
A small beam of mass m moving with velocity v gets threaded on a stationary semicircular ring of mass m and radius R kept on a horizontal table. The ring rotates freely about its center o. The bead comes to rest relative to the ring. Then, the final angular velocity of the system,
A. $v/R$
B. $2v/R$
C. $v/2R$
D. $3v/R$
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint:First, we should use the equation of linear angular momentum of the system, ${L_i} = mvR$to calculate the initial angular velocity of the system and $I = m{R^2}$ to calculate the inertia of the system. Then calculate the final angular momentum as ${L_f} = I\omega $ and put it in $I = m{R^2}$. Then, apply the law of conservation of angular momentum to calculate final angular momentum
Complete step by step solution:
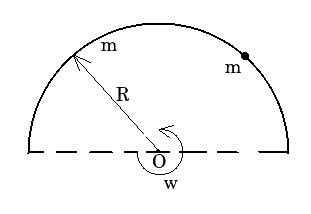
Given,
The velocity of the small beam is $v{\rm{ }}$
The mass of the small beam is $m$
The radius of the ring is $R$
The initial angular velocity is ${\omega _i} = 0\,$.
The final angular velocity is ${\omega _f}$.
The equation of initial angular momentum of the beam of mass$m$ and velocity $v{\rm{ }}$moving in a circular ring of radius $R$can be written as,
${L_i} = mvR$ …… (1)
The net inertia of the system can be written as,
${I_{system}} = {I_{bead}} + {I_{ring}}$ …… (2)
The inertia of the bead and ring can be written as,
${I_{bead}} = {I_{ring}} = m{R^2}$ …… (3)
Substituting equation (3) in equation (2) we get,
${I_{system}} = m{R^2} + m{R^2} = 2m{R^2}$ …… (4)
Again, we have,
${L_f} = {I_{system}}{\omega _f}$ …… (5)
Applying law of conservation of angular momentum, we have,
${L_i} = {L_f}$ …… (6)
Substituting equation (1) in equation (6) and equation (5) in equation (6) we have,
$mvR = {I_{system}}{\omega _f}$ …… (7)
Substituting value of ${I_{system}}$from equation (4) in equation (7) we get,
$\begin{array}{l}mvR = (2m{R^2}){\omega _f}\\ \Rightarrow {\omega _f} = \dfrac{v}{{2R}}\end{array}$
Hence, the correct answer is (C).
Note: The beam moves with a linear velocity $v{\rm{ }}$ and its angular velocity is zero. The ring rotates with angular velocity \[{\omega _f}\]. In the solution, the students can use the law of conservation of angular momentum where the initial momentum is equal to the final momentum.
Complete step by step solution:

Given,
The velocity of the small beam is $v{\rm{ }}$
The mass of the small beam is $m$
The radius of the ring is $R$
The initial angular velocity is ${\omega _i} = 0\,$.
The final angular velocity is ${\omega _f}$.
The equation of initial angular momentum of the beam of mass$m$ and velocity $v{\rm{ }}$moving in a circular ring of radius $R$can be written as,
${L_i} = mvR$ …… (1)
The net inertia of the system can be written as,
${I_{system}} = {I_{bead}} + {I_{ring}}$ …… (2)
The inertia of the bead and ring can be written as,
${I_{bead}} = {I_{ring}} = m{R^2}$ …… (3)
Substituting equation (3) in equation (2) we get,
${I_{system}} = m{R^2} + m{R^2} = 2m{R^2}$ …… (4)
Again, we have,
${L_f} = {I_{system}}{\omega _f}$ …… (5)
Applying law of conservation of angular momentum, we have,
${L_i} = {L_f}$ …… (6)
Substituting equation (1) in equation (6) and equation (5) in equation (6) we have,
$mvR = {I_{system}}{\omega _f}$ …… (7)
Substituting value of ${I_{system}}$from equation (4) in equation (7) we get,
$\begin{array}{l}mvR = (2m{R^2}){\omega _f}\\ \Rightarrow {\omega _f} = \dfrac{v}{{2R}}\end{array}$
Hence, the correct answer is (C).
Note: The beam moves with a linear velocity $v{\rm{ }}$ and its angular velocity is zero. The ring rotates with angular velocity \[{\omega _f}\]. In the solution, the students can use the law of conservation of angular momentum where the initial momentum is equal to the final momentum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

India is a sovereign socialist secular democratic republic class 12 social science CBSE

How many states of matter are there in total class 12 chemistry CBSE

What are the advantages of vegetative propagation class 12 biology CBSE

Suicide bags of cells are aEndoplasmic reticulum bLysosome class 12 biology CBSE

What is the Full Form of PVC, PET, HDPE, LDPE, PP and PS ?




