
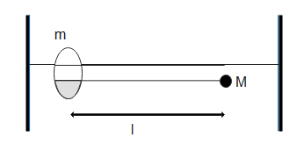
A smooth ring of mass \[m\] which is free to slide along a rigid horizontal wire, is connected to a particle of mass $M$ by a string of length $l$. The system is released from rest when the string is horizontal. At an instant when string becomes vertical, the speed of the particle
A. $0$
B. $\sqrt {2gl\dfrac{{(m + M)}}{m}} $
C. $m\sqrt {\dfrac{{2gl}}{{M(m + M)}}} $
D. $m\sqrt {\dfrac{{2gl}}{{m(m + M)}}} $

Answer
505.2k+ views
Hint: We are given a ring that is free to slide along a rigid horizontal wire and it is connected to a particle of mass and then the system is released when the string is horizontal and we need to find the speed of the particle when the string becomes vertical.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the momentum of the ring and the particle connected to it will be equal
$mv = MV$
Where $v$ and $V$ are the velocities of the ring and the particle respectively.
Hence $u = \dfrac{{MV}}{m}$ where $u$ is the initial velocity of the ring when the string is released. Now the potential energy of the string will get converted into the kinetic energy of the ring as well as the particle therefore we have,
$Mgl = \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2} + \dfrac{1}{2}M{V^2}$
Substituting the value of the initial velocity of the ring we get
$ \Rightarrow 2Mgl = m{\left( {\dfrac{{MV}}{m}} \right)^2} + M{V^2}$
Further solving we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2Mgl = m\dfrac{{{M^2}{V^2}}}{{{m^2}}} + M{V^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 2gl = \dfrac{{M{V^2}}}{m} + {V^2}$
Rearranging the equation to get the desired expression for the speed of the particle
$ \Rightarrow 2gl = \dfrac{{(M + m)}}{m}{V^2}$
$ \Rightarrow V = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2mgl}}{{M + m}}} $
$\therefore V = m\sqrt {\dfrac{{2gl}}{{m(M + m)}}} $
Hence option D is the correct answer.
Note: The ring is attached to the horizontal wire and it can freely move only in the forwarding and backwards direction while the mass attached to the string can move in the upward and downward direction. So when the string is released the mass will move in the downward direction due to gravity and the string will become vertical. In the horizontal direction, there is no external force applied and therefore the momentum of the ring and the particle is conserved and that is why we equated them at the beginning of the solution.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the momentum of the ring and the particle connected to it will be equal
$mv = MV$
Where $v$ and $V$ are the velocities of the ring and the particle respectively.
Hence $u = \dfrac{{MV}}{m}$ where $u$ is the initial velocity of the ring when the string is released. Now the potential energy of the string will get converted into the kinetic energy of the ring as well as the particle therefore we have,
$Mgl = \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2} + \dfrac{1}{2}M{V^2}$
Substituting the value of the initial velocity of the ring we get
$ \Rightarrow 2Mgl = m{\left( {\dfrac{{MV}}{m}} \right)^2} + M{V^2}$
Further solving we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2Mgl = m\dfrac{{{M^2}{V^2}}}{{{m^2}}} + M{V^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 2gl = \dfrac{{M{V^2}}}{m} + {V^2}$
Rearranging the equation to get the desired expression for the speed of the particle
$ \Rightarrow 2gl = \dfrac{{(M + m)}}{m}{V^2}$
$ \Rightarrow V = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2mgl}}{{M + m}}} $
$\therefore V = m\sqrt {\dfrac{{2gl}}{{m(M + m)}}} $
Hence option D is the correct answer.
Note: The ring is attached to the horizontal wire and it can freely move only in the forwarding and backwards direction while the mass attached to the string can move in the upward and downward direction. So when the string is released the mass will move in the downward direction due to gravity and the string will become vertical. In the horizontal direction, there is no external force applied and therefore the momentum of the ring and the particle is conserved and that is why we equated them at the beginning of the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




