted that we considered the acceleration as the acceleration due to gravity as it acts vertically, where only acceleration due to gravity works if external acceleration is applied. In Case-2, the acceleration due to gravity is negative as it is in opposite to the direction of acceleration due to gravity.
Complete step by step answer:

Let us consider that the distance covered by the stone which is dropped from the top of the building be $h$.
According to the given question, the stone which is dropped from the top meets the stone which is thrown upward after $3{\text{ }}s$.
Let us use the motion’s equation,
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} - - - - \left( 1 \right)$
The variables are defined as,
$s = $ distance traversed by the body
$u = $ initial velocity
$a = $ acceleration of the body
$t = $ time
Case-1: The stone which is dropped from the top of the building
$s = h$
$u = 0$ [As the stone is dropped from rest]
$a = g = $ acceleration due to gravity$ = 9.8{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$
$t = 3{\text{ }}s$
Substituting all the values in equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get,
$h = 0 \times 3 + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 9.8 \times {3^2} = 44.1$
The distance covered by the stone dropped from the top of the building in $3{\text{ }}s$ is $44.1{\text{ }}m$.
Case-2: The stone thrown upward from the bottom of the building
Let the distance covered be $l$ in $3{\text{ }}s$.
Hence, $s = l$
$u = 20{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{s}$
$a = g = - 9.8\,{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$
$t = 3{\text{ }}s$
Substituting all the values in equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get,
$l = 20 \times 3 - \dfrac{1}{2} \times 9.8 \times {3^2} = 15.9$
The distance covered by the stone thrown upward from the bottom of the building is $15.9{\text{ }}m$.
Hence, the total height of the building$ = (44.1 + 15.9)m = 60{\text{ }}m$.
Note:It must be noted that we considered the acceleration as the acceleration due to gravity as it acts vertically, where only acceleration due to gravity works if external acceleration is applied. In Case-2, the acceleration due to gravity is negative as it is in opposite to the direction of acceleration due to gravity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




