
A solid consists of a cone on top of a cylinder with a radius equal to that of the cone. The height of the cone is 33 and the height of the cylinder is 13. If the volume of the solid is $256\pi $, what is the area of the base of the cylinder?
Answer
487.8k+ views
Hint: We first assume the radius as $r$ for both cone and the cylinder to calculate the total volume of the solid. We equate it with $256\pi $ and solve the equation. We then find the area of the base of the cylinder which is equal to \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\] square units.
Complete step by step answer:
The radius of the base of the cone and the cylinder is same. Let us assume the radius as $r$.The height of the cone is 33 and the height of the cylinder is 13. We assume the heights as \[{{h}_{1}}=33,{{h}_{2}}=13\]. The total volume of the solid is $256\pi $.
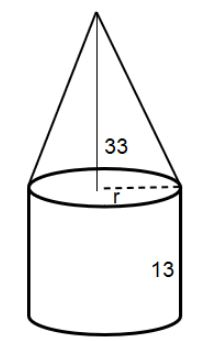
We find individual volumes. The formula of volumes for cone and cylinder are \[\dfrac{\pi {{r}^{2}}{{h}_{1}}}{3}\] and \[\pi {{r}^{2}}{{h}_{2}}\] respectively. The area of the base of the cylinder is \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\] square units.Therefore, the equality with $256\pi $ gives, \[\dfrac{\pi {{r}^{2}}{{h}_{1}}}{3}+\pi {{r}^{2}}{{h}_{2}}=256\pi \].
Putting the values, we get
\[\dfrac{\pi {{r}^{2}}\times 33}{3}+\pi {{r}^{2}}\times 13=256\pi \\
\Rightarrow 11{{r}^{2}}+13{{r}^{2}}=256 \\
\Rightarrow 24{{r}^{2}}=256 \\
\]
We simplify the equation to find the value of \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\].
\[24{{r}^{2}}=256 \\
\therefore \pi {{r}^{2}}=\dfrac{256\pi }{24}=33.51 \]
Therefore, the area of the base of the cylinder is \[33.51\] square units.
Note: We need to be careful about the difference between height and slant height.The slant height is used for the lateral surface area of the cone. In the case of total surface area, we add one base area instead of two.
Complete step by step answer:
The radius of the base of the cone and the cylinder is same. Let us assume the radius as $r$.The height of the cone is 33 and the height of the cylinder is 13. We assume the heights as \[{{h}_{1}}=33,{{h}_{2}}=13\]. The total volume of the solid is $256\pi $.

We find individual volumes. The formula of volumes for cone and cylinder are \[\dfrac{\pi {{r}^{2}}{{h}_{1}}}{3}\] and \[\pi {{r}^{2}}{{h}_{2}}\] respectively. The area of the base of the cylinder is \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\] square units.Therefore, the equality with $256\pi $ gives, \[\dfrac{\pi {{r}^{2}}{{h}_{1}}}{3}+\pi {{r}^{2}}{{h}_{2}}=256\pi \].
Putting the values, we get
\[\dfrac{\pi {{r}^{2}}\times 33}{3}+\pi {{r}^{2}}\times 13=256\pi \\
\Rightarrow 11{{r}^{2}}+13{{r}^{2}}=256 \\
\Rightarrow 24{{r}^{2}}=256 \\
\]
We simplify the equation to find the value of \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\].
\[24{{r}^{2}}=256 \\
\therefore \pi {{r}^{2}}=\dfrac{256\pi }{24}=33.51 \]
Therefore, the area of the base of the cylinder is \[33.51\] square units.
Note: We need to be careful about the difference between height and slant height.The slant height is used for the lateral surface area of the cone. In the case of total surface area, we add one base area instead of two.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




