
A small air bubble is trapped inside a transparent cube of size $12\;cm$. When viewed from one of the vertical faces, the bubble appears to be at $5\;cm$ from it. When viewed from opposite face, it appears at $3\;cm$ from it
(has multiple correct answer)
A. The distance of the air bubble from the first face is $7.5\;cm$
B. The distance of the air bubble from the first face is $9\;cm$
C. Refractive index of the material of the prism is $2$
D. Refractive index of the material of the prism is $1.5\;$
Answer
542.1k+ views
Hint: We know that light undergoes refraction when it travels from one medium to another. From Snell’s law we also know that the angle of the refracted light also depends on the medium i.e. the refractive index of the medium and also on the nature of the light. We also know that this shift results in apparent depth of the objects.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{sin (i)}{sin (r)}=\dfrac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}=\dfrac{v_2}{v_1}$
$\mu=\dfrac{R.D}{A.D}$
Complete step by step solution:
Consider the figure shown below. Let the side of the cube be $12\;cm$ and let $F_1$ and $F_2$ be the faces of the cube through which the bubble $B$ is seen. Let $H$ be the distance of the bubble from the $F_2$ and then the bubble is at a distance $12-H$ from $F_1$. Let the refractive index of the medium inside the cube be $\mu_1$ and that outside the cube be $\mu_2$.
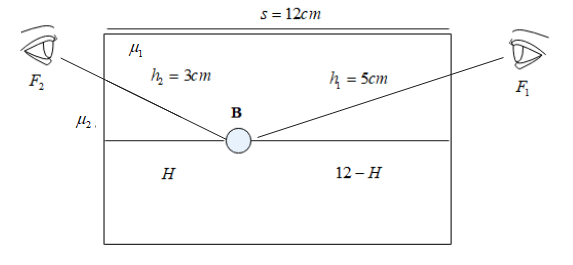
From Snell’s law, we can say that $\mu_{1} sin( i)=\mu_{2} sin( r)$
$\implies \dfrac{sin (i)}{sin (r)}=\dfrac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}=\dfrac{v_2}{v_1}$
where $i$ is the angle of incidence of the light ray from the medium one whose refractive index is given as $\mu_{1}$ and velocity $v_1$, while $r$ is the angle of refraction of the light ray at the second medium whose refractive index is given as $\mu_{2}$ and velocity $v_2$.
Due to this bending of light at the interfaces, the bubble inside the cube looks much closer as compared to without the interface.
From apparent depth, we know that,
$\mu=\dfrac{R.D}{A.D}$
Where, $\mu$ is the refractive index of the medium and R.D and A.D are the real depth and the apparent depth of the object.
Here, the refractive index of the interface is given as $\mu=\dfrac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}$
Clearly, at $F_1$ $R.D=12-H$ and $A.D=5cm$
Then, we have $\dfrac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}=\dfrac{12-H}{5}$
$\implies 12-H=\dfrac{5\mu_1}{\mu_2}$
Similarly, at $F_2$ $R.D=H$ and $A.D=3cm$
Then, we have $\dfrac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}=\dfrac{H}{3}$
$\implies H=\dfrac{3\mu_1}{\mu_2}$
From the two, we have
$\implies 12-\dfrac{3\mu_1}{\mu_2}=\dfrac{5\mu_1}{\mu_2}$
$\implies 12=\dfrac{8\mu_1}{\mu_2}$
$\implies \dfrac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}=\dfrac{12}{8}=1.5$
Then, from $H=\dfrac{3\mu_1}{\mu_2}$, we have
$\implies H=3\times 1.5=7.5cm$
Hence the correct answer is
A. the distance of the air bubble from the first face is $7.5\;cm$ and D. Refractive index of the material of the prism is $1.5\;$
Note: This is a very easy sum, provided one draws the question and knows the relationship between the apparent depth and real depth. Also, it is important for one to assume the refractive index and the real depths to solve the problem, as that is what is asked for in the question.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{sin (i)}{sin (r)}=\dfrac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}=\dfrac{v_2}{v_1}$
$\mu=\dfrac{R.D}{A.D}$
Complete step by step solution:
Consider the figure shown below. Let the side of the cube be $12\;cm$ and let $F_1$ and $F_2$ be the faces of the cube through which the bubble $B$ is seen. Let $H$ be the distance of the bubble from the $F_2$ and then the bubble is at a distance $12-H$ from $F_1$. Let the refractive index of the medium inside the cube be $\mu_1$ and that outside the cube be $\mu_2$.

From Snell’s law, we can say that $\mu_{1} sin( i)=\mu_{2} sin( r)$
$\implies \dfrac{sin (i)}{sin (r)}=\dfrac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}=\dfrac{v_2}{v_1}$
where $i$ is the angle of incidence of the light ray from the medium one whose refractive index is given as $\mu_{1}$ and velocity $v_1$, while $r$ is the angle of refraction of the light ray at the second medium whose refractive index is given as $\mu_{2}$ and velocity $v_2$.
Due to this bending of light at the interfaces, the bubble inside the cube looks much closer as compared to without the interface.
From apparent depth, we know that,
$\mu=\dfrac{R.D}{A.D}$
Where, $\mu$ is the refractive index of the medium and R.D and A.D are the real depth and the apparent depth of the object.
Here, the refractive index of the interface is given as $\mu=\dfrac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}$
Clearly, at $F_1$ $R.D=12-H$ and $A.D=5cm$
Then, we have $\dfrac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}=\dfrac{12-H}{5}$
$\implies 12-H=\dfrac{5\mu_1}{\mu_2}$
Similarly, at $F_2$ $R.D=H$ and $A.D=3cm$
Then, we have $\dfrac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}=\dfrac{H}{3}$
$\implies H=\dfrac{3\mu_1}{\mu_2}$
From the two, we have
$\implies 12-\dfrac{3\mu_1}{\mu_2}=\dfrac{5\mu_1}{\mu_2}$
$\implies 12=\dfrac{8\mu_1}{\mu_2}$
$\implies \dfrac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}=\dfrac{12}{8}=1.5$
Then, from $H=\dfrac{3\mu_1}{\mu_2}$, we have
$\implies H=3\times 1.5=7.5cm$
Hence the correct answer is
A. the distance of the air bubble from the first face is $7.5\;cm$ and D. Refractive index of the material of the prism is $1.5\;$
Note: This is a very easy sum, provided one draws the question and knows the relationship between the apparent depth and real depth. Also, it is important for one to assume the refractive index and the real depths to solve the problem, as that is what is asked for in the question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




