
A sine wave has amplitude A and wavelength \[\lambda \]. If V be the wave velocity and v be the maximum particle velocity, then:
A. V = v if A = \[\dfrac{\lambda }{2\pi }\]
B. V = v if A = \[2\pi \lambda \]
C. V = v if A = \[\pi \lambda \]
D. V can never be equal to v
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: This question needs to be approached in a different way. We have been given the statements and asked to check which is correct with our given conditions. So as we see in options we need to find the velocity of the particle and velocity of the wave. We will then equate the two velocities and if any one of the three statements is checked to be true that will be considered as our answer. If none of the three statements is true it will be clear that option D is our answer.
Formula Used: v = A \[\omega \]
Where, A = amplitude and \[\omega \] = angular frequency of the particle
V = f\[\lambda \]
Where, f= frequency of the wave and \[\lambda \] = wavelength
Complete step-by-step solution:
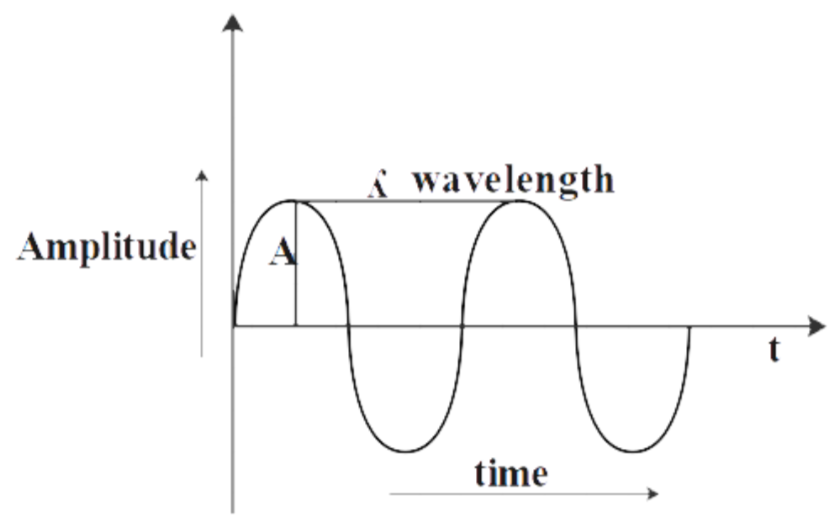
In the diagram above, the amplitude A is half of the total vibration path of the vibrating body. It is a measure of the change in a single period of time. In a sine or cosine wave amplitude is the perpendicular distance between the maximum height and the sinusoidal axis. Similarly, the wavelength is the distance between two crests or troughs of a wave.
We know that velocity of wave is given by the equation
V = f\[\lambda \]
We also know that frequency of a wave,
f = \[\dfrac{\omega }{2\pi }\]
Substitute the value of frequency in equation (1)
We get,
V = (\[\dfrac{\omega }{2\pi }\])(\[\lambda \]) ……………………… (A)
Similarly velocity of particle is given by,
v = A \[\omega \] ………………….. (B)
Now, let us assume V = v
Therefore,
From (A) and (B)
We can write,
(\[\dfrac{\omega }{2\pi }\])(\[\lambda \]) = A \[\omega \]
On dividing both sides by \[\omega \]
We get,
A = \[\dfrac{\lambda }{2\pi }\]
Therefore, the reverse statement that if A = \[\dfrac{\lambda }{2\pi }\] then V = v is true then by symmetric rule the statement V = v if A = \[\dfrac{\lambda }{2\pi }\] is also true.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A.
Note: There is no other way to solve this question. We must make the assumption that V = v and check if the statement holds true. In a sinusoidal wave moving at constant speed the frequency is inversely proportional to the wavelength \[\lambda \].
Formula Used: v = A \[\omega \]
Where, A = amplitude and \[\omega \] = angular frequency of the particle
V = f\[\lambda \]
Where, f= frequency of the wave and \[\lambda \] = wavelength
Complete step-by-step solution:

In the diagram above, the amplitude A is half of the total vibration path of the vibrating body. It is a measure of the change in a single period of time. In a sine or cosine wave amplitude is the perpendicular distance between the maximum height and the sinusoidal axis. Similarly, the wavelength is the distance between two crests or troughs of a wave.
We know that velocity of wave is given by the equation
V = f\[\lambda \]
We also know that frequency of a wave,
f = \[\dfrac{\omega }{2\pi }\]
Substitute the value of frequency in equation (1)
We get,
V = (\[\dfrac{\omega }{2\pi }\])(\[\lambda \]) ……………………… (A)
Similarly velocity of particle is given by,
v = A \[\omega \] ………………….. (B)
Now, let us assume V = v
Therefore,
From (A) and (B)
We can write,
(\[\dfrac{\omega }{2\pi }\])(\[\lambda \]) = A \[\omega \]
On dividing both sides by \[\omega \]
We get,
A = \[\dfrac{\lambda }{2\pi }\]
Therefore, the reverse statement that if A = \[\dfrac{\lambda }{2\pi }\] then V = v is true then by symmetric rule the statement V = v if A = \[\dfrac{\lambda }{2\pi }\] is also true.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A.
Note: There is no other way to solve this question. We must make the assumption that V = v and check if the statement holds true. In a sinusoidal wave moving at constant speed the frequency is inversely proportional to the wavelength \[\lambda \].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




