
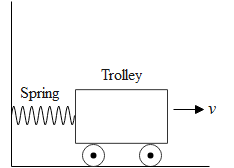
A spring is compressed by a small trolley of mass 0.5kg lying on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the adjacent fig. When the trolley is released it is found to move with a speed of $2m{{s}^{-1}}$ what potential energy did the spring possess when compressed.
a) 2.0J
b) 0.25J
c) 1.0J
d) 10J

Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: When a spring is compressed it possesses some potential energy. In the above diagram if we see, as soon as the spring is released the trolley will start moving. Hence we can say that the potential energy of compression of the spring is getting converted to the kinetic energy of the motion of the trolley. Therefore the kinetic energy gained by the trolley will be equal to the potential energy of the spring.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us say all the potential energy of the compression of the spring is converted to the kinetic energy of the motion. Now let us say we compress the spring along with the trolley such that both are at rest. As soon as the force of compression is removed, the trolley will start moving. The velocity of the trolley will keep on changing till the entire potential energy of the spring gets converted to kinetic energy of the trolley. Therefore we can write this mathematically as,
Potential Energy of spring=${{K}_{F}}-{{K}_{I}}$ where ${{K}_{F}}$ is the final kinetic energy and ${{K}_{I}}$ is the initial kinetic energy of the trolley.
The kinetic energy of motion of any body is given by $K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}\text{ J}$ where m is the mass of the body and v is the velocity of motion of the body. The trolley in the above case will accelerate from initial velocity i.e. ${{v}_{INITIAL}}$ to final velocity i.e. ${{v}_{FINAL}}$ till all the potential energy of the spring gets converted to kinetic energy of trolley and move with constant velocity i.e. ${{v}_{INITIAL}}$. Hence the potential energy of the spring can also be written as,
Potential Energy of spring=$\dfrac{1}{2}m{{\left( {{v}_{FINAL}} \right)}^{2}}-\dfrac{1}{2}m{{\left( {{v}_{INITIAL}} \right)}^{2}}$. The trolley is released from rest. Hence the adjacent equation becomes.
$\text{Potential Energy of spring}=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{\left( {{v}_{FINAL}} \right)}^{2}}$ It is given that the mass of the trolley is 0.5kg and the final velocity is $2m{{s}^{-1}}$. Hence the potential energy of the spring from the above equation can be written as,
Potential Energy of spring = $\dfrac{1}{2}m{{\left( {{v}_{FINAL}} \right)}^{2}}$
Potential Energy of spring = $\dfrac{1}{2}\times 0.5\times {{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}=2\times 0.5$
Potential Energy of spring = 1 J
Hence the correct answer is option c.
Note:
In the above question the surface on which the trolley is moving is considered to be frictionless. Therefore no potential energy is required to overcome the force of friction. It is also to be noted that the dimension of mass always has to be in kg as the SI unit of energy is given in terms of kg.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us say all the potential energy of the compression of the spring is converted to the kinetic energy of the motion. Now let us say we compress the spring along with the trolley such that both are at rest. As soon as the force of compression is removed, the trolley will start moving. The velocity of the trolley will keep on changing till the entire potential energy of the spring gets converted to kinetic energy of the trolley. Therefore we can write this mathematically as,
Potential Energy of spring=${{K}_{F}}-{{K}_{I}}$ where ${{K}_{F}}$ is the final kinetic energy and ${{K}_{I}}$ is the initial kinetic energy of the trolley.
The kinetic energy of motion of any body is given by $K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}\text{ J}$ where m is the mass of the body and v is the velocity of motion of the body. The trolley in the above case will accelerate from initial velocity i.e. ${{v}_{INITIAL}}$ to final velocity i.e. ${{v}_{FINAL}}$ till all the potential energy of the spring gets converted to kinetic energy of trolley and move with constant velocity i.e. ${{v}_{INITIAL}}$. Hence the potential energy of the spring can also be written as,
Potential Energy of spring=$\dfrac{1}{2}m{{\left( {{v}_{FINAL}} \right)}^{2}}-\dfrac{1}{2}m{{\left( {{v}_{INITIAL}} \right)}^{2}}$. The trolley is released from rest. Hence the adjacent equation becomes.
$\text{Potential Energy of spring}=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{\left( {{v}_{FINAL}} \right)}^{2}}$ It is given that the mass of the trolley is 0.5kg and the final velocity is $2m{{s}^{-1}}$. Hence the potential energy of the spring from the above equation can be written as,
Potential Energy of spring = $\dfrac{1}{2}m{{\left( {{v}_{FINAL}} \right)}^{2}}$
Potential Energy of spring = $\dfrac{1}{2}\times 0.5\times {{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}=2\times 0.5$
Potential Energy of spring = 1 J
Hence the correct answer is option c.
Note:
In the above question the surface on which the trolley is moving is considered to be frictionless. Therefore no potential energy is required to overcome the force of friction. It is also to be noted that the dimension of mass always has to be in kg as the SI unit of energy is given in terms of kg.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




