
A solution contains 1 millicurie of L-phenylalanine \[^{{\mathbf{14}}}{\mathbf{C}}\](uniformly labelled) in $2.0$ mL solution. The specific activity of the labelled sample is given as 150 millicuries/mmol. The activity of the solution in terms of counting per minute/mL at a counting efficiency of 80% is :
A. \[88.8 \times {10^7}{\text{cpm/L}}\]
B. \[88.8 \times {10^6}{\text{cpm/mL}}\]
C. \[88.8 \times {10^5}{\text{cpm/mL}}\]
D. \[88.8 \times {10^7}{\text{cpm/mL}}\]
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you should recall the concept of the specific activity of a labelled sample. The specific activity can be defined as the activity per quantity of a radionuclide and it is a physical property of that radionuclide.
Formula used: \[{\text{molarity}} = \dfrac{{{\text{moles (in mmol)}}}}{{{\text{V (in mL)}}}}\]
Complete Step by step solution:
To answer this question let us first calculate the concentration of the given labelled sample.
(a) 1 mmole = 150 millicurie, using unitary method
1 millicurie=$\dfrac{1}{{150}}$ mmol
Now, concentration can be calculated by dividing the moles with the given volume
\[{\text{molarity}} = \dfrac{{{\text{moles (in mmol)}}}}{{{\text{V (in mL)}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{150 \times 2}} = 3.33 \times {10^{ - 3}}{\text{M}}\]
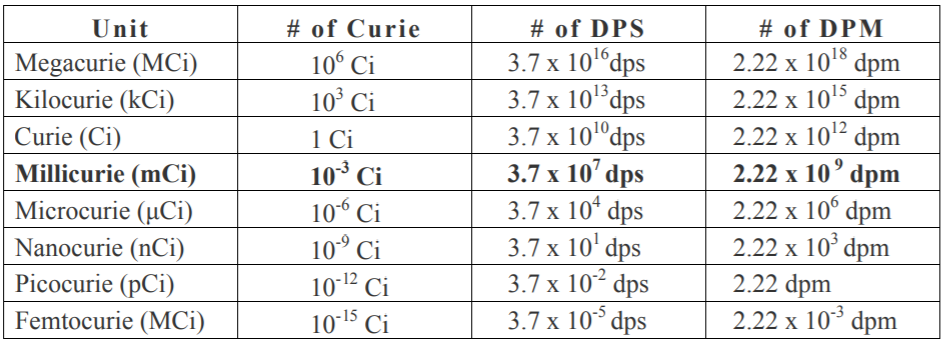
b) We know that 1 curie = \[3.7 \times {10^{10}}{\text{dps}}\]= \[3.7 \times {10^{10}} \times 60{\text{ dpm}}\] . This can be converted to counting per minute:
\[ \Rightarrow 3.7 \times {10^{10}} \times 60 \times \dfrac{{80}}{{100}}\] counting per minute
$\therefore $ 1 millicurie = \[3.7 \times {10^{10}} \times 60 \times \dfrac{{80}}{{100}} \times {10^{ - 3}}{\text{cpm}}\].
To achieve the final answer we need to divide this value with volume.
\[ \Rightarrow 3.7 \times {10^{10}} \times 60 \times \dfrac{{80}}{{100}} \times {10^{ - 3}} \times \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 88.8 \times {10^7}{\text{cpm/mL}}\]
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option D.
Additional information: The emissions in most of the spontaneous radioactive decays involve alpha $(\alpha )$particle, the beta $(\beta )$ particle, the gamma-ray, and the neutrino. The alpha particle is the nucleus of doubly charged ${\text{He}}_2^4$. Beta particles can be beta minus beta plus. Beta minus is an electron created in the nucleus during beta decay. Beta plus particle is also known as a positron, is the antiparticle of the electron; when brought together, two such particles will mutually annihilate each other.
Note: To answer the questions related to radioactivity you need to know the important conversion units regarding the disintegration of a radioactive compound.
Formula used: \[{\text{molarity}} = \dfrac{{{\text{moles (in mmol)}}}}{{{\text{V (in mL)}}}}\]
Complete Step by step solution:
To answer this question let us first calculate the concentration of the given labelled sample.
(a) 1 mmole = 150 millicurie, using unitary method
1 millicurie=$\dfrac{1}{{150}}$ mmol
Now, concentration can be calculated by dividing the moles with the given volume
\[{\text{molarity}} = \dfrac{{{\text{moles (in mmol)}}}}{{{\text{V (in mL)}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{150 \times 2}} = 3.33 \times {10^{ - 3}}{\text{M}}\]
b) We know that 1 curie = \[3.7 \times {10^{10}}{\text{dps}}\]= \[3.7 \times {10^{10}} \times 60{\text{ dpm}}\] . This can be converted to counting per minute:
\[ \Rightarrow 3.7 \times {10^{10}} \times 60 \times \dfrac{{80}}{{100}}\] counting per minute
$\therefore $ 1 millicurie = \[3.7 \times {10^{10}} \times 60 \times \dfrac{{80}}{{100}} \times {10^{ - 3}}{\text{cpm}}\].
To achieve the final answer we need to divide this value with volume.
\[ \Rightarrow 3.7 \times {10^{10}} \times 60 \times \dfrac{{80}}{{100}} \times {10^{ - 3}} \times \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 88.8 \times {10^7}{\text{cpm/mL}}\]
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option D.
Additional information: The emissions in most of the spontaneous radioactive decays involve alpha $(\alpha )$particle, the beta $(\beta )$ particle, the gamma-ray, and the neutrino. The alpha particle is the nucleus of doubly charged ${\text{He}}_2^4$. Beta particles can be beta minus beta plus. Beta minus is an electron created in the nucleus during beta decay. Beta plus particle is also known as a positron, is the antiparticle of the electron; when brought together, two such particles will mutually annihilate each other.
Note: To answer the questions related to radioactivity you need to know the important conversion units regarding the disintegration of a radioactive compound.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




