
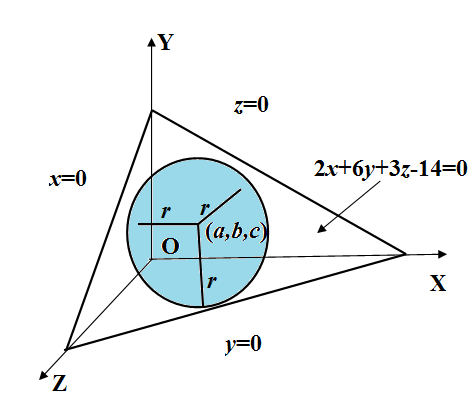
A sphere is inscribed in the tetrahedron whose faces are $x=0,y=0,z=0$ and $2x+6y+3z-14=0$. Find its center and radius.
$\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{. }\left( \dfrac{7}{2},\dfrac{7}{2},\dfrac{7}{2} \right),\dfrac{7}{2} \\
& \text{B}\text{. }\left( \dfrac{7}{9},\dfrac{7}{9},\dfrac{7}{9} \right),\dfrac{7}{9} \\
& \text{C}\text{. }\left( \dfrac{7}{2},\dfrac{7}{2},\dfrac{7}{2} \right),\dfrac{7}{9} \\
& \text{D}\text{. None of these} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: As given in the question the sphere is inscribed in the tetrahedron, so the length of the perpendicular from the center upon each of the faces of the tetrahedron is equal to the radius of the sphere. Then, by using the distance formula of a point from the plane is used to obtain the desired answer.
If $\left( l,m,n \right)$ is a point and $ax+by+cz=d$ is a plane, the distance formula will be
$\dfrac{d-ax-by-cz}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
If $\left( l,m,n \right)$ is a point and $ax+by+cz=d$ is a plane, the distance formula will be
$\dfrac{d-ax-by-cz}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}}$
We have given that a sphere is inscribed in the tetrahedron whose faces are $x=0,y=0,z=0$ and $2x+6y+3z-14=0$.
We have to find its center and radius.
Let $\left( a,b,c \right)$ be the center and $r$ is the radius of the sphere inscribed in the tetrahedron.
As given the sphere is inscribed in the tetrahedron, so the length of the perpendicular from the center $\left( a,b,c \right)$ upon each of the faces of the tetrahedron is equal to the radius of the sphere. So, mathematically we represent it as
$\dfrac{a}{1}=\dfrac{b}{1}=\dfrac{c}{1}=r..............(i)$
Now, we know that the distance formula is given as $\dfrac{d-ax-by-cz}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}}$
Where, $\left( l,m,n \right)$ is a point and $ax+by+cz=d$ is a plane
Now, we have points $\left( a,b,c \right)$ and plane given in the question is $2x+6y+3z-14=0$
When we substitute the values in the distance formula, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{14-2a-6b-3c}{\sqrt{{{2}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}}+{{3}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{14-2a-6b-3c}{\sqrt{4+36+9}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{14-2a-6b-3c}{\sqrt{49}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{14-2a-6b-3c}{7}.....................(ii) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, equating equation (i) and (ii), we get
\[a=b=c=r=\dfrac{14-2a-6b-3c}{7}\]
\[a=b=c=r=\dfrac{14-2a-6b-3c}{7}\]
As $a=b=c$ , so the above equation becomes
\[\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{14-2a-6a-3a}{7} \\
& 7a=14-11a \\
&\Rightarrow 7a+11a=14 \\
&\Rightarrow 18a=14 \\
&\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{14}{18} \\
&\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{7}{9} \\
\end{align}\]
As $a=b=c$, so \[a=\dfrac{7}{9};b=\dfrac{7}{9};c=\dfrac{7}{9};r=\dfrac{7}{9}\]
We get center of the sphere $\left( \dfrac{7}{9},\dfrac{7}{9},\dfrac{7}{9} \right)$ and radius $\dfrac{7}{9}$.
So the option B is the correct answer.
Note: We note the equations of the given planes $x=0,y=0,z=0$ correspond to coordinate planes $yz-$plane, $zx-$plane and $xy-$plane respectively in space. So $\left( a,b,c \right)$ represent direction ratios of the line passing through origin and $\left( a,b,c \right)$ and hence $\dfrac{a}{1},\dfrac{b}{1},\dfrac{c}{1}$ becomes the distance from $yz-$plane, $zx-$plane and $xy-$plane respectively. The sphere inscribed in a polyhedron is called insphere. We can alternatively solve using the equation touching the coordinate planes ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}-2\lambda \left( x+y+z \right)+2{{\lambda }^{2}}=0$ where center is $\left( \lambda ,\lambda ,\lambda \right)$ and radius $\lambda $.
If $\left( l,m,n \right)$ is a point and $ax+by+cz=d$ is a plane, the distance formula will be
$\dfrac{d-ax-by-cz}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
If $\left( l,m,n \right)$ is a point and $ax+by+cz=d$ is a plane, the distance formula will be
$\dfrac{d-ax-by-cz}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}}$
We have given that a sphere is inscribed in the tetrahedron whose faces are $x=0,y=0,z=0$ and $2x+6y+3z-14=0$.
We have to find its center and radius.
Let $\left( a,b,c \right)$ be the center and $r$ is the radius of the sphere inscribed in the tetrahedron.
As given the sphere is inscribed in the tetrahedron, so the length of the perpendicular from the center $\left( a,b,c \right)$ upon each of the faces of the tetrahedron is equal to the radius of the sphere. So, mathematically we represent it as
$\dfrac{a}{1}=\dfrac{b}{1}=\dfrac{c}{1}=r..............(i)$

Now, we know that the distance formula is given as $\dfrac{d-ax-by-cz}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}}$
Where, $\left( l,m,n \right)$ is a point and $ax+by+cz=d$ is a plane
Now, we have points $\left( a,b,c \right)$ and plane given in the question is $2x+6y+3z-14=0$
When we substitute the values in the distance formula, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{14-2a-6b-3c}{\sqrt{{{2}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}}+{{3}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{14-2a-6b-3c}{\sqrt{4+36+9}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{14-2a-6b-3c}{\sqrt{49}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{14-2a-6b-3c}{7}.....................(ii) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, equating equation (i) and (ii), we get
\[a=b=c=r=\dfrac{14-2a-6b-3c}{7}\]
\[a=b=c=r=\dfrac{14-2a-6b-3c}{7}\]
As $a=b=c$ , so the above equation becomes
\[\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{14-2a-6a-3a}{7} \\
& 7a=14-11a \\
&\Rightarrow 7a+11a=14 \\
&\Rightarrow 18a=14 \\
&\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{14}{18} \\
&\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{7}{9} \\
\end{align}\]
As $a=b=c$, so \[a=\dfrac{7}{9};b=\dfrac{7}{9};c=\dfrac{7}{9};r=\dfrac{7}{9}\]
We get center of the sphere $\left( \dfrac{7}{9},\dfrac{7}{9},\dfrac{7}{9} \right)$ and radius $\dfrac{7}{9}$.
So the option B is the correct answer.
Note: We note the equations of the given planes $x=0,y=0,z=0$ correspond to coordinate planes $yz-$plane, $zx-$plane and $xy-$plane respectively in space. So $\left( a,b,c \right)$ represent direction ratios of the line passing through origin and $\left( a,b,c \right)$ and hence $\dfrac{a}{1},\dfrac{b}{1},\dfrac{c}{1}$ becomes the distance from $yz-$plane, $zx-$plane and $xy-$plane respectively. The sphere inscribed in a polyhedron is called insphere. We can alternatively solve using the equation touching the coordinate planes ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}-2\lambda \left( x+y+z \right)+2{{\lambda }^{2}}=0$ where center is $\left( \lambda ,\lambda ,\lambda \right)$ and radius $\lambda $.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




