
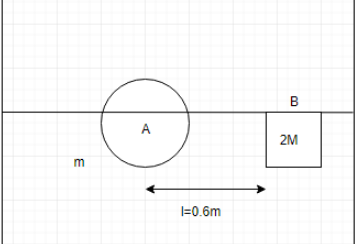
A small ring of mass m is attached at one end of a light string of length, l= 0.6 cm.The other end of the string is tied to a small block B of mass 2m. the ring is free to move on a fixed smooth horizontal rod. The block B is released from rest from the position as shown. The velocity of the ring when the string becomes vertical is ?
A. 4
B. 3
C. 3.5
D. 2.5

Answer
555.3k+ views
Hint: The ring cannot move freely on the string until the string is not made vertical and after the string has been made vertical, the ring comes into motion, assuming the velocity of the ring be v. Since, no external force acts on the system energy must remain conserved. So, we can make use of the law of conservation of energy to solve this problem.
Complete step by step answer:
Initially the ring was at rest, so it possesses only potential energy. When it hit the block it has only kinetic energy, so using conservation of energy:
$mgx=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow gx=\dfrac{{{v}^{2}}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{2gx} \\
\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{2\times 10\times 0.6} \\
\therefore v=3.5$
So, the velocity comes out to be 3.5 m/s.
So, the correct option is C.
Note: Work-energy theorem states that the net work done by the forces on an object equals the change in its kinetic energy. But here we had used the law of conservation of energy instead of the work energy theorem. Energy is a scalar quantity, i.e., it does not depend on direction, and it is always positive. Kinetic energy being negative does not make any sense because we are having a square of velocity and for sure mass can never be negative.
Complete step by step answer:
Initially the ring was at rest, so it possesses only potential energy. When it hit the block it has only kinetic energy, so using conservation of energy:
$mgx=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow gx=\dfrac{{{v}^{2}}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{2gx} \\
\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{2\times 10\times 0.6} \\
\therefore v=3.5$
So, the velocity comes out to be 3.5 m/s.
So, the correct option is C.
Note: Work-energy theorem states that the net work done by the forces on an object equals the change in its kinetic energy. But here we had used the law of conservation of energy instead of the work energy theorem. Energy is a scalar quantity, i.e., it does not depend on direction, and it is always positive. Kinetic energy being negative does not make any sense because we are having a square of velocity and for sure mass can never be negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




