
A small ball is projected up a smooth inclined plane with an initial speed of $10\,m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 1}}$ along the direction at ${30^ \circ }$ to the bottom edge of the slope. It returns to the edge after $2\,s$ . The ball is in contact with the inclined plane throughout the process. What is the inclination angle of the plane?

Answer
487.2k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, one must know about motion in projectile, here we have redrawn the figure which is given above after that applying equation of motion in the y-axis we have solved for the required data i.e., inclination angle of the plane or the same question is done with the help of the formula of time of flight.
Formula used:
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
$t = \dfrac{{2u\sin \theta }}{g}$
Where, $s$ is the distance, $u$ is the initial velocity, $t$ is the time, $a$ is acceleration and
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
Complete step by step answer:
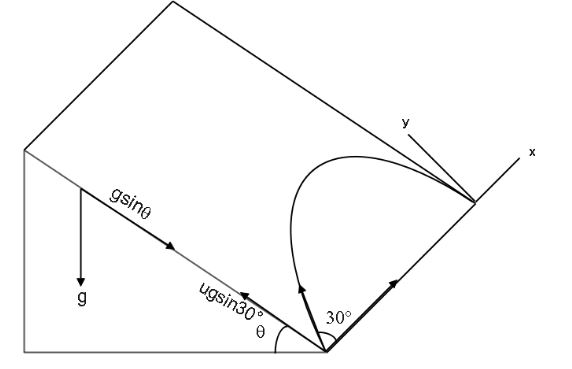
According to the question, the initial speed of the ball is $10\,m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 1}}$.Angle with the ball on the slope is, ${30^ \circ }$. The net acceleration towards the bottom is, $g\sin \theta $. And assuming acceleration due to gravity along the slope is, $10\,m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 2}}$.
We can say that in the direction motion the final displacement is zero because from where the ball starts comes to the same position in the y-axis. So, using equation of motion, along y-axis,
${S_y} = {u_y} + t + \dfrac{1}{2}{a_y}{t^2}$
$\Rightarrow {S_y} = 0$
$\Rightarrow t = 2s$
$\Rightarrow {u_y} = 10\sin {30^ \circ } = 5m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 1}}$
And $a = g\sin \theta $
So,
$0 = 5 \times 2 - \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10\sin \theta \times 4 \\
\Rightarrow 2\sin \theta = 1 \\
\Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{1}{2} \\ $
$\therefore \theta = {30^ \circ }$
Hence, ${30^ \circ }$ is the inclination angle of the plane.
Note: Note that we can easily done same question, by using the formula of time of flight i.e., $T = \dfrac{{2u\sin \theta }}{g}$
As the time of flight is given i.e., $T = 2s$
$g = g\sin \theta $
And $u = 10m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 1}}$
so simply putting the value and solving for \[\theta \] .
$2 = \dfrac{{2 \times 10\sin {{30}^ \circ }}}{{g\sin \theta }}$
$\Rightarrow 2 = \dfrac{{2 \times 10\sin {{30}^ \circ }}}{{g\sin \theta }} \\
\Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\therefore \theta = {30^ \circ } \\ $
The motion of an item hurled or projected into the air, subject only to gravity's acceleration, is known as projectile motion. The object is known as a projectile, and the course it takes is known as a trajectory. Falling object motion is a simple one-dimensional type of projectile motion with no horizontal movement, as described in Problem-Solving Basics for One-Dimensional Kinematics.
Formula used:
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
$t = \dfrac{{2u\sin \theta }}{g}$
Where, $s$ is the distance, $u$ is the initial velocity, $t$ is the time, $a$ is acceleration and
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
Complete step by step answer:

According to the question, the initial speed of the ball is $10\,m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 1}}$.Angle with the ball on the slope is, ${30^ \circ }$. The net acceleration towards the bottom is, $g\sin \theta $. And assuming acceleration due to gravity along the slope is, $10\,m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 2}}$.
We can say that in the direction motion the final displacement is zero because from where the ball starts comes to the same position in the y-axis. So, using equation of motion, along y-axis,
${S_y} = {u_y} + t + \dfrac{1}{2}{a_y}{t^2}$
$\Rightarrow {S_y} = 0$
$\Rightarrow t = 2s$
$\Rightarrow {u_y} = 10\sin {30^ \circ } = 5m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 1}}$
And $a = g\sin \theta $
So,
$0 = 5 \times 2 - \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10\sin \theta \times 4 \\
\Rightarrow 2\sin \theta = 1 \\
\Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{1}{2} \\ $
$\therefore \theta = {30^ \circ }$
Hence, ${30^ \circ }$ is the inclination angle of the plane.
Note: Note that we can easily done same question, by using the formula of time of flight i.e., $T = \dfrac{{2u\sin \theta }}{g}$
As the time of flight is given i.e., $T = 2s$
$g = g\sin \theta $
And $u = 10m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 1}}$
so simply putting the value and solving for \[\theta \] .
$2 = \dfrac{{2 \times 10\sin {{30}^ \circ }}}{{g\sin \theta }}$
$\Rightarrow 2 = \dfrac{{2 \times 10\sin {{30}^ \circ }}}{{g\sin \theta }} \\
\Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\therefore \theta = {30^ \circ } \\ $
The motion of an item hurled or projected into the air, subject only to gravity's acceleration, is known as projectile motion. The object is known as a projectile, and the course it takes is known as a trajectory. Falling object motion is a simple one-dimensional type of projectile motion with no horizontal movement, as described in Problem-Solving Basics for One-Dimensional Kinematics.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




