
A square and an equilateral triangle have equal perimeters. If the diagonal of the square is $12\sqrt 2 cm$then area of the triangle is
A. $24\sqrt 2 c{m^2}$
B. $24\sqrt 3 c{m^2}$
C. $48\sqrt 3 c{m^2}$
D. $64\sqrt 3 c{m^2}$
Answer
613.2k+ views
Hint-In this question square and triangle have the same perimeter. Find the relation between their sides. Calculate the side of the square first. Find the area of the triangle directly using the basic formula of area of equilateral triangle and the relation obtained.
Complete step by step answer:
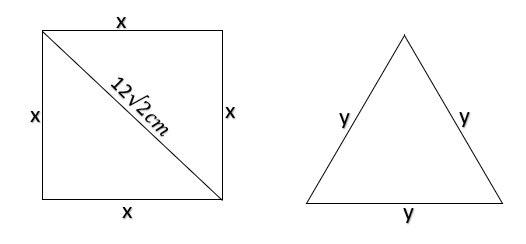
Let side of square be $x$units
Side of equilateral triangle be $y$ units
Given, both have equal perimeters
$ \Rightarrow 4x = 3y$
Diagonal of square = $12\sqrt 2 $
Using Pythagoras theorem
$
{x^2} + {x^2} = {(12\sqrt 2 )^2} \\
2{x^2} = 144 \times 2 \\
{x^2} = 144 \\
x = 12{\text{ units}} \\
\\
\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{4}{3}x = \dfrac{4}{3} \times 12 = 16{\text{ units}} \\
{\text{Area of equilateral triangle = }}\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{\left( y \right)^2} \\
= \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4} \times 16 \times 16 \\
= 64\sqrt 3 c{m^2} \\
$
Therefore, the area of triangle is $64\sqrt 3 c{m^2}$
Note- In order to solve such problems students must start with considering the sides of the given geometrical figures in terms of some unknown variable. Also, students must remember the formula for the area and the perimeter for some common geometrical figures, some of them are mentioned in the solution.
Complete step by step answer:

Let side of square be $x$units
Side of equilateral triangle be $y$ units
Given, both have equal perimeters
$ \Rightarrow 4x = 3y$
Diagonal of square = $12\sqrt 2 $
Using Pythagoras theorem
$
{x^2} + {x^2} = {(12\sqrt 2 )^2} \\
2{x^2} = 144 \times 2 \\
{x^2} = 144 \\
x = 12{\text{ units}} \\
\\
\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{4}{3}x = \dfrac{4}{3} \times 12 = 16{\text{ units}} \\
{\text{Area of equilateral triangle = }}\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{\left( y \right)^2} \\
= \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4} \times 16 \times 16 \\
= 64\sqrt 3 c{m^2} \\
$
Therefore, the area of triangle is $64\sqrt 3 c{m^2}$
Note- In order to solve such problems students must start with considering the sides of the given geometrical figures in terms of some unknown variable. Also, students must remember the formula for the area and the perimeter for some common geometrical figures, some of them are mentioned in the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




