
A steady current $I$ flows along an infinitely long hollow cylindrical conductor of radius $R$. This cylinder is placed coaxially inside an infinite solenoid of radius $2\;R$. The solenoid has $n$ turns per unit length and carries a steady current $I$. Consider a point $P$ at a distance $r$ from the common axis. The correct statements are: ( This question has multiple correct answers)
A. in the region $0 < r < R$, the magnetic field is non-zero,
B. in the region $R < r < 2R$, the magnetic field is along the common on axis
C. in the region $R < r < 2R$, the magnetic field is tangential to the circle of radius r, centred on the axis
D. in the region $r > 2R$, the magnetic field is non-zero
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: We know that a current carrying conductor can produce magnetic fields around itself. And we also know that current can be produced by a varying magnetic field. The current produced is called induced current and its direction is given by right hand thumb rule.
Complete Answer:
Consider a hollow cylinder of radius $R$ and an infinite solenoid of radius $2\;R$ to carry current $I$ in the direction as shown in the figure below.
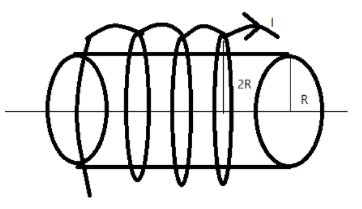
We know that the current in the solenoid induces a magnetic field in the hollow cylinder. Then, for any point $r$ which $0 < r < R$, clearly, there exists a magnetic field. Thus option A is correct.
Due to the current in the solenoid, there is an induced current in the hollow cylinder. The current in the cylinder produces a magnetic field in the outer of the solenoid also. Then we can say that, for a point $r > 2R$, there exists some magnetic field. Thus the option D is also correct.
Hence the correct answer is A. in the region $0 < r < R$, the magnetic field is non-zero, and D. in the region $r > 2R$, the magnetic field is non-zero.
Note:
Here, option B and C are incorrect, as clearly, $R < r < 2R$, it doesn’t lie on the common axis. Also, the magnetic field is a vector sum and hence it cannot lie on the tangent of the solenoid. We also know that direction of current and the direction of magnetic field are interrelated; when one is given the other can be found using the right hand thumb rule.
Complete Answer:
Consider a hollow cylinder of radius $R$ and an infinite solenoid of radius $2\;R$ to carry current $I$ in the direction as shown in the figure below.

We know that the current in the solenoid induces a magnetic field in the hollow cylinder. Then, for any point $r$ which $0 < r < R$, clearly, there exists a magnetic field. Thus option A is correct.
Due to the current in the solenoid, there is an induced current in the hollow cylinder. The current in the cylinder produces a magnetic field in the outer of the solenoid also. Then we can say that, for a point $r > 2R$, there exists some magnetic field. Thus the option D is also correct.
Hence the correct answer is A. in the region $0 < r < R$, the magnetic field is non-zero, and D. in the region $r > 2R$, the magnetic field is non-zero.
Note:
Here, option B and C are incorrect, as clearly, $R < r < 2R$, it doesn’t lie on the common axis. Also, the magnetic field is a vector sum and hence it cannot lie on the tangent of the solenoid. We also know that direction of current and the direction of magnetic field are interrelated; when one is given the other can be found using the right hand thumb rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




