
A smooth wedge of angle θ with horizontal is fixed to an elevator moving downwards with the acceleration $\dfrac{g}{3}$ the acceleration of a block kept on the wedge with respect to the elevator is:
$\begin{align}
& A.\dfrac{g}{3}\sin \theta \\
& B.g \\
& C.\dfrac{2g}{3}\sin \theta \\
& D.\dfrac{g}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint: You could first make a free body diagram of the given block. Then you could find the net force on the block by balancing the forces on the block. Using Newton's second law of motion, you could find the acceleration of the block kept on wedge with respect to the elevator. You should note that there is a requirement of introduction of pseudo force.
Formula used:
$F=m\times a$
Complete step by step solution:
In the question we are given a smooth wedge of angle $\theta$ and this wedge is fixed to an elevator accelerating downwards at$\dfrac{g}{3}$. We are supposed to find the acceleration of the block on the wedge with respect to the elevator.
In order to answer this question, we have to form a free body diagram of the given wedge along with the block of mass m.
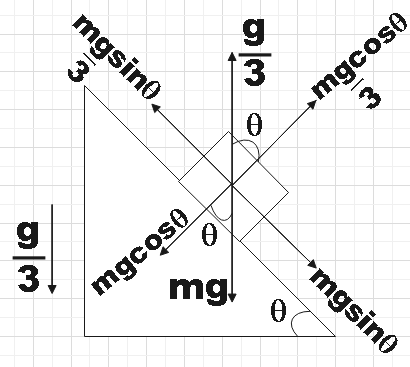
We should note that the given system is a non inertial frame of reference and hence it is required for us to introduce a pseudo force on the block. So we have a pseudo acceleration $\dfrac{g}{3}$ marked in the free body diagram that is directed upwards and this force keeps the block pressed against the wedge and hence at rest.
The net force on the block can be given by,
${{F}_{net}}=mg\sin \theta -m\dfrac{g}{3}\sin \theta$
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=mg\sin \theta \left( 1-\dfrac{1}{3} \right)=\dfrac{2}{3}mg\sin \theta$
From Newton’s second law of motion we have,
$F=ma$
$\Rightarrow ma=\dfrac{2}{3}mg\sin \theta$
$\therefore a=\dfrac{2}{3}g\sin \theta$
Therefore, we found the acceleration of the block to be$a=\dfrac{2}{3}g\sin \theta$. Hence, option C is found to be the answer.
Note: When we apply force on a body it will start changing its velocity with the time. We can easily calculate the acceleration of the block by finding the net force acting on the block. Introduction of a pseudo force is a must in case of a non inertial frame of reference. A frame of reference that undergoes acceleration with respect to the inertial frame of reference is called a non inertial frame of reference.
Formula used:
$F=m\times a$
Complete step by step solution:
In the question we are given a smooth wedge of angle $\theta$ and this wedge is fixed to an elevator accelerating downwards at$\dfrac{g}{3}$. We are supposed to find the acceleration of the block on the wedge with respect to the elevator.
In order to answer this question, we have to form a free body diagram of the given wedge along with the block of mass m.

We should note that the given system is a non inertial frame of reference and hence it is required for us to introduce a pseudo force on the block. So we have a pseudo acceleration $\dfrac{g}{3}$ marked in the free body diagram that is directed upwards and this force keeps the block pressed against the wedge and hence at rest.
The net force on the block can be given by,
${{F}_{net}}=mg\sin \theta -m\dfrac{g}{3}\sin \theta$
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=mg\sin \theta \left( 1-\dfrac{1}{3} \right)=\dfrac{2}{3}mg\sin \theta$
From Newton’s second law of motion we have,
$F=ma$
$\Rightarrow ma=\dfrac{2}{3}mg\sin \theta$
$\therefore a=\dfrac{2}{3}g\sin \theta$
Therefore, we found the acceleration of the block to be$a=\dfrac{2}{3}g\sin \theta$. Hence, option C is found to be the answer.
Note: When we apply force on a body it will start changing its velocity with the time. We can easily calculate the acceleration of the block by finding the net force acting on the block. Introduction of a pseudo force is a must in case of a non inertial frame of reference. A frame of reference that undergoes acceleration with respect to the inertial frame of reference is called a non inertial frame of reference.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




