
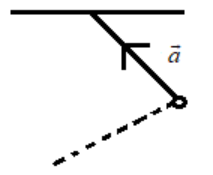
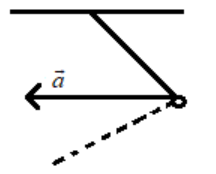
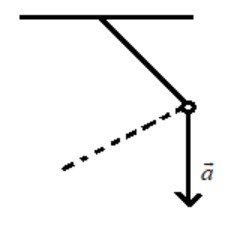
A simple pendulum is oscillating without damping. When the displacement of the bob is less than maximum, its acceleration vector $\vec{a}$ is correctly shown in
A).
B).
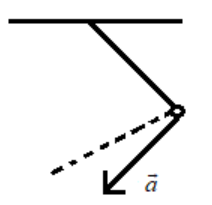
C).
D).




Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: We are given a simple pendulum that is oscillating without any damping. We know for a simple pendulum there is tangential acceleration and radial acceleration. The resultant acceleration vector is the sum of these two acceleration vectors. Hence we first find the radial acceleration and tangential acceleration and sum them.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In the question it is said that a simple pendulum is oscillating without damping.
We are asked to find the direction of the acceleration vector $\vec{a}$ when the displacement of the pendulum is less than maximum displacement.
Now, let us consider a pendulum as said in the question.
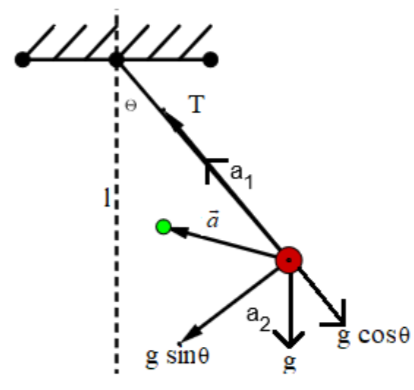
We know that the bob has both tangential acceleration and radial acceleration.
In the figure, $'{{a}_{1}}'$ is radial acceleration and $'{{a}_{2}}'$ is tangential acceleration.
Therefore, from the figure we can say that,
Radial acceleration
${{\vec{a}}_{1}}=\dfrac{T}{m}-g\cos \theta $ , Where ‘T’ is the tension acting on the string, ‘m’ is mass of the bob, ‘g’ is acceleration due to gravity and $'\theta '$ is the angle of displacement.
And tangential acceleration can be written as,
${{\vec{a}}_{2}}=g\sin \theta $
We have to find the resultant acceleration vector $'\vec{a}'$ which is the sum of tangential acceleration and radial acceleration.
$\vec{a}={{\vec{a}}_{1}}+{{\vec{a}}_{2}}$
And this is represented as,
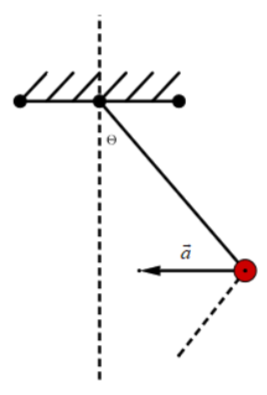
Hence the correct answer is option C.
Note: This is a case of circular motion. Movement of an object along the circumference of a circle is circular motion. I.e. the distance from the centre point will always remain the same in such an oscillation. We have uniform circular motion and non – uniform circular motion.
When the speed of the object in circular motion is constant, then it is a uniform circular motion.
Some examples are; hour hand of a clock, rotation of blades in a ceiling fan etc.
When the speed of the object in circular motion is not constant, then it is a non-uniform circular motion.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In the question it is said that a simple pendulum is oscillating without damping.
We are asked to find the direction of the acceleration vector $\vec{a}$ when the displacement of the pendulum is less than maximum displacement.
Now, let us consider a pendulum as said in the question.

We know that the bob has both tangential acceleration and radial acceleration.
In the figure, $'{{a}_{1}}'$ is radial acceleration and $'{{a}_{2}}'$ is tangential acceleration.
Therefore, from the figure we can say that,
Radial acceleration
${{\vec{a}}_{1}}=\dfrac{T}{m}-g\cos \theta $ , Where ‘T’ is the tension acting on the string, ‘m’ is mass of the bob, ‘g’ is acceleration due to gravity and $'\theta '$ is the angle of displacement.
And tangential acceleration can be written as,
${{\vec{a}}_{2}}=g\sin \theta $
We have to find the resultant acceleration vector $'\vec{a}'$ which is the sum of tangential acceleration and radial acceleration.
$\vec{a}={{\vec{a}}_{1}}+{{\vec{a}}_{2}}$
And this is represented as,

Hence the correct answer is option C.
Note: This is a case of circular motion. Movement of an object along the circumference of a circle is circular motion. I.e. the distance from the centre point will always remain the same in such an oscillation. We have uniform circular motion and non – uniform circular motion.
When the speed of the object in circular motion is constant, then it is a uniform circular motion.
Some examples are; hour hand of a clock, rotation of blades in a ceiling fan etc.
When the speed of the object in circular motion is not constant, then it is a non-uniform circular motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




