
A solid cylinder of mass 50kg and radius 0.5m is free to rotate about the horizontal axis. A massless string is wound round the cylinder with one end attached to it and other hanging freely. Tension in the string required to produce an angular acceleration of 2 $ { revolutions }/{ { s }^{ -2 } }$ is:-
A. 25 N
B. 50 N
C. 78.5 N
D. 157 N
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Use the formula of torque in terms of tension and radius. But we know, torque is also related to angular acceleration and inertia. Now, write inertia in terms of mass and radius. Substitute the values and calculate tension in the string.
Formula used:
$ \tau \quad =\quad T\quad \times \quad r$
$ \tau \quad =\quad I\quad \times \quad \alpha$
$ I\quad =\quad \dfrac { m{ R }^{ 2 } }{ 2 }$
Complete answer:
Given: Mass of solid cylinder (m) = 50kg
Radius of cylinder (R)= 0.5m
Angular acceleration ($\alpha$)= $ 2\quad { rev }/{ { s }^{ -2 } }$ = $ 2\quad \times \quad 2\pi { { rad }/{ { s }^{ -2 } } }$
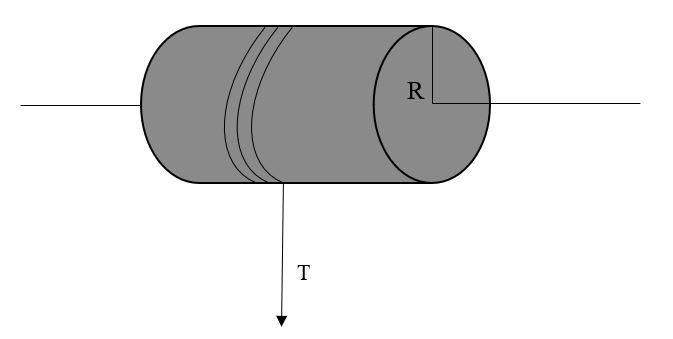
Torque is given by,
$ \tau \quad =\quad T\quad \times \quad r$ …(1)
where, $\tau$ : Torque
T : Tension in the string
R: Radius of cylinder
Rearranging equation.(1) we get,
$ T=\quad \dfrac { \tau }{ R }$ …(2)
We know, $ \tau \quad =\quad I\quad \times \quad \alpha$
Therefore, equation.(2) becomes
$ T\quad =\quad \dfrac { I\quad \times \quad \alpha }{ R }$
where, I: Rotational Inertia
But, $ I\quad =\quad \dfrac { m{ R }^{ 2 } }{ 2 }$
$ \Rightarrow T\quad =\quad \dfrac { m{ R }^{ 2 } }{ 2 } \times \quad \dfrac { \alpha }{ R }$
$ \Rightarrow T\quad =\quad \dfrac { m{ R }\alpha }{ 2 }$
$ \Rightarrow T\quad =\quad \dfrac { 50\quad \times \quad { 0.5\quad \times \quad }4\pi }{ 2 }$
$ \Rightarrow T\quad =\quad 157.08$
Therefore, tension in the string required to produce an angular acceleration of 2 revolutions $ { s }^{ -2 }$ is 157N.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Make sure you convert unit of angular acceleration from $ { revolutions }/{ { s }^{ -2 } }$ to $ { { rad }/{ { s }^{ -2 } } }$. There are 2$\pi$ radians in a complete revolution. So to get total angular acceleration, multiply $ { revolutions }/{ { s }^{ -2 } }$ with $ 2\pi { { rad }/{ { s }^{ -2 } } }$.
Formula used:
$ \tau \quad =\quad T\quad \times \quad r$
$ \tau \quad =\quad I\quad \times \quad \alpha$
$ I\quad =\quad \dfrac { m{ R }^{ 2 } }{ 2 }$
Complete answer:
Given: Mass of solid cylinder (m) = 50kg
Radius of cylinder (R)= 0.5m
Angular acceleration ($\alpha$)= $ 2\quad { rev }/{ { s }^{ -2 } }$ = $ 2\quad \times \quad 2\pi { { rad }/{ { s }^{ -2 } } }$

Torque is given by,
$ \tau \quad =\quad T\quad \times \quad r$ …(1)
where, $\tau$ : Torque
T : Tension in the string
R: Radius of cylinder
Rearranging equation.(1) we get,
$ T=\quad \dfrac { \tau }{ R }$ …(2)
We know, $ \tau \quad =\quad I\quad \times \quad \alpha$
Therefore, equation.(2) becomes
$ T\quad =\quad \dfrac { I\quad \times \quad \alpha }{ R }$
where, I: Rotational Inertia
But, $ I\quad =\quad \dfrac { m{ R }^{ 2 } }{ 2 }$
$ \Rightarrow T\quad =\quad \dfrac { m{ R }^{ 2 } }{ 2 } \times \quad \dfrac { \alpha }{ R }$
$ \Rightarrow T\quad =\quad \dfrac { m{ R }\alpha }{ 2 }$
$ \Rightarrow T\quad =\quad \dfrac { 50\quad \times \quad { 0.5\quad \times \quad }4\pi }{ 2 }$
$ \Rightarrow T\quad =\quad 157.08$
Therefore, tension in the string required to produce an angular acceleration of 2 revolutions $ { s }^{ -2 }$ is 157N.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Make sure you convert unit of angular acceleration from $ { revolutions }/{ { s }^{ -2 } }$ to $ { { rad }/{ { s }^{ -2 } } }$. There are 2$\pi$ radians in a complete revolution. So to get total angular acceleration, multiply $ { revolutions }/{ { s }^{ -2 } }$ with $ 2\pi { { rad }/{ { s }^{ -2 } } }$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




