
A soldier directs a laser beam on an enemy by reflecting the beam from a mirror. If the mirror is rotated by an angle $\theta $ by what angle will the reflected beam rotate?
A. $\dfrac{\theta }{2}$
B. $\theta $
C. $2\theta $
D. None of these
Answer
507.3k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question we need to understand reflection. Reflection means incident light when it falls on an interface at some angle then it gets reflected back in the same medium but in a different direction. Reflection is of two types, diffused and regular reflection. Diffused reflection is a reflection in which incident angle is not equal to reflected angle whereas in case of regular reflection incident angle is equal to reflected angle.
Complete step by step answer:
Let the mirror AB initially be along the x axis and the normal be ${N_1}{N_1}'$. Let the incident ray XO make an angle “I” with normal ${N_1}{N_1}'$ , since the reflection is regular so reflected ray OY makes an angle “r” equal to incident angle which is $i = r$. Now let the mirror AB be rotated by angle $\theta $ so the new mirror be $A'B'$ and the new normal be ${N_2}{N_2}'$.
So the angle between two normal is also $\theta $ from geometry which is $\angle {N_1}O{N_2} = \;\theta $. Let again incident ray XO falls on mirror at angle $i'$ and reflected beam $OY'$ makes an angle $r'$ with new normal ${N_2}{N_2}'$.
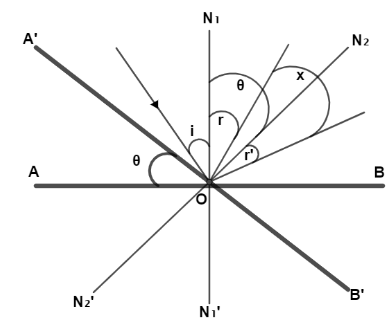
From figure $i' = i + \theta $ also $i' = r'$. Let the new reflected ray rotate by an angle “x” from old reflected beams which is $\angle YOY' = x$.
So from geometry, $\angle YOY' = \angle {N_1}OY' - \angle {N_1}OY$
Or, $\angle YOY' = (\angle {N_1}O{N_2} + \angle {N_2}OY') - \angle {N_1}OY$
Putting values we get, $x = (\theta + r') - r$
Or, $x = (\theta + i') - r$
$x = (\theta + i + \theta ) - r$
Since $i = r$
$\therefore x = 2\theta $
So the correct option is C.
Note: It should be remembered that laser beams used are monochromatic in nature meaning the incident light contains only one wavelength. If the incident light is not monochromatic in nature then it contains multiple wavelengths so different refractive index and different speed. Also due to reflection a phase difference of $\pi $ so a path difference is created and that is why the reflected beam is in a different direction from the incident beam.
Complete step by step answer:
Let the mirror AB initially be along the x axis and the normal be ${N_1}{N_1}'$. Let the incident ray XO make an angle “I” with normal ${N_1}{N_1}'$ , since the reflection is regular so reflected ray OY makes an angle “r” equal to incident angle which is $i = r$. Now let the mirror AB be rotated by angle $\theta $ so the new mirror be $A'B'$ and the new normal be ${N_2}{N_2}'$.
So the angle between two normal is also $\theta $ from geometry which is $\angle {N_1}O{N_2} = \;\theta $. Let again incident ray XO falls on mirror at angle $i'$ and reflected beam $OY'$ makes an angle $r'$ with new normal ${N_2}{N_2}'$.

From figure $i' = i + \theta $ also $i' = r'$. Let the new reflected ray rotate by an angle “x” from old reflected beams which is $\angle YOY' = x$.
So from geometry, $\angle YOY' = \angle {N_1}OY' - \angle {N_1}OY$
Or, $\angle YOY' = (\angle {N_1}O{N_2} + \angle {N_2}OY') - \angle {N_1}OY$
Putting values we get, $x = (\theta + r') - r$
Or, $x = (\theta + i') - r$
$x = (\theta + i + \theta ) - r$
Since $i = r$
$\therefore x = 2\theta $
So the correct option is C.
Note: It should be remembered that laser beams used are monochromatic in nature meaning the incident light contains only one wavelength. If the incident light is not monochromatic in nature then it contains multiple wavelengths so different refractive index and different speed. Also due to reflection a phase difference of $\pi $ so a path difference is created and that is why the reflected beam is in a different direction from the incident beam.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




