
A sector is removed from a metallic disc and the remaining region is bent into the shape of a circular conical funnel with volume $2\sqrt{3}\pi $. The least possible diameter of the disc is
(a) 4
(b) 6
(c) 8
(d) 12
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: First of all, we will equate the value of volume given in the question with volume of cone which can be given as, $Volume=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{R}^{2}}H$. Then making R as subject we will find our expression in terms of H. Then using the formula of slant height of cone we will find relation between r, R and H. Then, we will differentiate the obtained expression to find the maximum or minimum value of r, as we know that the value of equation is minimum or maximum at a point where differentiation is zero. So, using this fact we will find our final answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In question, we are given that a sector is removed from a metallic disc and then the remaining disc is bent in the shape of conical funnel whose volume is $2\sqrt{3}\pi $, and we are asked to find the radius of the disc, so first of all we will draw the figure of disc along the sector,
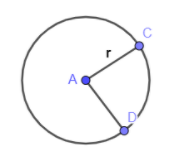
Now, after bending the disc the conical funnel can be seen as,
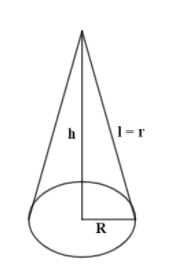
Now, as the disc is bent into the shape of conical funnel the radius r becomes slant height l of the cone. Now, the volume of cone can be given by the formula,
$Volume=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{R}^{2}}H$ ……………..(i)
Where, R is radius of base of cone, H is height of cone. Now, in question the volume of conical funnel is given as, $2\sqrt{3}\pi $, so on substituting the value in expression (i) we will get,
$2\sqrt{3}\pi =\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{R}^{2}}H$
Making R as main component of equation and simplifying the equation further we will get,
$\dfrac{3\times 2\sqrt{3}}{H}={{R}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{R}^{2}}=\dfrac{6\sqrt{3}}{H}$ ……….(ii)
Now, we know that relation between slant height l, radius R and height H of cone can be given as,
$l=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+{{H}^{2}}}$
Here, $l=r$ so, the expression becomes, $r=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+{{H}^{2}}}$.
Now, on substituting the value of ${{R}^{2}}$ from expression (ii) we will get,
$r=\sqrt{\dfrac{6\sqrt{3}}{H}+{{H}^{2}}}$………………(iii)
From expression (iii) we can say that value of r depends on value of height H, and we are asked to find the minimum value of r, so first of all we have to find the minimum value of H. Now, we know that the maximum or minimum value at which the differentiation of the expression is zero is called its maximum or minimum value.
So, the differentiation of expression (iii) can be given as,
\[\dfrac{dr}{dH}=\dfrac{d}{dH}\left( \dfrac{6\sqrt{3}}{H}+{{H}^{2}} \right)=0\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{d}{dH}\left( 6\sqrt{3}{{H}^{-1}}+{{H}^{2}} \right)=0\]
On differentiating further, we will get,
\[\left( \left( -1 \right)6\sqrt{3}{{H}^{-1-1}}+2{{H}^{2-1}} \right)=0\]
\[\Rightarrow -6\sqrt{3}{{H}^{-2}}+2H=0\Rightarrow \dfrac{-6\sqrt{3}}{{{H}^{2}}}+2H=0\]
On taking LCM and solving further we will get,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{-6\sqrt{3}}{{{H}^{2}}}+\dfrac{2H\times {{H}^{2}}}{{{H}^{2}}}=0\Rightarrow \dfrac{-6\sqrt{3}+2{{H}^{3}}}{{{H}^{2}}}=0\]
\[\Rightarrow -6\sqrt{3}+2{{H}^{3}}=0\Rightarrow {{H}^{3}}=\dfrac{6\sqrt{3}}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow -6\sqrt{3}+2{{H}^{3}}=0\Rightarrow {{H}^{3}}=3\sqrt{3}\]
Now, value of $3\times \sqrt{3}$ is 5.1961, now taking its cube root i.e. $\sqrt[3]{5.1961}$ we will get its value as 1.7320, which is equal to value of $\sqrt{3}$.
\[\therefore H=\sqrt{3}\]
Now, substituting this value in expression (ii) we will get,
${{R}^{2}}=\dfrac{6\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=6$
Now, taking square roots on both sides we will get,
$\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}}=\sqrt{6}\Rightarrow R=\pm \sqrt{6}$
Now, the value of R can not be negative so we will consider $R=\sqrt{6}$. Now, on substituting the values of R and H in expression $r=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+{{H}^{2}}}$, we will get,
$r=\sqrt{6+{{\left( \sqrt{3} \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{9}=3$
Now, diameter can be given as, $d=2r=2\times 3=6$
Thus, the minimum value of diameter is 6.
Hence, option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: Students might consider the radius of cone as the radius of disc due to that the expression might become, $\Rightarrow {{R}^{2}}=\dfrac{6\sqrt{3}}{H}={{r}^{2}}$, so the final answer according to that will be ${{R}^{2}}=\dfrac{6\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=6\Rightarrow r=\sqrt{6}$, which is incorrect. So, students must understand the problem properly and work accordingly.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In question, we are given that a sector is removed from a metallic disc and then the remaining disc is bent in the shape of conical funnel whose volume is $2\sqrt{3}\pi $, and we are asked to find the radius of the disc, so first of all we will draw the figure of disc along the sector,

Now, after bending the disc the conical funnel can be seen as,

Now, as the disc is bent into the shape of conical funnel the radius r becomes slant height l of the cone. Now, the volume of cone can be given by the formula,
$Volume=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{R}^{2}}H$ ……………..(i)
Where, R is radius of base of cone, H is height of cone. Now, in question the volume of conical funnel is given as, $2\sqrt{3}\pi $, so on substituting the value in expression (i) we will get,
$2\sqrt{3}\pi =\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{R}^{2}}H$
Making R as main component of equation and simplifying the equation further we will get,
$\dfrac{3\times 2\sqrt{3}}{H}={{R}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{R}^{2}}=\dfrac{6\sqrt{3}}{H}$ ……….(ii)
Now, we know that relation between slant height l, radius R and height H of cone can be given as,
$l=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+{{H}^{2}}}$
Here, $l=r$ so, the expression becomes, $r=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+{{H}^{2}}}$.
Now, on substituting the value of ${{R}^{2}}$ from expression (ii) we will get,
$r=\sqrt{\dfrac{6\sqrt{3}}{H}+{{H}^{2}}}$………………(iii)
From expression (iii) we can say that value of r depends on value of height H, and we are asked to find the minimum value of r, so first of all we have to find the minimum value of H. Now, we know that the maximum or minimum value at which the differentiation of the expression is zero is called its maximum or minimum value.
So, the differentiation of expression (iii) can be given as,
\[\dfrac{dr}{dH}=\dfrac{d}{dH}\left( \dfrac{6\sqrt{3}}{H}+{{H}^{2}} \right)=0\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{d}{dH}\left( 6\sqrt{3}{{H}^{-1}}+{{H}^{2}} \right)=0\]
On differentiating further, we will get,
\[\left( \left( -1 \right)6\sqrt{3}{{H}^{-1-1}}+2{{H}^{2-1}} \right)=0\]
\[\Rightarrow -6\sqrt{3}{{H}^{-2}}+2H=0\Rightarrow \dfrac{-6\sqrt{3}}{{{H}^{2}}}+2H=0\]
On taking LCM and solving further we will get,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{-6\sqrt{3}}{{{H}^{2}}}+\dfrac{2H\times {{H}^{2}}}{{{H}^{2}}}=0\Rightarrow \dfrac{-6\sqrt{3}+2{{H}^{3}}}{{{H}^{2}}}=0\]
\[\Rightarrow -6\sqrt{3}+2{{H}^{3}}=0\Rightarrow {{H}^{3}}=\dfrac{6\sqrt{3}}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow -6\sqrt{3}+2{{H}^{3}}=0\Rightarrow {{H}^{3}}=3\sqrt{3}\]
Now, value of $3\times \sqrt{3}$ is 5.1961, now taking its cube root i.e. $\sqrt[3]{5.1961}$ we will get its value as 1.7320, which is equal to value of $\sqrt{3}$.
\[\therefore H=\sqrt{3}\]
Now, substituting this value in expression (ii) we will get,
${{R}^{2}}=\dfrac{6\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=6$
Now, taking square roots on both sides we will get,
$\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}}=\sqrt{6}\Rightarrow R=\pm \sqrt{6}$
Now, the value of R can not be negative so we will consider $R=\sqrt{6}$. Now, on substituting the values of R and H in expression $r=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+{{H}^{2}}}$, we will get,
$r=\sqrt{6+{{\left( \sqrt{3} \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{9}=3$
Now, diameter can be given as, $d=2r=2\times 3=6$
Thus, the minimum value of diameter is 6.
Hence, option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: Students might consider the radius of cone as the radius of disc due to that the expression might become, $\Rightarrow {{R}^{2}}=\dfrac{6\sqrt{3}}{H}={{r}^{2}}$, so the final answer according to that will be ${{R}^{2}}=\dfrac{6\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=6\Rightarrow r=\sqrt{6}$, which is incorrect. So, students must understand the problem properly and work accordingly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




