
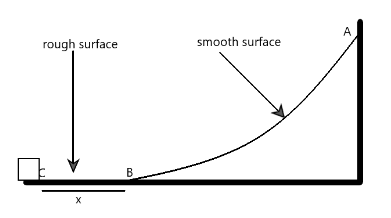
A small block of mass $ m $ is released from point A on a fixed smooth wedge as shown in figure. Bottom of the wedge is marked as B and at point C the block stops moving because the straight part of the floor is rough.
(a) Work done by normal reaction is zero during the movement of the block
(b) From point A to B only
(c) From B to C only
(d) From A to C
None of the above
The friction coefficient at the block with floor is
(A) $ \dfrac{h}{{{x_0}}} $
(B) $ \dfrac{{{x_0}}}{h} $
(C) Zero
(D) 1

Answer
557.1k+ views
Hint: The normal reaction force is always perpendicular to the surface. Work is done by forces which move an object in a direction the same as theirs. The potential energy of the block at point A is converted to kinetic energy at point B, which friction then reduces to zero.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
$ {P_E} = mgh $ where $ {P_E} $ is the potential energy of a body, $ m $ is the mass of the body, $ g $ is the acceleration due to gravity, and $ h $ is the height of the body.
$ w = \mu mgd $ where $ w $ is the work done by friction on a body, $ \mu $ is the coefficient of friction, $ d $ is the distance moved by the object before coming to a stop.
Complete Step-by-Step solution
For part A, we note that for work to be done by a force, it has to be in the direction of motion or at least have a component in that direction. The normal reaction acting on a body is always perpendicular to the surface, and the body is always moving parallel to the surface. Hence, the work done by normal reaction is zero from A to C.
on that note, the answer is C
For part b, the coefficient of friction can be calculated if we note that the gravitational potential energy at point A is converted to kinetic energy at point B, in which work is then done to reduce it to zero. In essence, the potential energy is converted to frictional work done on the body.
Potential energy can be given by
$ {P_E} = mgh $ where $ m $ is the mass of the body, $ g $ is the acceleration due to gravity, and $ h $ is the height of the body. And frictional work can be given as
$ w = \mu mgd $ where $ \mu $ is the coefficient of friction, $ d $ is the distance moved by the object before coming to a stop.
Then,
$ \mu mg{x_0} = mgh $
By making $ \mu $ subject of the formula, we have
$ \mu = \dfrac{h}{{{x_0}}} $
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note
For clarity, the normal reaction is always perpendicular to the surface because by definition, the normal reaction is the reaction of the surface on the body which prevents the body from penetrating into the surface.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
$ {P_E} = mgh $ where $ {P_E} $ is the potential energy of a body, $ m $ is the mass of the body, $ g $ is the acceleration due to gravity, and $ h $ is the height of the body.
$ w = \mu mgd $ where $ w $ is the work done by friction on a body, $ \mu $ is the coefficient of friction, $ d $ is the distance moved by the object before coming to a stop.
Complete Step-by-Step solution
For part A, we note that for work to be done by a force, it has to be in the direction of motion or at least have a component in that direction. The normal reaction acting on a body is always perpendicular to the surface, and the body is always moving parallel to the surface. Hence, the work done by normal reaction is zero from A to C.
on that note, the answer is C
For part b, the coefficient of friction can be calculated if we note that the gravitational potential energy at point A is converted to kinetic energy at point B, in which work is then done to reduce it to zero. In essence, the potential energy is converted to frictional work done on the body.
Potential energy can be given by
$ {P_E} = mgh $ where $ m $ is the mass of the body, $ g $ is the acceleration due to gravity, and $ h $ is the height of the body. And frictional work can be given as
$ w = \mu mgd $ where $ \mu $ is the coefficient of friction, $ d $ is the distance moved by the object before coming to a stop.
Then,
$ \mu mg{x_0} = mgh $
By making $ \mu $ subject of the formula, we have
$ \mu = \dfrac{h}{{{x_0}}} $
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note
For clarity, the normal reaction is always perpendicular to the surface because by definition, the normal reaction is the reaction of the surface on the body which prevents the body from penetrating into the surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




