
A solid uniform ball having volume V and density \[\rho \] floats at the interface of two immiscible liquids as shown in figure. The densities of the upper and the lower liquids are \[{\rho _1}\] and \[{\rho _2}\] respectively, such that \[{\rho _1} < \rho < {\rho _2}\]. What fraction of the volume of the ball will be in the lower liquid:-
A. \[\dfrac{{\rho - {\rho _2}}}{{{\rho _1} - {\rho _2}}}\]
B. \[\dfrac{{{\rho _1}}}{{{\rho _1} - {\rho _2}}}\]
C. \[\dfrac{{{\rho _1} - \rho }}{{{\rho _1} - {\rho _2}}}\]
D. \[\dfrac{{{\rho _1} - {\rho _2}}}{{{\rho _2}}}\]
Answer
605.4k+ views
Hint: We know that when a body is immersed in a fluid it experiences an upward force called buoyant force which is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Formula used –
1) For a stationary body in a fluid, buoyant force=weight of the body immersed.
2) Force acting on the body immersed in the fluid, $F = V\rho g$
Given, Volume of the body=V
Density of the body=\[\rho \]
Density of upper liquid=\[{\rho _1}\]
Density of lower liquid= \[{\rho _2}\]
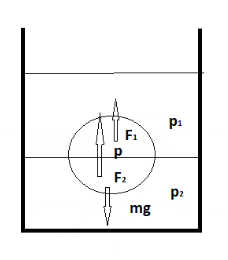
Let the volume of the body in upper liquid be ${v_1}$ and the volume in lower liquid be ${v_2}$.
V=${v_1}$+${v_2}$
Since the ball is stationary at the interface, therefore the net buoyant force on the body is equal to the weight of the body.
Let the buoyant force due to upper liquid be ${F_1}$and due to the lower liquid be ${F_2}$.
${F_1}$+${F_2}$=mg…..(i)
${F_1} = {v_1}{\rho _1}g$
And ${F_2} = {v_2}{\rho _2}g$
Putting these in equation (i)
\[{v_1}{\rho _1}g + {v_2}{\rho _2}g = ({v_1} + {v_2})\rho g\]
Eliminating g on both sides, we get
\[{v_1}{\rho _1} + {v_2}{\rho _2} = {v_1}\rho + {v_2}\rho \]
$
{v_1}{\rho _1} + (V - {v_1}){\rho _2} = {v_1}\rho + (V - {v_1})\rho \\
{v_1}({\rho _1} - {\rho _2}) + V{\rho _2} = {v_1}(\rho - \rho ) + V\rho \\
{v_1}({\rho _1} - {\rho _2}) = V(\rho - {\rho _2}) \\
\dfrac{{{v_1}}}{V} = \dfrac{{(\rho - {\rho _2})}}{{({\rho _1} - {\rho _2})}} \\
\dfrac{{{v_2}}}{V} = 1 - \dfrac{{{v_1}}}{V} = 1 - \dfrac{{(\rho - {\rho _2})}}{{({\rho _1} - {\rho _2})}} \\
\dfrac{{{v_2}}}{V} = \dfrac{{{\rho _1} - \rho }}{{{\rho _1} - {\rho _2}}} \\
$
Hence the correct option is C.
Note: The buoyant force on a body immersed is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced and for a stationary body both the buoyant force and weight of the body should be equal and balanced.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Formula used –
1) For a stationary body in a fluid, buoyant force=weight of the body immersed.
2) Force acting on the body immersed in the fluid, $F = V\rho g$
Given, Volume of the body=V
Density of the body=\[\rho \]
Density of upper liquid=\[{\rho _1}\]
Density of lower liquid= \[{\rho _2}\]

Let the volume of the body in upper liquid be ${v_1}$ and the volume in lower liquid be ${v_2}$.
V=${v_1}$+${v_2}$
Since the ball is stationary at the interface, therefore the net buoyant force on the body is equal to the weight of the body.
Let the buoyant force due to upper liquid be ${F_1}$and due to the lower liquid be ${F_2}$.
${F_1}$+${F_2}$=mg…..(i)
${F_1} = {v_1}{\rho _1}g$
And ${F_2} = {v_2}{\rho _2}g$
Putting these in equation (i)
\[{v_1}{\rho _1}g + {v_2}{\rho _2}g = ({v_1} + {v_2})\rho g\]
Eliminating g on both sides, we get
\[{v_1}{\rho _1} + {v_2}{\rho _2} = {v_1}\rho + {v_2}\rho \]
$
{v_1}{\rho _1} + (V - {v_1}){\rho _2} = {v_1}\rho + (V - {v_1})\rho \\
{v_1}({\rho _1} - {\rho _2}) + V{\rho _2} = {v_1}(\rho - \rho ) + V\rho \\
{v_1}({\rho _1} - {\rho _2}) = V(\rho - {\rho _2}) \\
\dfrac{{{v_1}}}{V} = \dfrac{{(\rho - {\rho _2})}}{{({\rho _1} - {\rho _2})}} \\
\dfrac{{{v_2}}}{V} = 1 - \dfrac{{{v_1}}}{V} = 1 - \dfrac{{(\rho - {\rho _2})}}{{({\rho _1} - {\rho _2})}} \\
\dfrac{{{v_2}}}{V} = \dfrac{{{\rho _1} - \rho }}{{{\rho _1} - {\rho _2}}} \\
$
Hence the correct option is C.
Note: The buoyant force on a body immersed is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced and for a stationary body both the buoyant force and weight of the body should be equal and balanced.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




