
A simple pendulum of length $l$ has maximum angular displacement $\theta $ . The maximum kinetic energy of the bob of mass $m$ is:
(a). $\dfrac{1}{2}m\left( {\dfrac{l}{g}} \right)$
(b). $mgl(1 - \cos \theta )$
(c). $\dfrac{{(mgl\sin \theta )}}{2}$
(d). $\dfrac{{mg}}{{2l}}$
Answer
495k+ views
Hint: To answer this type of question firstly we will draw the diagram to find the height and then we will apply energy conservation and then put all the values in the equation and will get the required answer. Check the note part for a shortcut.
Formula used:
$P.E = mgh$
Where,
$m$ is the mass of the bob,
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and
$h$ is the height.
Complete answer:
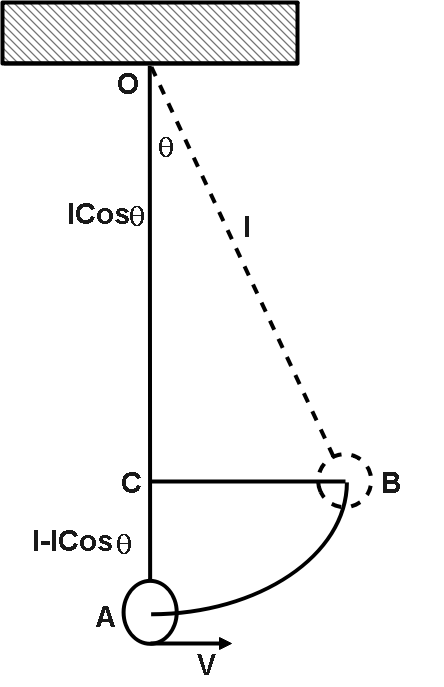
Kinetic energy of the bob is maximum at the mean position of oscillation.
This means that at point A. Also, we know that conservation of energy says that this kinetic energy is converted into the potential energy as the bob reaches at the maximum position i.e., at point B.
So, from the figure we can say that,
$AC = AO - OC$
$
\therefore AC = l - l\cos \theta \\
\Rightarrow AC = l(1 - \cos \theta ) \\
$
And we know that potential energy is maximum at point B
$\therefore P.E = mgh$
Here, $h = AC = l(1 - \cos \theta )$
Now, putting the value in the above equation.
$ \Rightarrow P.E = mgl(1 - \cos \theta )$
So, the maximum kinetic energy of the bob is $mgl(1 - \cos \theta )$ .
Hence the correct option is (b).
Note:
We will find $l\cos \theta $ from the triangle OCB.
Let’s see another approach (shortcut).
We know that maximum K.E equals to work done.
So, work done is $mgh$
And we know from the figure the value of h and simply putting the value in above equation we will get the required solution.
$
mgh = mg(l - l\cos \theta ) \\
\Rightarrow mgh = mgl(1 - \cos \theta ) \\
$
Formula used:
$P.E = mgh$
Where,
$m$ is the mass of the bob,
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and
$h$ is the height.
Complete answer:

Kinetic energy of the bob is maximum at the mean position of oscillation.
This means that at point A. Also, we know that conservation of energy says that this kinetic energy is converted into the potential energy as the bob reaches at the maximum position i.e., at point B.
So, from the figure we can say that,
$AC = AO - OC$
$
\therefore AC = l - l\cos \theta \\
\Rightarrow AC = l(1 - \cos \theta ) \\
$
And we know that potential energy is maximum at point B
$\therefore P.E = mgh$
Here, $h = AC = l(1 - \cos \theta )$
Now, putting the value in the above equation.
$ \Rightarrow P.E = mgl(1 - \cos \theta )$
So, the maximum kinetic energy of the bob is $mgl(1 - \cos \theta )$ .
Hence the correct option is (b).
Note:
We will find $l\cos \theta $ from the triangle OCB.
Let’s see another approach (shortcut).
We know that maximum K.E equals to work done.
So, work done is $mgh$
And we know from the figure the value of h and simply putting the value in above equation we will get the required solution.
$
mgh = mg(l - l\cos \theta ) \\
\Rightarrow mgh = mgl(1 - \cos \theta ) \\
$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




