
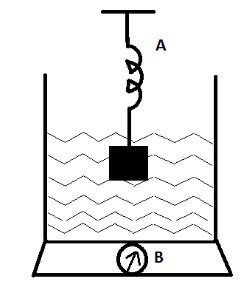
A spring balance A reads 2kg when a block of mass m is suspended from it. Another balance B reads 5kg when a beaker with a liquid is put on its pan. The two balances are now so arranged that the hanging mass m is fully immersed inside the liquid in the beaker as shown in the figure. In this situation
A. The balance A will read 2kg
B. The balance B will read 5kg
C. The balance A will read less than 2kg and B will read between 3kg and 5kg
D. The balance A and B will read 2kg and 5kg.

Answer
561k+ views
Hint: The true weights of the beaker and the block of mass m are given as 5kg and 2 kg respectively. These are the true weights as there is no other force acting upon the weights while measuring them. In the case of the mass submerged into the beaker, there will be force buoyancy acting upon the weight balances.
Complete answer:
When the spring balance A reads 2kg when the block of mass is suspended from it, then there is no other force acting upon it except for the force due to the mass and the gravity of the earth, hence its true weight can be seen through it.
Now, when a beaker is put on a pan with liquid inside the beaker, then the balance B reads 5kg and this is also the true weight of the beaker as there is no other force acting upon it and the weight is only due to the acceleration due to gravity, volume of the liquid and the density of the liquid.
Now, when both the systems are submerge into each other, there is displacement of water due to the mass, and hence there will be an upthrust, that is buoyancy force acting upon the mass on the opposite direction of the gravity and hence the spring balance A will read less than 2kg, while as the water is displaced by the mass, the balance B will read between 3kg and 5kg due to displacement of water.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note: Here, the spring compression is only used to measure the mass of the block and the spring balance does not act any other force on the mass like tension due to the spring and the only force acting on it is due to the gravitational force. Hence, here we assume that the spring in the spring balance is massless.
Complete answer:
When the spring balance A reads 2kg when the block of mass is suspended from it, then there is no other force acting upon it except for the force due to the mass and the gravity of the earth, hence its true weight can be seen through it.
Now, when a beaker is put on a pan with liquid inside the beaker, then the balance B reads 5kg and this is also the true weight of the beaker as there is no other force acting upon it and the weight is only due to the acceleration due to gravity, volume of the liquid and the density of the liquid.
Now, when both the systems are submerge into each other, there is displacement of water due to the mass, and hence there will be an upthrust, that is buoyancy force acting upon the mass on the opposite direction of the gravity and hence the spring balance A will read less than 2kg, while as the water is displaced by the mass, the balance B will read between 3kg and 5kg due to displacement of water.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note: Here, the spring compression is only used to measure the mass of the block and the spring balance does not act any other force on the mass like tension due to the spring and the only force acting on it is due to the gravitational force. Hence, here we assume that the spring in the spring balance is massless.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




