
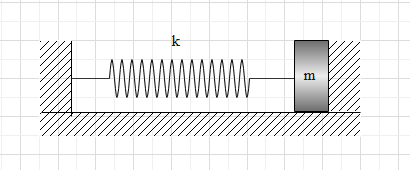
A spring block system is placed on a horizontal surface so as to just fit within the vertical walls. The spring is initially unstretched. The coefficient of restitution for collision is $e = \dfrac{1}{2}$ . The block is pulled to the left by a distance \[x = 1\,cm\] and released from rest. The time between second and third collision of the block with the wall is
A. $2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{m}{k}} $
B. $\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{m}{k}} $
C. $\dfrac{\pi }{2}\sqrt {\dfrac{m}{k}} $
D. $\dfrac{\pi }{4}\sqrt {\dfrac{m}{k}} $

Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint-
Coefficient of restitution for an object colliding with a perfectly rigid wall is defined as the ratio of final velocity to initial velocity or the speed of separation to speed of approach
Therefore,
$e = \dfrac{{{v_s}}}{{{v_a}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Where,${v_s}$ is the velocity of separation,${v_a}$ is the velocity of approach
Time period in simple harmonic motion is independent of the amplitude. It is given by the equation,
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{m}{k}} $
Where, $m$ is the mass and $k$ is the spring constant.
Coefficient of restitution is given as$\dfrac{1}{2}$ . It means that velocity becomes twice in second collision
Since velocity and time are inversely related. The time becomes $\dfrac{1}{2}$
That is, time for second oscillation
$t = \dfrac{T}{2}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given,
Coefficient of restitution for collision is , $e = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Coefficient of restitution for an object colliding with a perfectly rigid wall is defined as the ratio of final velocity to initial velocity or the speed of separation to speed of approach
Therefore,
$e = \dfrac{{{v_s}}}{{{v_a}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Where, ${v_s}$ is the velocity of separation, ${v_a}$ is the velocity of approach.
When the block strikes the wall, it bounces back because of the normal reaction exerted by the wall
The motion here is simple harmonic motion.
A simple harmonic motion is a periodic motion in which the restoring force is directly proportional to the displacement and acting towards the equilibrium position
Time period in simple harmonic motion is independent of the amplitude. It is given by the equation,
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{m}{k}} $
Where, $m$ is the mass and $k$ is the spring constant.
Since, the coefficient of restitution is given as $\dfrac{1}{2}$. It means that velocity becomes twice in a second collision.
Since velocity and time are inversely related. The time becomes $\dfrac{1}{2}$
That is, time for second oscillation,
$t = \dfrac{T}{2}$
Therefore,
\[
t = \dfrac{{2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{m}{k}} }}{2} \\
= \pi \sqrt {\dfrac{m}{k}} \\
\]
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
Formulas to remember-
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{m}{k}} $
Where, $T$ is the time period in simple harmonic motion, $m$ is the mass and $k$ is the spring constant.
Coefficient of restitution for collision,
$e = \dfrac{{{v_s}}}{{{v_a}}}$
Where, ${v_s}$ is the velocity of separation, ${v_a}$ is the velocity of approach.
Coefficient of restitution for an object colliding with a perfectly rigid wall is defined as the ratio of final velocity to initial velocity or the speed of separation to speed of approach
Therefore,
$e = \dfrac{{{v_s}}}{{{v_a}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Where,${v_s}$ is the velocity of separation,${v_a}$ is the velocity of approach
Time period in simple harmonic motion is independent of the amplitude. It is given by the equation,
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{m}{k}} $
Where, $m$ is the mass and $k$ is the spring constant.
Coefficient of restitution is given as$\dfrac{1}{2}$ . It means that velocity becomes twice in second collision
Since velocity and time are inversely related. The time becomes $\dfrac{1}{2}$
That is, time for second oscillation
$t = \dfrac{T}{2}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given,
Coefficient of restitution for collision is , $e = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Coefficient of restitution for an object colliding with a perfectly rigid wall is defined as the ratio of final velocity to initial velocity or the speed of separation to speed of approach
Therefore,
$e = \dfrac{{{v_s}}}{{{v_a}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Where, ${v_s}$ is the velocity of separation, ${v_a}$ is the velocity of approach.
When the block strikes the wall, it bounces back because of the normal reaction exerted by the wall
The motion here is simple harmonic motion.
A simple harmonic motion is a periodic motion in which the restoring force is directly proportional to the displacement and acting towards the equilibrium position
Time period in simple harmonic motion is independent of the amplitude. It is given by the equation,
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{m}{k}} $
Where, $m$ is the mass and $k$ is the spring constant.
Since, the coefficient of restitution is given as $\dfrac{1}{2}$. It means that velocity becomes twice in a second collision.
Since velocity and time are inversely related. The time becomes $\dfrac{1}{2}$
That is, time for second oscillation,
$t = \dfrac{T}{2}$
Therefore,
\[
t = \dfrac{{2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{m}{k}} }}{2} \\
= \pi \sqrt {\dfrac{m}{k}} \\
\]
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
Formulas to remember-
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{m}{k}} $
Where, $T$ is the time period in simple harmonic motion, $m$ is the mass and $k$ is the spring constant.
Coefficient of restitution for collision,
$e = \dfrac{{{v_s}}}{{{v_a}}}$
Where, ${v_s}$ is the velocity of separation, ${v_a}$ is the velocity of approach.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




