
A staircase has $5$ steps each $10cm$ high and $10cm$ wide. What is the minimum horizontal velocity to be given to the ball so that it hits directly the lowest plane from the top of the staircase? $(g = 10m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 2}})$
A. $2{m^{ - 1}}$
B. $1{m^{ - 1}}$
C. $\sqrt 2 m{s^{ - 1}}$
D. $\dfrac{1}{2}m{s^{ - 1}}$
Answer
497.1k+ views
Hint: In order to answer this question, first we convert the given height and width from $cm{\text{ to m}}$ then we would use equation of motion i.e. $h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$ along the horizontal axis to get the velocity of projection to hit the lowest floor.
Formula used:
$h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Where,
\[h\] is the height,
$u$ is the initial velocity,
$a$ is the acceleration and
$t$ is the time.
Complete step by step solution:
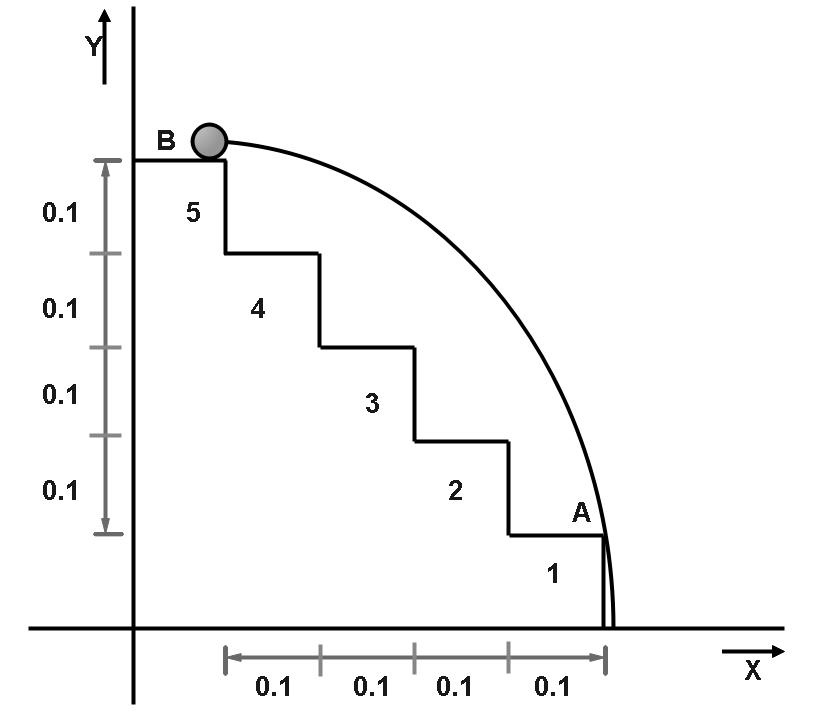
According to question,
\[Height{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}each{\text{ }}step = 10cm = 0.1m\]
\[Width{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}each{\text{ }}step = 10cm = 0.1m\]
The ball needs to just cross the point $A$ of the step number $1$ in order to hit the lowest floor.
So,
${\text{Total horizontal distance till A = 0}}{\text{.1}} \times {\text{4 = 0}}{\text{.4m}}$
${\text{Total vertical distance required}} = 0.1 \times 4 = 0.4m$
And in doing so,
\[let{\text{ }}time{\text{ }}taken = t\]
Or in moving from ${\text{B to A}}$
First calculating along y-axis
We have,
$
S = 0.4m{\text{ (displacement along y - axis)}} \\
u = 0m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 1}}{\text{ (initial velocity along y - axis)}} \\
v = ?{\text{ (final velocity along y - axis)}} \\
t = ?{\text{ (time taken to move from B to A)}} \\
a = 10m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 2}}{\text{ (acceleration due to gravity)}} \\
$
Now, using equation of motion to find the time i.e.
$h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
$
\Rightarrow S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} \\
\Rightarrow 0.4 = 0 + \dfrac{1}{2}( - 10){t^2} \\
\Rightarrow {t^2} = + 0.8 = \dfrac{{0.08}}{{100}} \\
\Rightarrow t = \pm \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 }}{{10}} \\
$
$\because $ Time can not be negative
So, $t = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 }}{{10}}$
Now, solving along horizontal axis,
$
S = 0.4m{\text{ (displacement along x - axis)}} \\
u = v{\text{ (initial velocity along x - axis i}}{\text{.e}}{\text{. projection velocity)}} \\
T = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 }}{{10}}{\text{(time taken which is eventually t)}} \\
{\text{V = v (final velocity which is equal to initial velocity}}\because {\text{a = 0)}} \\
a = 0{\text{ (acceleration along x axis)}} \\
$
So, using equation of motion,
$
h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} \\
\Rightarrow S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} \\
\Rightarrow + 0.4 = v\dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 }}{{10}} + \dfrac{1}{2}(0){t^2} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{{2\sqrt 2 }} = v \\
\Rightarrow v = \sqrt 2 \\
$
So, we get $v = \sqrt 2 $ which is the required horizontal velocity i.e. the projection velocity.
Hence, Option C is correct.
Additional information:
Projectile motion is the motion of an object thrown or projected into the air, subject to only the acceleration of gravity. The object is called a projectile, and its path is called its trajectory. Projectile motion is a two-dimensional projectile motion.
Note:
To solve this problem we must have knowledge of equations of motion. It defines or gives the relation of a particular system with regards to motion as a time function.
Fact: Here we got the value of time both negative as well as positive,
$\because $ As per our knowledge time can not be negative,
$\therefore $ The positive part was considered.
Formula used:
$h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Where,
\[h\] is the height,
$u$ is the initial velocity,
$a$ is the acceleration and
$t$ is the time.
Complete step by step solution:

According to question,
\[Height{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}each{\text{ }}step = 10cm = 0.1m\]
\[Width{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}each{\text{ }}step = 10cm = 0.1m\]
The ball needs to just cross the point $A$ of the step number $1$ in order to hit the lowest floor.
So,
${\text{Total horizontal distance till A = 0}}{\text{.1}} \times {\text{4 = 0}}{\text{.4m}}$
${\text{Total vertical distance required}} = 0.1 \times 4 = 0.4m$
And in doing so,
\[let{\text{ }}time{\text{ }}taken = t\]
Or in moving from ${\text{B to A}}$
First calculating along y-axis
We have,
$
S = 0.4m{\text{ (displacement along y - axis)}} \\
u = 0m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 1}}{\text{ (initial velocity along y - axis)}} \\
v = ?{\text{ (final velocity along y - axis)}} \\
t = ?{\text{ (time taken to move from B to A)}} \\
a = 10m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 2}}{\text{ (acceleration due to gravity)}} \\
$
Now, using equation of motion to find the time i.e.
$h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
$
\Rightarrow S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} \\
\Rightarrow 0.4 = 0 + \dfrac{1}{2}( - 10){t^2} \\
\Rightarrow {t^2} = + 0.8 = \dfrac{{0.08}}{{100}} \\
\Rightarrow t = \pm \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 }}{{10}} \\
$
$\because $ Time can not be negative
So, $t = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 }}{{10}}$
Now, solving along horizontal axis,
$
S = 0.4m{\text{ (displacement along x - axis)}} \\
u = v{\text{ (initial velocity along x - axis i}}{\text{.e}}{\text{. projection velocity)}} \\
T = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 }}{{10}}{\text{(time taken which is eventually t)}} \\
{\text{V = v (final velocity which is equal to initial velocity}}\because {\text{a = 0)}} \\
a = 0{\text{ (acceleration along x axis)}} \\
$
So, using equation of motion,
$
h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} \\
\Rightarrow S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2} \\
\Rightarrow + 0.4 = v\dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 }}{{10}} + \dfrac{1}{2}(0){t^2} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{{2\sqrt 2 }} = v \\
\Rightarrow v = \sqrt 2 \\
$
So, we get $v = \sqrt 2 $ which is the required horizontal velocity i.e. the projection velocity.
Hence, Option C is correct.
Additional information:
Projectile motion is the motion of an object thrown or projected into the air, subject to only the acceleration of gravity. The object is called a projectile, and its path is called its trajectory. Projectile motion is a two-dimensional projectile motion.
Note:
To solve this problem we must have knowledge of equations of motion. It defines or gives the relation of a particular system with regards to motion as a time function.
Fact: Here we got the value of time both negative as well as positive,
$\because $ As per our knowledge time can not be negative,
$\therefore $ The positive part was considered.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




