
A small mass and a thin uniform rod, each of mass ‘m’ are positioned along the same straight line as shown. The force of gravitational attraction exerted by the rod on the small mass is
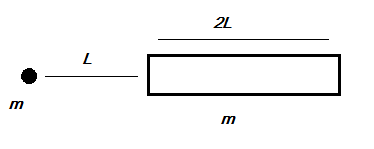
$
A.\dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{2{L^2}}} \\
B.\dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{3{L^2}}} \\
C.\dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{4{L^2}}} \\
D.\dfrac{{3G{m^2}}}{{4{L^2}}} \\
$

Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint:
In this question, we need to determine the force of gravitational attraction on the small mass by the rod. For this, we need to use the standard formula for the force of gravitation, which is given as $F = \dfrac{{G{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$ where G is the gravitational constant, ${m_1}{\text{ and }}{m_2}$ are the mass of the objects, and r is the distance between the objects.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider a small section in the thin uniform rod of mass, which is ‘x’ meters away from the starting of the rod with the width be ‘dx’ and mass be ‘dm’.
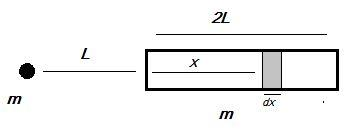
The gravitational force acting between the two masses is given as $F = \dfrac{{G{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$ where G is the gravitational constant, ${m_1}{\text{ and }}{m_2}$ are the mass of the objects, and r is the distance between the objects.
So, substitute ${m_1} = m,{m_2} = dm{\text{ and }}r = (L + x)$ in the formula $F = \dfrac{{G{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$ to determine the force of gravitation due to the elementary mass ‘dm’ on the small mass ‘m’.
$
dF = \dfrac{{G{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}} \\
= \dfrac{{Gmdm}}{{{{(L + x)}^2}}} - - - - (i) \\
$
It is given in the question that the mass of the ‘2L’ meters long and thin rod is ‘m’; therefore, the mass of the small elementary section ‘dx’ on the rod is given as: $dm = \dfrac{{mdx}}{{2L}}$
Substitute $dm = \dfrac{{mdx}}{{2L}}$ in the equation (i) we get:
$
dF = \dfrac{{Gm}}{{{{(L + x)}^2}}} \times \dfrac{{mdx}}{{2L}} \\
= \dfrac{{G{m^2}dx}}{{2L{{(L + x)}^2}}} - - - - (ii) \\
$
Now, to determine the gravitational force for the whole rod on the small mass ‘m’, we have to integrate the equation (ii) under the definite limits of 0 to ‘2L’.
$
\int {dF} = \int\limits_0^{2L} {\dfrac{{G{m^2}dx}}{{2L{{(L + x)}^2}}}} \\
F = \dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{2L}}\int\limits_0^{2L} {\dfrac{{dx}}{{{{(L + x)}^2}}}} \\
= \dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{2L}}\left[ {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{{L + x}}} \right]_0^{2L} \\
= \dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{2L}}\left( {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{{L + 2L}} - \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{L + 0}}} \right) \\
= \dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{2L}}\left( {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{{3L}} + \dfrac{1}{L}} \right) \\
= \dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{2L}}\left( {\dfrac{{ - 1 + 3}}{{3L}}} \right) \\
= \dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{2L}}\left( {\dfrac{2}{{3L}}} \right) \\
= \dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{3{L^2}}} \\
$
Hence, the force of gravitation attraction exerted by the rod on the small mass is $\dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{3{L^2}}}$
Option B is correct.
Note: Students should be aware while taking the bounded region for the integrating purpose. Here, as we can see that the length of the rod varies from the 0 to 2L meters so, we have taken the limits from 0 to 2L only.
In this question, we need to determine the force of gravitational attraction on the small mass by the rod. For this, we need to use the standard formula for the force of gravitation, which is given as $F = \dfrac{{G{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$ where G is the gravitational constant, ${m_1}{\text{ and }}{m_2}$ are the mass of the objects, and r is the distance between the objects.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider a small section in the thin uniform rod of mass, which is ‘x’ meters away from the starting of the rod with the width be ‘dx’ and mass be ‘dm’.

The gravitational force acting between the two masses is given as $F = \dfrac{{G{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$ where G is the gravitational constant, ${m_1}{\text{ and }}{m_2}$ are the mass of the objects, and r is the distance between the objects.
So, substitute ${m_1} = m,{m_2} = dm{\text{ and }}r = (L + x)$ in the formula $F = \dfrac{{G{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$ to determine the force of gravitation due to the elementary mass ‘dm’ on the small mass ‘m’.
$
dF = \dfrac{{G{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}} \\
= \dfrac{{Gmdm}}{{{{(L + x)}^2}}} - - - - (i) \\
$
It is given in the question that the mass of the ‘2L’ meters long and thin rod is ‘m’; therefore, the mass of the small elementary section ‘dx’ on the rod is given as: $dm = \dfrac{{mdx}}{{2L}}$
Substitute $dm = \dfrac{{mdx}}{{2L}}$ in the equation (i) we get:
$
dF = \dfrac{{Gm}}{{{{(L + x)}^2}}} \times \dfrac{{mdx}}{{2L}} \\
= \dfrac{{G{m^2}dx}}{{2L{{(L + x)}^2}}} - - - - (ii) \\
$
Now, to determine the gravitational force for the whole rod on the small mass ‘m’, we have to integrate the equation (ii) under the definite limits of 0 to ‘2L’.
$
\int {dF} = \int\limits_0^{2L} {\dfrac{{G{m^2}dx}}{{2L{{(L + x)}^2}}}} \\
F = \dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{2L}}\int\limits_0^{2L} {\dfrac{{dx}}{{{{(L + x)}^2}}}} \\
= \dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{2L}}\left[ {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{{L + x}}} \right]_0^{2L} \\
= \dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{2L}}\left( {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{{L + 2L}} - \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{L + 0}}} \right) \\
= \dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{2L}}\left( {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{{3L}} + \dfrac{1}{L}} \right) \\
= \dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{2L}}\left( {\dfrac{{ - 1 + 3}}{{3L}}} \right) \\
= \dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{2L}}\left( {\dfrac{2}{{3L}}} \right) \\
= \dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{3{L^2}}} \\
$
Hence, the force of gravitation attraction exerted by the rod on the small mass is $\dfrac{{G{m^2}}}{{3{L^2}}}$
Option B is correct.
Note: Students should be aware while taking the bounded region for the integrating purpose. Here, as we can see that the length of the rod varies from the 0 to 2L meters so, we have taken the limits from 0 to 2L only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




