
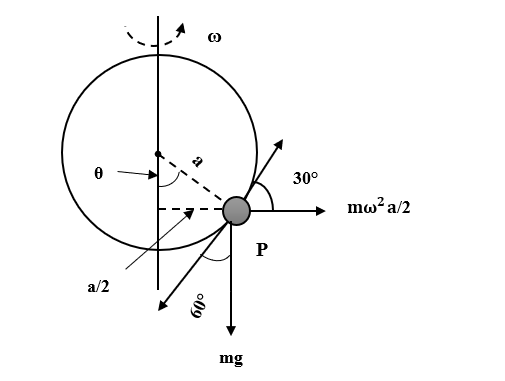
A smooth wire is bent into a vertical circle of radius a. A bead P can slide smoothly on the wire. The circle is rotated about diameter AB as axis with a speed $\omega$ as shown in figure. The bead P is at rest with respect to the circular ring in the position shown. Then ${ \omega }^{ 2 }$ is equal to-
A. $\dfrac {2g}{a}$
B. $\dfrac { 2g }{ a\sqrt { 3 } }$
C. $\dfrac { g\sqrt { 3 } g }{ a }$
D. $\dfrac { 2a }{ g\sqrt { 3 } }$

Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem, first find the components of normal reaction. Note the horizontal and vertical components of the normal reaction. Divide these two equations and obtain an expression in terms of ${ \omega }^{ 2 }$. Then, with the help of the figure find the angle of $\theta$. Substitute this value in the expression for ${ \omega }^{ 2 }$. This will give the value for ${ \omega }^{ 2 }$.
Complete answer:
Let N be the normal reaction on the bead. After resolving the normal reaction into two components we get,
$N\cos { \theta } =mg$ …(1)
$N\sin { \theta } =\dfrac { m\omega ^{ 2 }a }{ 2 }$ …(1)
Dividing equation. (1) by (2) we get,
$\Rightarrow \tan { \theta }=\dfrac { \dfrac { m{ \omega }^{ 2 }a }{ 2 } }{mg} $
$\Rightarrow \tan { \theta }=\dfrac { a{ \omega }^{ 2 } } {2g} $
$\Rightarrow { \omega }^{ 2 }=\dfrac { 2g\tan { \theta } }{a}$ …(2)
From the figure,
$\sin { \theta }=\dfrac { a }{ 2a } $
$\Rightarrow \sin { \theta }=\dfrac { 1 }{ 2 } $
$\Rightarrow \theta =30°$
Substituting this value in the equation. (2) we get,
${ \omega }^{ 2 }=\dfrac { 2g\tan { 30° } }{ a } $
$\Rightarrow { \omega }^{ 2 }=\dfrac { 2g }{ a\sqrt { 3 } }$
Hence, ${ \omega }^{ 2 }$ is equal to $\dfrac { 2g }{ a\sqrt { 3 } }$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
The normal force plays an important role in friction. It defines the coefficient of static friction. Students must remember that normal force is a contact force. It only exists if two surfaces are in contact with each other otherwise it doesn’t exist. Generally, the normal force is equal to the weight of the object but this is true only if the normal force is the only thing counteracting the force. Students should be careful to calculate any force by applying Newton’s law.
Complete answer:
Let N be the normal reaction on the bead. After resolving the normal reaction into two components we get,
$N\cos { \theta } =mg$ …(1)
$N\sin { \theta } =\dfrac { m\omega ^{ 2 }a }{ 2 }$ …(1)
Dividing equation. (1) by (2) we get,
$\Rightarrow \tan { \theta }=\dfrac { \dfrac { m{ \omega }^{ 2 }a }{ 2 } }{mg} $
$\Rightarrow \tan { \theta }=\dfrac { a{ \omega }^{ 2 } } {2g} $
$\Rightarrow { \omega }^{ 2 }=\dfrac { 2g\tan { \theta } }{a}$ …(2)
From the figure,
$\sin { \theta }=\dfrac { a }{ 2a } $
$\Rightarrow \sin { \theta }=\dfrac { 1 }{ 2 } $
$\Rightarrow \theta =30°$
Substituting this value in the equation. (2) we get,
${ \omega }^{ 2 }=\dfrac { 2g\tan { 30° } }{ a } $
$\Rightarrow { \omega }^{ 2 }=\dfrac { 2g }{ a\sqrt { 3 } }$
Hence, ${ \omega }^{ 2 }$ is equal to $\dfrac { 2g }{ a\sqrt { 3 } }$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
The normal force plays an important role in friction. It defines the coefficient of static friction. Students must remember that normal force is a contact force. It only exists if two surfaces are in contact with each other otherwise it doesn’t exist. Generally, the normal force is equal to the weight of the object but this is true only if the normal force is the only thing counteracting the force. Students should be careful to calculate any force by applying Newton’s law.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




