
A smooth track in the form of a quarter circle of radius $6\,m$ lies in a vertical plane. A particle moves from ${P_1}$ to ${P_2}$ undergo the forces $\overrightarrow {{F_1}} $, $\overrightarrow {{F_2}} $,$\overrightarrow {{F_3}} $. Force $\overrightarrow {{F_1}} $ is always towards ${P_2}$ and is always $20\,N$ in magnitude, force $\overrightarrow {{F_2}} $ always acts tangentially and it is always $15\,N$ in magnitude. Force $\overrightarrow {{F_3}} $ always acts horizontally is of magnitude $30\,N$. Select the correct alternative(s):
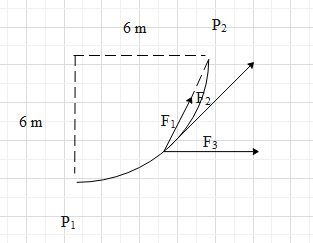
A. work done by $\overrightarrow {{F_1}} $ is $120J$
B. work done by $\overrightarrow {{F_2}} $ is $45\pi J$
C. work done by $\overrightarrow {{F_3}} $ is $180\,J$
D. $\overrightarrow {{F_1}} $ is conservative in nature.

Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint-
Work done is the product of force and displacement of force in the direction of force.
Work is represented in equation form as
In the case of ${F_1}$
Here, $ds$ which is the displacement in the direction of $\overrightarrow {{F_1}} $ is the distance from ${P_{1\,}}$ to ${P_2}$.
In the case of ${F_2}$
Work done by ${F_2}$ is along the arc ${P_1}{P_2}$
${W_{{F_2}}} = \int {{F_2}} ds$
Given arc is a quarter of a full circle.
Therefore, arc length is circumference of the circle divided by 4.
In case of ${F_3}$
Here displacement along direction of ${F_3}$ is the horizontal displacement which is $6\,m$
A force is said to be conservative, if the work done by it is path independent.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Work done is the product of force and displacement of force in the direction of force.
Work is represented in equation form as
In the case of ${F_1}$
Given${F_1} = 20N$
$ds$ which is the displacement in the direction of $\overrightarrow {{F_1}} $ is the distance from ${P_{1\,}}$ to ${P_2}$.
Using Pythagoras theorem, we get distance of line
${P_1}{P_2} = \sqrt {{6^2} + {6^2}\,} $
${P_1}{P_2} = 6\sqrt 2 $
Substituting the given values, we get,
${W_{{F_1}}} = 20N \times 6\sqrt 2 = 120\sqrt 2 J$
In the case of ${F_2}$
Work done by ${F_2}$ is along the arc ${P_1}{P_2}$
${W_{{F_2}}} = \int {{F_2}} ds$
Given arc is a quarter of a full circle.
Therefore, arc length is circumference of the circle divided by 4.
${p_1}{p_2} = \dfrac{{2\pi r}}{4} = \dfrac{{\pi r}}{2}$
$
{W_{{F_2}}} = 15 \times \dfrac{{\pi r}}{2} \\
= 15 \times \pi \times \dfrac{6}{2} \\
= 45\pi J \\
$
In case of ${F_3}$
Here displacement along direction of ${F_3}$ is the horizontal displacement which is $6\,m$
\[
{W_{{F_3}}} = 30 \times 6 \\
= 180J \\
\]
Now a force is said to be conservative, if the work done by it is path independent. Since work done by $\overrightarrow {{F_1}} $ depends only on initial and final position, we can say that ${F_1}$ is conservation.
So, the correct options are option B, C and D
Note: Remember that while calculating work the force should be multiplied by the displacement in the direction of force. In each cases of work for forces $\overrightarrow {{F_1}} $, $\overrightarrow {{F_2}} $, $\overrightarrow {{F_3}} $ the displacement will differ according to the direction of these forces. So, in each case consider the component of displacement in the direction of corresponding force.
Work done is the product of force and displacement of force in the direction of force.
Work is represented in equation form as
In the case of ${F_1}$
Here, $ds$ which is the displacement in the direction of $\overrightarrow {{F_1}} $ is the distance from ${P_{1\,}}$ to ${P_2}$.
In the case of ${F_2}$
Work done by ${F_2}$ is along the arc ${P_1}{P_2}$
${W_{{F_2}}} = \int {{F_2}} ds$
Given arc is a quarter of a full circle.
Therefore, arc length is circumference of the circle divided by 4.
In case of ${F_3}$
Here displacement along direction of ${F_3}$ is the horizontal displacement which is $6\,m$
A force is said to be conservative, if the work done by it is path independent.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Work done is the product of force and displacement of force in the direction of force.
Work is represented in equation form as
In the case of ${F_1}$
Given${F_1} = 20N$
$ds$ which is the displacement in the direction of $\overrightarrow {{F_1}} $ is the distance from ${P_{1\,}}$ to ${P_2}$.
Using Pythagoras theorem, we get distance of line
${P_1}{P_2} = \sqrt {{6^2} + {6^2}\,} $
${P_1}{P_2} = 6\sqrt 2 $
Substituting the given values, we get,
${W_{{F_1}}} = 20N \times 6\sqrt 2 = 120\sqrt 2 J$
In the case of ${F_2}$
Work done by ${F_2}$ is along the arc ${P_1}{P_2}$
${W_{{F_2}}} = \int {{F_2}} ds$
Given arc is a quarter of a full circle.
Therefore, arc length is circumference of the circle divided by 4.
${p_1}{p_2} = \dfrac{{2\pi r}}{4} = \dfrac{{\pi r}}{2}$
$
{W_{{F_2}}} = 15 \times \dfrac{{\pi r}}{2} \\
= 15 \times \pi \times \dfrac{6}{2} \\
= 45\pi J \\
$
In case of ${F_3}$
Here displacement along direction of ${F_3}$ is the horizontal displacement which is $6\,m$
\[
{W_{{F_3}}} = 30 \times 6 \\
= 180J \\
\]
Now a force is said to be conservative, if the work done by it is path independent. Since work done by $\overrightarrow {{F_1}} $ depends only on initial and final position, we can say that ${F_1}$ is conservation.
So, the correct options are option B, C and D
Note: Remember that while calculating work the force should be multiplied by the displacement in the direction of force. In each cases of work for forces $\overrightarrow {{F_1}} $, $\overrightarrow {{F_2}} $, $\overrightarrow {{F_3}} $ the displacement will differ according to the direction of these forces. So, in each case consider the component of displacement in the direction of corresponding force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




