
A small wooden block is floating in a tub of water. The water is gradually heated. The volume of the wooden block visible above the water surface.
A. fluctuates
B. decreases
C. increases
D. remains the same
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: One of the factors which are responsible for the change in the density of anything is temperature. Density is the ratio of the mass of the object and volume occupied by it. The SI unit of density is $kg{{m}^{-3}}$ denoted by $\rho$.
Complete step by step answer:
When the temperature of matter is increased or decreased there is a change in the density of the matter. The density of something is the ratio of its mass and its volume.
Mathematically,
\[\rho =\dfrac{m}{v}\]
Where m is mass
v is the volume
Usually, when we heat something there is an increase in the volume of the substance.
As we can see from the above formula, density is inversely proportional to the volume of the material $(\rho \propto \dfrac{1}{v})$.
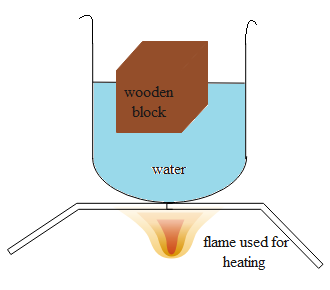
So, according to the situation mentioned in the question. When we heat the water there is an increase in the temperature of the water which increases the volume of the heated part of the water. As the volume increases there is a drop in the density of water.
The water portion with low density (heated water) starts to float over the water of low density (water which has to get heated).
If a wooden block is placed inside a water tub which is being heated. The wooden block will remain at its initial position and heated water will rise over it. This is due to the reason that wood is a poor conductor of heat. So no difference will occur due to the heating of the water. As a result, the visibility of the wooden block floating on the water will start to decrease.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Every matter which exists has a particular mass and density. Components that have lower density tend to float over the one with higher density. The density of a material depends on its external surrounding factors such as temperature and pressure.
Complete step by step answer:
When the temperature of matter is increased or decreased there is a change in the density of the matter. The density of something is the ratio of its mass and its volume.
Mathematically,
\[\rho =\dfrac{m}{v}\]
Where m is mass
v is the volume
Usually, when we heat something there is an increase in the volume of the substance.
As we can see from the above formula, density is inversely proportional to the volume of the material $(\rho \propto \dfrac{1}{v})$.

So, according to the situation mentioned in the question. When we heat the water there is an increase in the temperature of the water which increases the volume of the heated part of the water. As the volume increases there is a drop in the density of water.
The water portion with low density (heated water) starts to float over the water of low density (water which has to get heated).
If a wooden block is placed inside a water tub which is being heated. The wooden block will remain at its initial position and heated water will rise over it. This is due to the reason that wood is a poor conductor of heat. So no difference will occur due to the heating of the water. As a result, the visibility of the wooden block floating on the water will start to decrease.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Every matter which exists has a particular mass and density. Components that have lower density tend to float over the one with higher density. The density of a material depends on its external surrounding factors such as temperature and pressure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




