
A square coil of 0.5 m has a movable side. It is placed such that its plane is perpendicular to uniform magnetic field of induction 0.2T. If all the sides are allowed to move at a speed \[0.1\text{ m}{{\text{s}}^{-1}}\] for 4 seconds outwards, average induced emf will be,
A. Zero
B. 0.01 V
C. 0.028 V
D. 0.072 V
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: Obtain the mathematical expression for magnetic flux and induced emf. Put the expression for magnetic flux in the expression of induced emf to find the required expression to solve this question. Put the given values in the obtained mathematical expression to get the required solution.
Formula used:
$\begin{align}
& \phi =\vec{B}.\vec{A} \\
& e=-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt} \\
\end{align}$
Complete step by step answer:
In the figure below, initially the coil has side 0.5 m. It will move outward for 4 sec at a speed \[0.1\text{ m}{{\text{s}}^{-1}}\]. So, finally the side of the square will increase in each side.
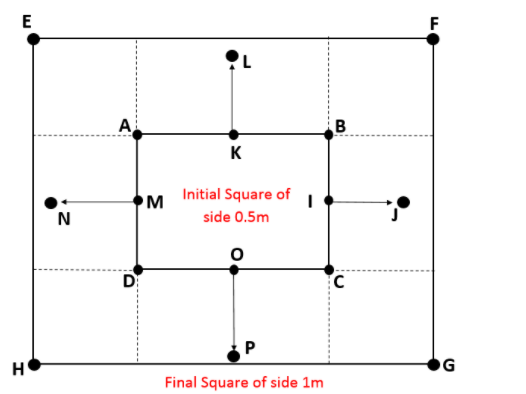
The magnetic field B is perpendicular to the plane of the coil.
Again, the area vector will be in the perpendicular direction to the plane of the square. So, the magnetic field will be parallel with the area vector.
So, we can give magnetic flux as,
$\begin{align}
& \phi =\vec{B}.\vec{A} \\
& \phi =BA\cos \theta \text{ } \\
\end{align}$
Where, $\theta $ is the angle between magnetic field and area vector, B Is the magnetic field, A is the area vector and $\phi $ is the magnetic flux
Since, the magnetic field is parallel to the area vector the value of $\theta $ will be 0.
$\begin{align}
& \phi =BA\cos 0 \\
& \phi =BA \\
\end{align}$
Now, the induced emf can be given as,
$\begin{align}
& e=-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt} \\
& e=-\dfrac{d\left( BA \right)}{dt} \\
\end{align}$
$e=-B\dfrac{dA}{dt}\text{ }\to \text{ 1}$
Now, we have to find change in the area of the square.
Initially, the area of the square will be,
$\begin{align}
& {{A}_{i}}={{\left( 0.5 \right)}^{2}}{{m}^{2}} \\
& {{A}_{i}}=0.25{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
The side of the square will move outwards with a speed of \[0.1\text{ m}{{\text{s}}^{-1}}\] for 4 second. So, it will move outward by distance,
$\begin{align}
& s=vt \\
& s=0.1m{{s}^{-1}}\times 4s \\
& s=o.4m \\
\end{align}$
So, the side of the square will be,
$\begin{align}
& a=\left( 0.5+0.4+0.4 \right)m \\
& a=1.3m \\
\end{align}$
We have added 0.4 twice because the sides will increase towards both directions.
Final area of the square will be,
$\begin{align}
& {{A}_{f}}={{1.3}^{2}}{{m}^{2}} \\
& {{A}_{f}}=1.69{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, from equation 1,
$\begin{align}
& e=-B\dfrac{dA}{dt} \\
& e=-0.2T\times \dfrac{{{A}_{f}}-{{A}_{i}}}{dt} \\
& e=-0.2T\times \dfrac{\left( 1.69-0.25 \right){{m}^{2}}}{4s} \\
& e=-0.2T\times \dfrac{1.44{{m}^{2}}}{4s} \\
& e=-0.072V \\
\end{align}$
Taking magnitude, the average emf produced will be e = 0.072 V.
The correct option is (D).
Note:
Electromotive force or emf is induced in a coil if the magnetic flux through the coil changes with time. Emf is directly proportional to the change in magnetic flux and inversely proportional to the time in which the change is made. So, if a large change in magnetic flux occurs in a small time period, induced emf will be more. If the time period is more, the induced emf will be less.
Here, we found that the value of emf is negative. But we are considering only the magnitude and that’s why we take only the positive value.
Formula used:
$\begin{align}
& \phi =\vec{B}.\vec{A} \\
& e=-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt} \\
\end{align}$
Complete step by step answer:
In the figure below, initially the coil has side 0.5 m. It will move outward for 4 sec at a speed \[0.1\text{ m}{{\text{s}}^{-1}}\]. So, finally the side of the square will increase in each side.

The magnetic field B is perpendicular to the plane of the coil.
Again, the area vector will be in the perpendicular direction to the plane of the square. So, the magnetic field will be parallel with the area vector.
So, we can give magnetic flux as,
$\begin{align}
& \phi =\vec{B}.\vec{A} \\
& \phi =BA\cos \theta \text{ } \\
\end{align}$
Where, $\theta $ is the angle between magnetic field and area vector, B Is the magnetic field, A is the area vector and $\phi $ is the magnetic flux
Since, the magnetic field is parallel to the area vector the value of $\theta $ will be 0.
$\begin{align}
& \phi =BA\cos 0 \\
& \phi =BA \\
\end{align}$
Now, the induced emf can be given as,
$\begin{align}
& e=-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt} \\
& e=-\dfrac{d\left( BA \right)}{dt} \\
\end{align}$
$e=-B\dfrac{dA}{dt}\text{ }\to \text{ 1}$
Now, we have to find change in the area of the square.
Initially, the area of the square will be,
$\begin{align}
& {{A}_{i}}={{\left( 0.5 \right)}^{2}}{{m}^{2}} \\
& {{A}_{i}}=0.25{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
The side of the square will move outwards with a speed of \[0.1\text{ m}{{\text{s}}^{-1}}\] for 4 second. So, it will move outward by distance,
$\begin{align}
& s=vt \\
& s=0.1m{{s}^{-1}}\times 4s \\
& s=o.4m \\
\end{align}$
So, the side of the square will be,
$\begin{align}
& a=\left( 0.5+0.4+0.4 \right)m \\
& a=1.3m \\
\end{align}$
We have added 0.4 twice because the sides will increase towards both directions.
Final area of the square will be,
$\begin{align}
& {{A}_{f}}={{1.3}^{2}}{{m}^{2}} \\
& {{A}_{f}}=1.69{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, from equation 1,
$\begin{align}
& e=-B\dfrac{dA}{dt} \\
& e=-0.2T\times \dfrac{{{A}_{f}}-{{A}_{i}}}{dt} \\
& e=-0.2T\times \dfrac{\left( 1.69-0.25 \right){{m}^{2}}}{4s} \\
& e=-0.2T\times \dfrac{1.44{{m}^{2}}}{4s} \\
& e=-0.072V \\
\end{align}$
Taking magnitude, the average emf produced will be e = 0.072 V.
The correct option is (D).
Note:
Electromotive force or emf is induced in a coil if the magnetic flux through the coil changes with time. Emf is directly proportional to the change in magnetic flux and inversely proportional to the time in which the change is made. So, if a large change in magnetic flux occurs in a small time period, induced emf will be more. If the time period is more, the induced emf will be less.
Here, we found that the value of emf is negative. But we are considering only the magnitude and that’s why we take only the positive value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




