
A special fully automatic car is designated by the Indian scientist in the Hindustan Automobiles Ltd. The car follows only the following instructions
\[{G_1}(x)\] : The car shall move forward to x meters
\[{G_2}(x)\]: The car shall turn in right direction and move x meters
\[{G_3}(x)\]: The car shall turn in left direction and move x meters
\[{G_4}(x)\]: The car shall move backward x meters
The car is given instruction \[{G_2}(50)\],\[{G_3}(30)\] and \[{G_4}(20)\]. Find the shortest distance of the car from the original position. Assume that car was initially at origin and facing the negative x-axis.
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: \[{G_1}(x),{G_2}(x),{G_3}(x),{G_4}(x)\] are the instructions the car follows.
First, we move the car by following instruction \[{G_2}(50)\]
Then \[{G_3}(30)\] and \[{G_4}(20)\]respectively.
After doing all these we need to find out the position of the car. Then by applying the distance formula we get the shortest distance of the car from the origin.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that the car is given instruction\[{G_2}(50)\],\[{G_3}(30)\] and\[{G_4}(20)\].
We assume that the car was initially at origin \[\left( {0,0} \right)\] and facing the negative x axis.
By following the instruction \[{G_2}(50)\]the car will move 50m in the right direction and be at the position\[\left( {0,50} \right)\] .
After that following the second instruction \[{G_3}(30)\]the car will move 30m in left direction then it will be along negative x axis from\[\left( {0,50} \right)\]and now the car will be at the position\[\left( { - 30,50} \right)\] .
Then following the final instruction \[{G_4}(20)\]the car will move 20m backwards and be at the position\[\left( { - 10,50} \right)\] .
Hence finally the car will reach the point\[\left( { - 10,50} \right)\].
This is being explained by the following figure
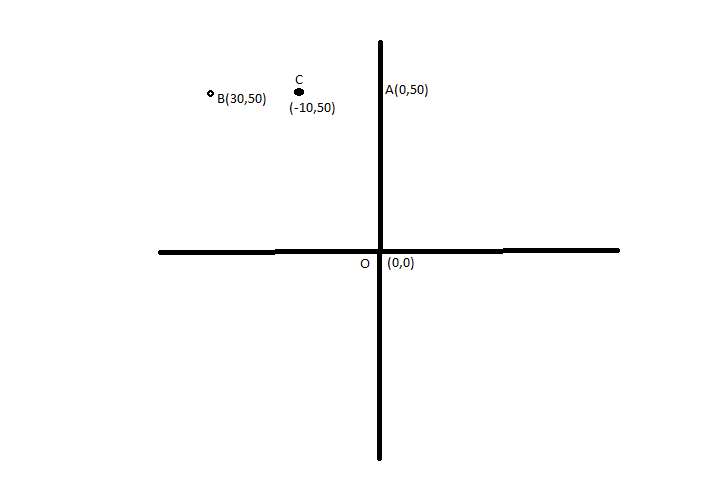
In the drawn figure O represents the initial position A is the position after the first movement B is the position of the car after the second movement and C is the final position of the car.
The distance between the points\[\left( {0,0} \right)\]and \[\left( { - 10,50} \right)\]is \[ = \sqrt {{{( - 10 - 0)}^2} + {{(50 - 0)}^2}} \]
Let us square the terms inside the root we get,
\[\sqrt {{{( - 10 - 0)}^2} + {{(50 - 0)}^2}} = \sqrt {100 + 2500} \]
On simplifying we get,
The distance travelled by the car\[ = \sqrt {2600} \]\[ = 10\sqrt {26} units\]
$\therefore$ The shortest distance of the car from the original position to the final position is \[10\sqrt {26} units\].
Note:
The shortest distance of two points \[({x_1},{y_1})\]and \[({x_2},{y_2})\]is given by the formula\[\sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} \] .
If the order of the given instruction changes the distance remains the same but the position of the car changes. That is even though the position of the car may change after the change in the order the distance traveled by car remains constant.
First, we move the car by following instruction \[{G_2}(50)\]
Then \[{G_3}(30)\] and \[{G_4}(20)\]respectively.
After doing all these we need to find out the position of the car. Then by applying the distance formula we get the shortest distance of the car from the origin.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that the car is given instruction\[{G_2}(50)\],\[{G_3}(30)\] and\[{G_4}(20)\].
We assume that the car was initially at origin \[\left( {0,0} \right)\] and facing the negative x axis.
By following the instruction \[{G_2}(50)\]the car will move 50m in the right direction and be at the position\[\left( {0,50} \right)\] .
After that following the second instruction \[{G_3}(30)\]the car will move 30m in left direction then it will be along negative x axis from\[\left( {0,50} \right)\]and now the car will be at the position\[\left( { - 30,50} \right)\] .
Then following the final instruction \[{G_4}(20)\]the car will move 20m backwards and be at the position\[\left( { - 10,50} \right)\] .
Hence finally the car will reach the point\[\left( { - 10,50} \right)\].
This is being explained by the following figure

In the drawn figure O represents the initial position A is the position after the first movement B is the position of the car after the second movement and C is the final position of the car.
The distance between the points\[\left( {0,0} \right)\]and \[\left( { - 10,50} \right)\]is \[ = \sqrt {{{( - 10 - 0)}^2} + {{(50 - 0)}^2}} \]
Let us square the terms inside the root we get,
\[\sqrt {{{( - 10 - 0)}^2} + {{(50 - 0)}^2}} = \sqrt {100 + 2500} \]
On simplifying we get,
The distance travelled by the car\[ = \sqrt {2600} \]\[ = 10\sqrt {26} units\]
$\therefore$ The shortest distance of the car from the original position to the final position is \[10\sqrt {26} units\].
Note:
The shortest distance of two points \[({x_1},{y_1})\]and \[({x_2},{y_2})\]is given by the formula\[\sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} \] .
If the order of the given instruction changes the distance remains the same but the position of the car changes. That is even though the position of the car may change after the change in the order the distance traveled by car remains constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




