
A spring of natural length $L$ is compressed to length $\dfrac{{7L}}{8}$ exerts a force ${F_o}$. The work done by the spring in restoring itself to natural length is:
\[(A)\dfrac{{{F_o}L}}{{25}}\]
\[(B)\dfrac{{{F_o}L}}{{16}}\]
\[(C)\dfrac{{3{F_o}L}}{{25}}\]
\[(D)\dfrac{{{F_o}L}}{8}\]
Answer
489.9k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we will firstly find the change in the length of the spring. Then with the help of it, we will find the spring constant. In the end, we will apply the concept that the work done by the spring is equal to the change in its potential energy.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question given to us, the diagram will be as follows,
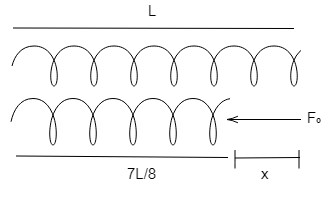
So, let the change in length of the spring caused by the compression be $x$
Now, this value of $x$ is given by,
$x = L - \dfrac{{7L}}{8}$
$x = \dfrac{{8L - 7L}}{8}$
$x = \dfrac{L}{8}$
Now, we know that the force acting on the spring is given by the expression,
\[{F_o} = kx.....(1)\]
Where $k$ is the spring constant.
On putting the value $x = \dfrac{L}{8}$ in equation (1), we get,
${F_o} = \dfrac{{kL}}{8}$
On taking $k$ on one side and all other terms on the other side, we get,
$k = \dfrac{{8{F_o}}}{L}$
Now, we know that the work done on a spring is equal to the change in its potential energy. So,
Work done = Change in the potential energy
$W = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}} \right|$
On putting the value of spring constant and the change in the length, we get,
$W = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{{8{F_o}}}{L} \times {\left( {\dfrac{L}{8}} \right)^2}$
$W = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{{8{F_o}}}{L} \times \dfrac{{{L^2}}}{{64}}$
On further solving, we get,
$W = \dfrac{{{F_o}L}}{{16}}$
The work done by the spring in restoring itself to natural length is $W = \dfrac{{{F_o}L}}{{16}}$.
So, the final answer is \[(B)\dfrac{{{F_o}L}}{{16}}\].
Note:
The concept of spring constant, which has been used to solve this question, has come from Hooke's law. The main purpose of the spring constant is to find out how much force will be required in order to deform a particular spring.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question given to us, the diagram will be as follows,

So, let the change in length of the spring caused by the compression be $x$
Now, this value of $x$ is given by,
$x = L - \dfrac{{7L}}{8}$
$x = \dfrac{{8L - 7L}}{8}$
$x = \dfrac{L}{8}$
Now, we know that the force acting on the spring is given by the expression,
\[{F_o} = kx.....(1)\]
Where $k$ is the spring constant.
On putting the value $x = \dfrac{L}{8}$ in equation (1), we get,
${F_o} = \dfrac{{kL}}{8}$
On taking $k$ on one side and all other terms on the other side, we get,
$k = \dfrac{{8{F_o}}}{L}$
Now, we know that the work done on a spring is equal to the change in its potential energy. So,
Work done = Change in the potential energy
$W = \left| {\dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}} \right|$
On putting the value of spring constant and the change in the length, we get,
$W = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{{8{F_o}}}{L} \times {\left( {\dfrac{L}{8}} \right)^2}$
$W = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{{8{F_o}}}{L} \times \dfrac{{{L^2}}}{{64}}$
On further solving, we get,
$W = \dfrac{{{F_o}L}}{{16}}$
The work done by the spring in restoring itself to natural length is $W = \dfrac{{{F_o}L}}{{16}}$.
So, the final answer is \[(B)\dfrac{{{F_o}L}}{{16}}\].
Note:
The concept of spring constant, which has been used to solve this question, has come from Hooke's law. The main purpose of the spring constant is to find out how much force will be required in order to deform a particular spring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




